Get started with Access 2007 security
Microsoft Office Access 2007 provides a number of new features that can help make your data and your computer more secure. In addition, these features can be easier to use than the security tools in previous versions of Access. This article explains how to use the most common security features in Office Access 2007. The information in this article is intended for new users who want to do the following tasks:
-
Trust (enable) the disabled content in a database
-
Use a password to encrypt or decrypt a database
-
Package, sign, and deploy an Office Access 2007 database
This article also provides background information about the new security features and architecture in Access 2007.
In this article
Security differences between Access 2007 and earlier versions of Access
If you used the security features in previous versions of Access, you had to make a series of choices. For example, you had to choose between security levels (Low, Medium, or High), and whether you wanted to run potentially unsafe code or not. You no longer have to make those kinds of decisions when you open a database in Access 2007. By default, Access 2007 disables all potentially unsafe code or other components, regardless of the version of Access that you used to create the database.
When it disables part or all of a database, Access informs you of the action by displaying the Message Bar.

If you see the Message Bar, you can choose to trust or not trust the disabled content in the database. If you choose to trust the disabled content, you can do so in two ways:
-
Trust the database only for the current session (while the database is open) Click Options on the Message Bar. A dialog box appears in which you can choose to trust the database. When you choose this option, you must repeat the procedure each time you open the database.
-
Trust the database permanently Place the database in a trusted location — a folder on a drive or network that you mark as trusted. When you choose this option, you no longer see the Message Bar, and you never have to make trust decisions as long as the database remains in the trusted folder.
If you don't want to trust the database Ignore the Message Bar. When you ignore the Message Bar, you can still view the data in the database and use any components in the database that Access has not disabled.
The following procedures explain how to trust a database for the current session and how to create a trusted location.
Trust a database for the current session
Note: If you have a database open, and you see the Message Bar, you can go directly to step 3.
-
Start Office Access 2007, and on the Getting Started with Microsoft Office Access page, under Featured Online Templates, click Assets to open the Assets template.
-
In the File Name box, type a name for the new database, and then click Download.
Access downloads the database template and creates a new database, and the Message Bar appears.
-
On the Message Bar, click Options.
The Microsoft Office Security Options dialog box appears.
-
Click Enable this content, and then click OK.
Create a trusted location
-
Start Office Access 2007 (you do not need to open a database to complete these steps).
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Access Options.
, and then click Access Options.The Access Options dialog box appears.
-
In the left pane of the dialog box, click Trust Center, and then click Trust Center Settings in the right pane.
The Trust Center dialog box appears.
-
In the left pane, click Trusted Locations.
-
Click Add new location.
The Microsoft Office Trusted Location dialog box appears.
-
In the Path box, type the file path and folder name of the location that you want to set as a trusted source, or click Browse to locate a folder. By default, the folder must reside on a local drive.
If you want to allow trusted network locations, in the Trust Center dialog box, click Allow Trusted Locations on my network (not recommended).
-
Click OK to close all dialog boxes.
Note: To finish the process, and so trust a database permanently, you must move that database to the trusted location. The next steps explain some of the most common ways to move a database.
Move a database to a trusted location
-
If you have a database open
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 .
. -
Point to Save As, and under Save the database in another format, click one of the available options.
-
In the Save As dialog box, navigate to the trusted location, and then click Save.
-
-
If you do not have a database open
-
Start Windows Explorer. To do so, in Microsoft Windows, click the Start button, point to All Programs, click Accessories, and then click Windows Explorer.
-
Locate and copy your database. To do so, right-click the file and click Copy on the shortcut menu.
-or-
Keyboard shortcut Select (highlight) the file and press CTRL+C.
-
Locate your trusted folder, open it, and right-click and then click Paste on the shortcut menu.
-or-
Keyboard shortcut Press CTRL+V to paste the database into the new location.
-
Use a database password to encrypt an Office Access 2007 database
The encryption tool in Office Access 2007 combines and improves on two older tools — database passwords and encoding. When you use a database password to encrypt a database, you make all data unreadable by other tools, and you force users to enter a password to use the database. The encryption applied in Access 2007 uses a stronger algorithm than was used in earlier versions of Access.
Encrypt by using a database password
-
Open the database (in Exclusive mode) that you want to encrypt.
Show me how to open the database in Exclusive mode
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, browse to the file that you want to open, and then select the file.
-
Click the arrow next to the Open button, and then click Open Exclusive.
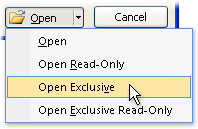
-
-
On the Database Tools tab, in the Database Tools group, click Encrypt with Password.
The Set Database Password dialog box appears.
-
Type your password in the Password box, and then type it again in the Verify box.
Notes:
-
Use strong passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Weak passwords don't mix these elements. Strong password: Y6dh!et5. Weak password: House27. Passwords should be 8 or more characters in length. A pass phrase that uses 14 or more characters is better.
-
It is critical that you remember your password. If you forget your password, Microsoft cannot retrieve it. Store the passwords that you write down in a secure place away from the information that they help protect.
-
-
Click OK.
Decrypt and open a database
-
Open the encrypted database as you open any other database.
The Password Required dialog box appears.
-
Type your password in the Enter database password box, and then click OK.
Remove a password
-
Open the database in Exclusive mode.
Show me how to open the database in Exclusive mode
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, browse to the file that you want to open, and then select the file.
-
Click the arrow next to the Open button, and then click Open Exclusive.

-
-
On the Database Tools tab, in the Database Tools group, click Decrypt Database.
The Unset Database Password dialog box appears.
-
Type your password in the Password box, and then click OK.
Package, sign, and distribute an Access 2007 database
Access 2007 makes it easier and faster to sign and distribute a database. When you create an .accdb file or .accde file, you can package the file, apply a digital signature to the package, and then distribute the signed package to other users. The Package-and-Sign feature places the database in an Access Deployment (.accdc) file, signs the package, and then places the code-signed package at a location that you determine.
Remember these facts as you proceed:
-
Packaging a database and signing the package are ways to convey trust. When you or your users receive the package, the signature confirms that the database has not been tampered with. If you trust the author, you can enable the content.
-
The new Package-and-Sign feature applies only to databases in the Office Access 2007 file format. Access 2007 provides the older tools that are needed to sign and distribute databases that were created in the earlier file format. Also, you cannot use the older tools to sign and deploy files that were created in the new file format. Put another way, you cannot apply a digital signature to an .accdb file unless you package the database.
-
You can add only one database to a package.
-
The process code-signs all of the objects in your databases, not just macros or code modules. The process also compresses the package file to help reduce download times.
-
You can extract databases from package files that are located on Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 servers.
The following sections explain how to create a signed package file and use the database in a signed package file.
To use this procedure, you must have at least one security certificate available. If you don't have a security certificate, you can create one by using the SelfCert tool.
Create a self-signed certificate
-
In Microsoft Windows, click the Start button, point to All Programs, point to Microsoft Office, point to Microsoft Office Tools, and then click Digital Certificate for VBA Projects.
-or-
Browse to the folder that contains your Office Professional 2007 program files. The default folder is Drive:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office12. In that folder, locate and double-click SelfCert.exe.
The Create Digital Certificate dialog box appears.
-
In the Your certificate's name box, type a name for the new certificate.
-
Click OK twice.
Note: If you don't see the Digital Certificate for VBA Projects command, or you can't find SelfCert.exe, you might need to install SelfCert.
Install SelfCert.exe
-
Start your Office Professional 2007 Setup CD or other installation media.
-
In Setup, click Add or Remove Features, and then click Continue.
Note: If you work in an environment in which Office Professional 2007 is installed on individual computers by IT administrators rather than by CD, follow these steps:
-
In Microsoft Windows, click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
-
Double-click Add or Remove Programs.
-
Select 2007 Microsoft Office system, and then click Change.
Setup starts.
-
Click Add or remove features, and then click Continue.
-
Continue with the following steps.
-
-
Expand the Microsoft Office and Office Shared Features nodes by clicking the plus signs (+) next to them.
-
Click Digital Certificate for VBA Projects.
-
Click Run from My Computer.
-
Click Continue to install the component.
-
Click Close after the installation finishes, and then go back to the first set of steps in this section.
Create a signed package
-
Open the database that you want to package and sign.
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , point to Publish, and then click Package and Sign.
, point to Publish, and then click Package and Sign. -
Select a digital certificate and then click OK.
The Create Microsoft Office Access Signed Package dialog box appears.
-
Select a location for your signed database package.
-
Enter a name for the signed package in the File name box, and then click Create.
Access creates the .accdc file and places it in the location that you choose.
Extract and use a signed package
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
Select Microsoft Office Access Signed Packages (*.accdc) as the file type.
-
Locate the folder that contains your .accdc file, select the file, and then click Open.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you have earlier chosen to trust the digital certificate that was applied to the deployment package, the Extract Database To dialog box appears. Go to the next step.
-
If you have not yet chosen to trust the digital certificate, an advisory message appears.
-
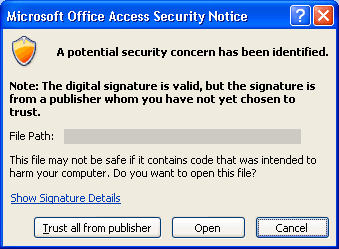
-
If you trust the database, click Open. If you trust any certificate from that provider, click Trust all from publisher and then click OK.
-
-
-
Optionally, select a location for the extracted database, and then in the File name box, enter a different name for the extracted database.
Use other security features
Office Access 2007 provides several other security features from previous versions, including user-level security and the ability to code sign modules of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) code. Typically, advanced users and developers use these tools.
Understand the Office Access 2007 security features and architecture
The information in the following sections describes the new security features in Access 2007 and explains the architecture that underlies these features.
New Access 2007 security features
Access 2007 provides an improved security model that helps to simplify the process of applying security to a database and of opening a database that has security enabled.
Note: Although the model and techniques discussed in this article enhance security, the most secure way to help protect your data is to store your tables on a server, such as a computer running Windows SharePoint Services 3.0, and to store your forms and reports on local computers or network shares.
The following is a list of what is new in Access 2007 security:
-
The ability to view data even when you don't want to enable any disabled VBA code or components in a database. In Office Access 2003, if you set your security level to High, you had to code sign and trust a database before you could view data. In Office Access 2007, you can open databases and view data without having to decide whether you should enable the contents of a database.
-
Greater ease of use. If you place database files (in either the new Office Access 2007 file format or the earlier file formats) in a trusted location, such as a file folder or network share that you designate as secure, those files will open and run without displaying warning messages or asking you to enable any disabled content. Also, if you open databases from earlier versions of Access, such as .mdb or .mde files, in Access 2007, and those databases were digitally signed and you chose to trust the publisher, those files will run without the need to make trust decisions. However, remember that VBA code in a signed database will not run until you trust the publisher, and it will not run if the digital signature becomes invalid. A signature becomes invalid when someone other than the person who signed it tampers with the content of a database.
-
The Trust Center. The Trust Center is a dialog box that provides a single location for setting and changing security settings for Access. You use the Trust Center to create or change trusted locations and to set security options for Office Access 2007. Those settings affect how new and existing databases behave when they are opened in that instance of Access. The Trust Center also contains logic for evaluating the components in a database and for determining if the database is safe to open or whether the Trust Center should disable the database and let you decide to enable it. For information about using the Trust Center with Access, see Create a trusted location, earlier in this article.
-
Fewer warning messages. Earlier versions of Access forced you to deal with a variety of alert messages — macro security and sandbox mode, just to name two. By default, if you open an Office Access 2007 database outside of a trusted location, you see only the Message Bar.

If you know that you can trust the contents of the database, you can use the Message Bar to enable all disabled components — action queries (queries that add, delete, or change data), macros, ActiveX controls, expressions, and VBA code — when you open a database that contains one or more of those components.
-
New ways to sign and distribute files created in the Office Access 2007 file format. In earlier versions of Access, you used the Visual Basic Editor to apply a security certificate to individual database components. In Access 2007, you package the database and then sign and distribute the package. If you extract a database from a signed package to a trusted location, the database runs without displaying the Message Bar. If you extract a database from a signed package to an untrusted location, but you trusted the package certificate and the signature is valid, you don't need to make a trust decision. When you package and sign a database that is untrusted or that contains an invalid digital signature, you must use the Message Bar to trust the database each time you open it, unless you place it in a trusted location.
-
A stronger algorithm for encrypting databases in the Office Access 2007 file format, which uses the database password feature. Encrypting a database scrambles the data in your tables and helps prevent unwanted users from reading your data.
-
A new subclass of macro actions that run when a database is disabled. These safer macros also contain error-handling capabilities. You can also embed macros (even those that contain actions that Access disables) directly into any form, report, or control property that would logically work with a module of VBA code or a macro from an earlier version of Access.
Finally, remember these rules as you proceed:
-
If you open the database in a trusted location, all components run without the need to make trust decisions.
-
If you package, sign, and deploy a database from an earlier version of Access (.mdb or .mde file), all components run without the need to make trust decisions if the database contains a valid digital signature from a trusted publisher, and you trust the certificate.
-
If you sign and deploy an untrusted database to an untrusted location, the Trust Center disables the database by default, and you must choose to enable the database each time you open it. For more information, see the section Trust a database for the current session, earlier in this article.
Office Access 2007 security architecture
To understand the Access 2007 security architecture, you need to remember that an Access database is not a file in the same sense as a Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbook or a Microsoft Office Word 2007 document. Instead, an Access database is a set of objects — tables, forms, queries, macros, reports, and modules — that often depend on each other to function. For example, if you create a data entry form, you cannot enter or store data with that form unless you bind (link) the controls in the form to a table.
Several Access components can pose security risks, including action queries (queries that insert, delete, or change data), macros, expressions (functions that return a single value), and VBA code. To help make your data more secure, Office Access 2007 and the Trust Center perform a set of security checks whenever you open a database. The process works as follows:
-
When you open an .accdb or .accde file in Office Access 2007, Access submits the location of the database to the Trust Center. If the location is trusted, the database runs with full functionality. If you open a database from an earlier version of Access in Access 2007, Access submits the location and details about the digital signature applied to that database, if any.
The Trust Center checks that evidence to evaluate trust for the database and then informs Access how to open the database. Access either disables the database or opens it with full functionality. When the Trust Center evaluates a database as untrusted, Office Access 2007 opens that database in Disabled mode — that is, it turns off all executable content. This is true for databases that were created in the new Access 2007 file format and for files created in earlier versions of Access.
Access 2007 disables the following components:
-
VBA code and any references in the VBA code, plus any unsafe expressions.
-
Unsafe actions in all macros. Unsafe actions are any actions that could allow a user to modify the database or gain access to resources outside the database. However, actions that Access disables can sometimes be considered safe. For example, if you trust the person who created the database, you can trust any unsafe macro actions in the database.
-
Several types of queries:
-
Action Queries These add, update, and delete data.
-
Data Definition Language (DDL) Queries These are used to create or alter objects in a database, such as tables and procedures.
-
SQL Pass-Through Queries These send commands directly to a database server that supports the Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) standard. Pass-through queries work with the tables on the server without involving the Access database engine.
-
-
ActiveX controls
Note: Remember that the settings you or your system administrator choose in the Trust Center control the trust decisions that occur when Access opens a database.
-
-
If the Trust Center disables any content, the Message Bar appears when the database opens.

To enable disabled content, you click Options and then choose the Enable this content option in the Microsoft Office Security Options dialog box. Access enables the disabled content, and the database reopens with full functionality. Otherwise, the disabled components will not work. For more information about choosing a trust option, see Trust a database for the current session, earlier in this article.
When a database opens, Access attempts to load any installed add-ins — programs that extend the functionality of either Access or the open database. You can also run wizards that create objects in the open database. When an add-in is loaded or a wizard starts, Access passes evidence to the Trust Center, which makes additional trust decisions and either enables or disables the object or action. Whenever the Trust Center disables a database and you disagree with that decision, you can almost always use the Message Bar to enable the content. Add-ins provide the exception to that rule. If, in the Trust Center dialog box (in the Add-ins pane), you select the Require Application Add-ins to be signed by Trusted Publisher check box, Access prompts you to enable the add-in, but that process does not involve the Message Bar.
For information about using the Trust Center, see Create a trusted location, earlier in this article.
How security works with databases from earlier versions of Access opened in Office Access 2007
When you open a database that was created in an earlier version of Access, any security features applied to that database still work. For example, if you applied user-level security to a database, the feature works in Access 2007.
By default, Access opens all older, untrusted databases in Disabled mode and keeps them in that state. You can choose to enable any disabled content each time you open the older database, you can apply a digital signature by using a certificate from a trusted publisher, or you can place the database in a trusted location.
For databases saved in versions of Access earlier than Office Access 2007, code signing is the process of applying a digital signature to the components in the database. A digital signature is an encrypted, electronic authentication stamp. It confirms that macros, code modules, and other executable components in the database originated with the signer and that no one has altered them since the database was signed.
To apply a signature to your database, you first need a digital certificate. If you create databases for commercial distribution, you must obtain a certificate from a commercial certificate authority (CA), such as VeriSign, Inc., or GTE. Certificate authorities do background checks to verify that the people who produce databases (known as publishers) are reputable.
If you want to use a database for personal or limited workgroup scenarios, Microsoft Office Professional 2007 provides a tool for creating a self-signed certificate.
Office Access 2007 and user-level security
Access 2007 does not provide user-level security for databases that are created in the new file format (.accdb and .accde files). However, if you open a database from an earlier version of Access in Access 2007 and that database has user-level security applied, those settings will still function.
If you convert a database that has user-level security from an earlier version of Access to the new file format, Access strips out all security settings automatically, and the rules for securing an .accdb or .accde file apply.
Finally, remember that all users can see all database objects when you open databases that were created in Office Access 2007.
No comments:
Post a Comment