Project management goal: Manage costs and the budget
| | If your project contains cost information for budgeting or for tracking project performance, this information isn't doing you much good unless you can view and analyze it. Without a solid understanding of where your costs are going in a project, the project can quickly fail and become unprofitable. This article is one of many project management goals on the Project Road Map. |
EXAMPLES FROM PROJECT MANAGEMENT . . .
Example One: The accidental project manager : You're a busy person with too much to do, and suddenly your boss hands you a project schedule And tells you to track costs on the project. Creating projects is something you're familiar with, but adding costs in Microsoft Project strikes you as hard enough without the additional nightmare of tracking them.
However, tracking costs in Microsoft Project isn't any more difficult than tracking work in a project. Besides, your boss probably isn't expected a complicated earned value analysis or a major portfolio treatment. Here are a few basics you should know first.
-
Know what costs are First, understand what costs are and what they aren't. The most critical costs in any project is the cost of people's work on projects, as well as consultant fees, and vendor costs from those individuals and organizations whom you are contracting with.
There are also costs associated with materials, such as cement, boards, scaffolding, heavy equipment, and computers. And if you plan on doing any business traveling on behalf of the project, you need to consider the cost of airfare, car rental, and accommodations as costs that also need to be added to the project. -
Enter costs OK, so now you know all about costs. Where do you enter it in Microsoft Project? The links toward the end of this article will help you. In general, most cost information is entered in the Resource sheet. It is there that you indicated whether a cost is for hourly workers, salaried workers, contractual costs for consultants, fixed or one-time costs for project materials, and so forth.
-
View cost information After you enter costs for resources, tasks, or both, you can examine them to see if they need to be adjusted to meet your goal for costs. At some point, stakeholders will be looking for this information.
-
Report cost information A quick way to create an impressive display of cost information is to export cost information to Excel, and then create Sparklines. Here is an example of cost information copied from the cost table in Project and pasted into Excel 2010 with a sparkline created for it showing the relative expense of the types.

Here are three steps to help grow your cost skills.
-
Start simple You don't have to enter all costs to learn basic cost management in Project. Start with basic costs like, such as a person's salary, using the Resource Sheet. Then assign this resource to a few tasks to learn about the relation of work to duration and cost. Now, bring up the Project Information dialog (Click the Projects tab, click Project Information., then click Advanced). Examine the total values for your Project's duration, work, and cost. Go back and forth between the Resource Sheet and the Project Information dialog box, making salary changes in the Resource sheet and seeing the totals change in the Project Information dialog box.
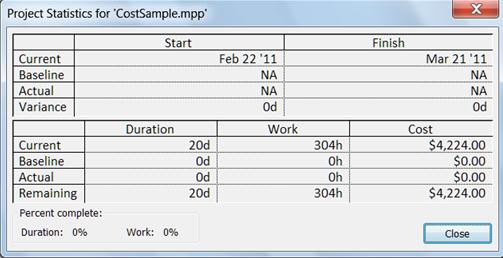
-
Grow your skills As you become more familiar with costs, start adding costs fir airfare hotel accommodations, fixed costs for reservations, and maybe vendor costs, like catering, tent displays, and so forth. You don't even have to tract costs or create a baseline for them (unless you want to use the more robust budgeting features of Project).
-
Learn from the experts Read the next section to learn how the experts deal with costs (Hint: this isn't beyond your reach either)
Example Two: You're a seasoned project manager : You've been a project manager for a long time, and you've used complicated project manager software in the past. You even know the difference between BAC from EAC and can calculate a project's net present value like nobody's business.
Now you want to figure out how to do the same in Project 2010. You'll find that Project provides robust features for controlling your budget by managing changes to your costs and cost baselines.
Keep in mind, though, that the bigger and more complicated your organization, the more things you have to worry about when it comes to entering, analyzing, and controlling costs.
-
Review historical data Examining the cost histories of similar projects helps you to better estimate the costs in a current project. If your organization has PMO (Project Management Office), consult with them about your cost and budget needs. One aspect of an organization with mature project management practices is a constantly evolving history of past projects so that mistakes aren't repeated and successes are continued.
-
Enter costs Most information is entered in the Resource sheet. It is there that you indicated whether a cost is for hourly employees and fixed or one-time costs for project materials. Don't forget the other costs that are involved in project management: cost of contracts, cost or contingency reserves for tasks that have high risk, costs for insurance or bonds.
Tracking and managing costs, especially if you're doing earned value analysis, requires that you enter cost information for resources who are assigned to tasks. It also requires that you set baselines.Warning: Your organization may have strict policies regarding costs incurred from contractual obligations. Make sure you understand corporate policies thoroughly regarding whether you should enter into contracts with, say a vendor, and what type of contract you can enter into. .
-
Create a baseline . Unless you create a baseline after entering costs, you won't be able to analyze or control them. A baseline is the plan as approved by all stakeholders. In Project, this is set on the Project tab. Keep in mind that when you set a baseline with Project, you set the baseline not only for costs, but for task durations and work estimates as well.
-
Always review your costs After you enter costs for resources, tasks, or both, you can examine them to see if they need to be adjusted to meet your goal for costs. At some point, stakeholders will be looking for this information
-
Use an expert to review your cost requirements Use an experienced and knowledgeable team member to review the cost estimates for tasks and resources. Larger organizations use a PMO (Project Management Office), or they'll hire a professional estimator.
-
Understand earned value . Earned value is an industry standard for analyzing cost variances throughout the length of your project. You don't want to discover toward the end of your project that you are overbudget and behind schedule.
-
Export cost information to other programs You may want to export cost information to another program for further analysis. A quick tool you can use are sparklines in Excel 2010. This example displays sparklines for earned value information copied from Project to Excel.
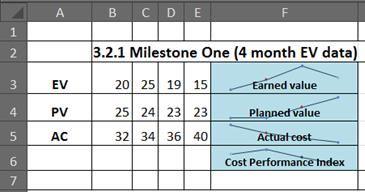
You can also use Visual Reports in Project to create a more sophisticated PivotChart of earned value (commonly known as an S curve).

-
You can even take your Project data further and create an advanced analysis using ANOVA or Monte Carlo. The skies the limit to analyzing Project information.
In this article
Step 1: Enter and view costs in your project
| Firsts things first—you need to enter costs for all the people, equipment, and other resources in your project. | |
| After you enter costs for resources, tasks, or both, you can examine them to see if they need to be adjusted to meet your goal for costs. | |
| Specifying when the actual costs are charged to your project (at the start, finish, or throughout the project) can help you establish a cash flow plan | |
| At some point, you will want to report on project costs to others in your organization. | |
| You can export project cost information to Visio or Excel for reporting or further analysis. | |
| When your cost estimates are in line with your goal for costs, you can establish them as your baseline plan. In this way, you can compare actual cost with your original plan as the project progresses. | |
| You compare the costs of one project against an earlier project using the compare versions feature in Project. | |
| Reviewing how the tasks are doing in your schedule tells you about where the costs are going. | |
| See what's driving the project finish date (critical path) | Task on the critical path can have the most impact on the costs of the project overall. Learn how to spot them. |
| Hide a column in a view | Hiding columns is an effective way to temporarily prevent the information from being seen by others. Don't worry—when you hide columns, cost data isn't going to be deleted. |
Step 2: Manage costs
| After you enter costs for resources, tasks, or both, you can examine them to see if they need to be adjusted to meet your goal for costs. | |
| Specifying when the actual costs are charged to your project (at the start, finish, or throughout the project) can help you establish a cash flow plan | |
| When your cost estimates are in line with your goal for costs, you can establish them as your baseline plan. In this way, you can compare actual cost with your original plan as the project progresses. | |
| Reviewing how the tasks are doing in your schedule tells you about where the costs are going. | |
| An earned value analysis indicates how much of the budget should have been spent, in view of the amount of work done so far and the baseline cost for the task, assignment, or resources. | |
| Learn how to export your schedule to a format that is UN/CEFACT compliant (United Nations Centre for Trade Faciltation and Electronic Business). | |
| See what's driving the project finish date (critical path) | Task on the critical path can have the most impact on the costs of the project overall. Learn how to spot them. |
| Hide a column in a view | You may not want everyone in your organization to view cost information, especial costs from people's salaries, costs from outside vendor contracts, or corporate budgets. Hiding columns is an effective way to temporarily prevent the information from being seen by others. Don't worry—When you hide columns, cost data isn't going to be deleted. Data can only be deleted from Project if you manually highlight rows or cells of data, not entire columns of data. |
| You can export project data to excel. For example, if you are analyzing an earned value analysis, you can export this information to view a standard S-curve of earned value information for further analysis. | |
| Use Sparklines in Excel 2010 to control costs | You may not want everyone in your organization to view cost information, especial costs from people's salaries, costs from outside vendor contracts, or corporate budgets. Hiding columns is an effective way to temporarily prevent the information from being seen by others. Don't worry—When you hide columns, cost data isn't going to be deleted. Data can only be deleted from Project if you manually highlight rows or cells of data, not entire columns of data. |

Hey, thanks for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
ReplyDeletesalesforce billing course online
learn salesforce billing online
Thanks for sharing this useful information; I've pinned this for future reference. I'm looking forward to hearing from you again soon.
ReplyDeleteVisit: project-time-tracking
Project management is skill and this always need to improve, I found this blog very useful for my PGDM course in project management. keep sharing.
ReplyDelete