Introduction to the Query Editor (Power Query)
Note: Power Query is known as Get & Transform in Excel 2016. Information provided here applies to both. To learn more, see Get & Transform in Excel 2016.
Query Editor only appears when you load, edit, or create a new query. The following video shows the Query Editor window appearing after editing a query from an Excel workbook. To view the Query Editor without loading or editing an existing workbook query, from the Get External Data section in the Power Query ribbon tab, select From Other Sources > Blank Query.
With Query Editor, you can navigate, define, and perform data transform operations over a data source. To display the Query Editor dialog box, connect to a data source, and click Edit Query in the Navigator pane or double-click a query in the Workbook Queries pane. To connect to a data source, see Import data from external data sources.
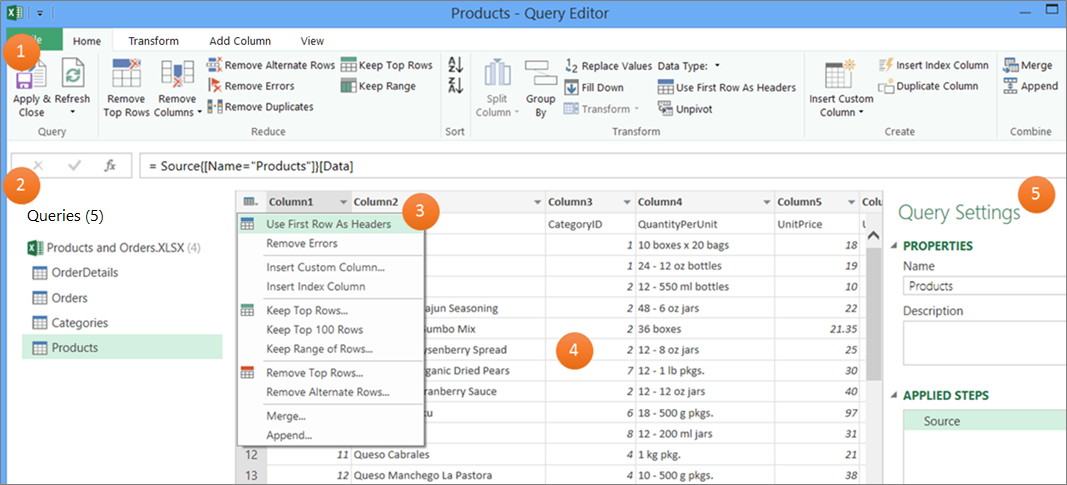
The query editor has the following user interface elements:
-
Query Editor ribbon.
-
Navigator pane that enables you to browse structured data sources to find the data table that you want to query.
-
Context menus are specific to an element, such as a table column, within the editor preview grid.
-
Preview grid that displays a preview of data from the results of each query step. You interact within the Preview pane to shape data to reduce and rearrange one or more tables into a subject table to match your data analysis requirements. For more information about shaping data, see Shape data.
-
Query Settings pane that includes each query step. A step is each of the data acquisition or data transformation tasks applied on a query. For more information about how to edit query steps, see Edit query step properties.
No comments:
Post a Comment