Present your data in a histogram
You can analyze your data and display it in a histogram (a column chart that displays frequency data) by using the Histogram tool of the Analysis ToolPak. This data analysis add-in is available when you install Excel, but it might not be loaded automatically.
Important: If you don't see the Data Analysis button in the Analysis group on the Data tab, you must load the Analysis ToolPak add-in.
What do you want to do?
Learn more about plotting data in a histogram
To create a histogram, you must organize the data in two columns on the worksheet. These columns must contain the following data:
-
Input data This is the data that you want to analyze by using the Histogram tool.
-
Bin numbers These numbers represent the intervals that you want the Histogram tool to use for measuring the input data in the data analysis.
When you use the Histogram tool, Excel counts the number of data points in each data bin. A data point is included in a particular bin if the number is greater than the lowest bound and equal to or less than the greatest bound for the data bin. If you omit the bin range, Excel creates a set of evenly distributed bins between the minimum and maximum values of the input data.
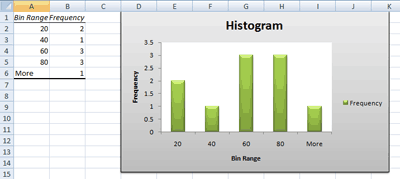
The output of the histogram analysis is displayed on a new worksheet (or in a new workbook) and shows a histogram table and a column chart that reflects the data in the histogram table.
Load the Analysis ToolPak
-
On the File tab, click Options. (In Excel 2007, click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Excel Options.)
, and then click Excel Options.) -
Click Add-Ins.
-
In the Manage box, click Excel Add-ins, and then click Go.
-
In the Add-Ins available box, do one of the following:
-
To load the Analysis ToolPak, select the Analysis ToolPak check box, and then click OK.
-
To include Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) functions for the Analysis ToolPak, select the Analysis ToolPak - VBA check box, and then click OK.
Tip: If Analysis ToolPak or Analysis ToolPak - VBA is not listed in the Add-Ins available box, click Browse to locate it.
-
-
If you see a message that the Analysis ToolPak is not currently installed on your computer, click Yes to install it.
Tip: After you load the Analysis ToolPak, the Data Analysis command is available in the Analysis group on the Data tab.
Create a histogram
-
To enter the data that you want to analyze in a histogram, do one of the following:
-
Copy the example worksheet data to your worksheet.
How to copy the example worksheet data
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note: Do not select the row or column headers.
 Selecting an example from Help
Selecting an example from Help -
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
-
|
|
-
On a worksheet, enter your own data as follows:
-
In one column, type the input data.
Note: You must enter quantitative numeric data (such as item amounts or test scores) in each cell of the input column — the Histogram tool does not work with qualitative numeric data (such as identification numbers).
-
In another column, type the bin numbers that you want to use for the analysis. The bin numbers must be entered in ascending order.
Note: If you don't enter the bin numbers on the worksheet, the Histogram tool automatically creates evenly distributed bin intervals by using the minimum and maximum values in the input range as start and end points. However, these bins may not be useful — we recommend that you use your own bin numbers.
-
If you want, you can add a label in the first cell of these columns:
-
On the Data tab, in the Analysis group, click Data Analysis.
-
In the Analysis Tools box, click Histogram, and then click OK.
-
Under Input, in the Input Range box, enter the cell reference for the range of data you want to analyze.
If you are using the sample worksheet data, type A1:A11.
You can also click the Collapse Dialog button
 , select the range on the worksheet, and then click the Collapse Dialog button again to return to the dialog box.
, select the range on the worksheet, and then click the Collapse Dialog button again to return to the dialog box. -
Under Input, in the Bin Range box, enter the cell reference to a range that contains an optional set of boundary values that define bin ranges.
If you are using the sample worksheet data, type B1:B5.
You can also click the Collapse Dialog button
 , select the range on the worksheet, and then click the Collapse Dialog button again to return to the dialog box.
, select the range on the worksheet, and then click the Collapse Dialog button again to return to the dialog box.Note: If you do not enter a range in the Bin Range box, the Histogram tool creates a set of evenly distributed bins between the data's minimum and maximum values. However, we recommend that you enter or select the bin range that you used on the worksheet.
-
If you included column labels when you selected the input and bin range data, select the Labels check box.
-
Under Output options, do one of the following:
-
To paste the output table on the same sheet, click Output Range, and then enter the cell reference of the upper-left cell of the output table.
Note: The Histogram tool automatically determines the size of the output area and displays a message if the output table will replace existing data.
-
To insert a new worksheet in the current workbook and paste the output table starting at cell A1 of the new worksheet, click New Worksheet Ply.
You can type a name in the New Worksheet Ply box.
-
To create a new workbook and paste the output table on a new worksheet in the new workbook, click New Workbook.
-
-
Under Output options, do any or all of the following:
-
To present data in the output table in descending order of frequency, select the Pareto (sorted histogram) check box.
-
To generate an output table column for cumulative percentages and to include a cumulative percentage line in the histogram chart, select the Cumulative Percentage check box.
-
To generate an embedded histogram chart with the output table, select the Chart Output check box.
-
-
Click OK.
Tip: After the bin and frequency table is generated, you can select any of the text and change the default labels. When you click the histogram, you can use the design, layout, and format options of the Chart Tools to change the display of the chart. For more information about changing the design and format of a chart, see the links in the See Also section.
No comments:
Post a Comment