Get a digital ID
A digital ID enables you to send digitally signed messages using Microsoft Outlook. A digital ID—also known as a digital certificate—helps prove your identity and helps prevent message tampering to protect the authenticity of an email message. You also can encrypt messages for greater privacy.
Note: A digital signature isn't the same as a message signature, which is a customizable salutation. A digital signature adds unique code to a message that only comes from the digital ID held by the true sender.
What would you like to do?
Get a digital ID from a certifying authority
A digital ID is issued by an independent certification authority. By using this procedure, you'll get a list of several certification authorities in your web browser. Your organization, however, may have policies that require a different procedure. See your network administrator for more information.
-
On the File tab, click Options > Trust Center.
-
Under Microsoft Outlook Trust Center, click Trust Center Settings.
-
On the E-mail Security tab, under Digital IDs (Certificates), click Get a Digital ID.
Note: Your web browser opens and displays a webpage on the Microsoft Office Online website that lists several certification authorities. Click the one that you want to use and follow the instructions on the webpage to register for a digital ID. The certification authority will then send you a digital ID and instructions via email.
Specify the digital ID to use
You might choose to have more than one digital ID—one for your digital signature, which in many areas can have legal significance, and another for encryption.
-
On the File tab, click Options > Trust Center.
-
Under Microsoft Outlook Trust Center, click Trust Center Settings.
-
On the E-mail Security tab, under Encrypted e-mail, click Settings.
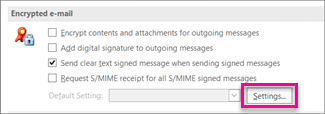
Note: If you have a digital ID, the settings to use the digital ID are automatically configured for you. If you want to use a different digital ID, follow the remaining steps in this procedure.
-
Under Security Setting Preferences, click New.
-
In the Security Settings Name box, enter a name.
-
In the Cryptography Format list, click S/MIME. Depending on your certificate type, you can choose Exchange Security instead.
-
Next to the Signing Certificate box, click Choose, and then select a certificate that is valid for digital signing.
Note: To learn if the certificate is intended for digital signing and encryption, in the Select Certificate dialog box, click View Certificate. An appropriate certificate for cryptographic messaging (such as digital signing) might state, for example, "Protects email messages."
-
Select the Send these certificates with signed messages check box unless you'll be sending and receiving signed messages only within your organization.
Note: The settings that you choose become the default when you send cryptographic messages. If you don't want these settings to be used by default for all cryptographic messages, clear the Default Security Setting for this cryptographic message format check box.
Add a recipient's digital ID to your Contacts
To send and receive encrypted email messages, both the sender and the receiver must share their digital ID certificates with each other.
-
Open a message that is digitally signed as indicated in the message list by a Signature icon.
-
Right-click the name in the From box, and then click Add to Outlook Contacts.
-
If you already have an entry for this person, in the Duplicate Contact Detected dialog box, select Update information of selected Contact.
Notes:
-
A backup copy is saved in the Deleted Items folder.
-
The certificate is now stored with your contact entry for this recipient. You can now send encrypted messages to this person.
-
To view the certificate for a contact, double-click the person's name, and then click the Certificates tab.
-
View a certificate for a contact
-
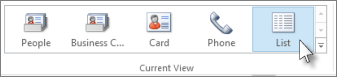
On the Navigation bar, click People.
-
On the Home tab, click List.
-
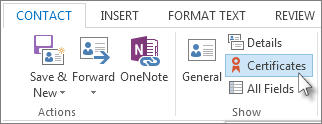
Double-click the person's name, and then on the Contact tab, click Certificates.
Get a digital ID for sending messages by using Microsoft Exchange
Note: This feature requires a Microsoft Exchange Server account.
To get an Exchange Server digital ID—for example, through Key Management Service—the administrator of your Exchange account must have security running on the server and give you a special password, which is known as a token. For more information, see your Exchange administrator.
-
On the File tab, > Options > Trust Center
-
Under Microsoft Outlook Trust Center, click Trust Center Settings.
-
On the E-mail Security tab, under Digital IDs (Certificates), click Get a Digital ID.
-
Click Set up Security for me on the Exchange > OK
-
In the Digital ID Name box, type your name.
-
In the Token box, type the special password that your Exchange administrator assigned to you.
-
In the Microsoft Office Outlook Security Password dialog box, type a different password for the digital ID, and then type the password again in the Confirm box.
Note: You'll receive a message in your Inbox from the Exchange administrator which requires you to enter the password created in this step.
-
In the dialog box that appears, enter your password, select the Remember password for check box, and then enter the number of minutes that you want Outlook to remember your password.
-
In the Root Certificate Store message that appears, click Yes.
What would you like to do?
Get a digital ID from a certifying authority
-
On the Tools menu, click Trust Center, and then click E-mail Security.
-
Under Digital IDs (Certificates), click Get a Digital ID.
-
Click Get an S/MIME certificate from an external Certification Authority, and then click OK.
Outlook starts your web browser and opens a webpage on the Microsoft Office Online website that lists several certification authorities. Click the one that you want to use and follow the instructions on the webpage to register for a digital ID. The certification authority will then send you a digital ID and instructions via e-mail.
Specify the digital ID to use
-
On the Tools menu, click Trust Center, and then click E-mail Security.
-
Under Encrypted e-mail, click Settings.
Note: If you have a digital ID, the settings to use the digital ID are automatically configured for you. If you want to use a different digital ID, specify the digital ID by following the remaining steps in this procedure.
-
At the bottom of the Security Setting Preferences section, click New.
-
In the Security Settings Name box, enter a name.
-
In the Cryptography Format list, click S/MIME. Depending on your certificate type, you can choose Exchange Security instead.
-
Next to the Signing Certificate box, click Choose, and then select a certificate that is valid for digital signing.
Note: To learn if the certificate is intended for digital signing and encryption, on the Select Certificate dialog box, click View Certificate. An appropriate certificate for cryptographic messaging (such as digital signing) might say, for example, "Protects e-mail messages."
-
Next to the Encryption Certificate box, click Choose, and then select a certificate that is valid for encryption.
-
Select the Send these certificates with signed messages check box unless you will be sending and receiving signed messages only within your organization.
Note: The settings that you choose become the default whenever you send cryptographic messages. If you do not want these settings to be used by default for all your cryptographic messages, clear the Default Security Setting for all cryptographic messages check box.
Add a recipient's certificate to your Contacts
-
Open a message that has been digitally signed.
-
Right-click the name in the From box, and then click Add to Outlook Contacts on the shortcut menu.
-
If you already have an entry for this person, in the Duplicate Contact Detected dialog box, select Update information of selected Contact. A backup copy will be saved in Deleted Items Folder.
The certificate is now stored with your contact entry for this recipient. You can now send encrypted e-mail messages to this person.
To view the certificate for a contact, double-click the person's name, and then click the Certificates tab.
Get a digital ID for sending messages by using Microsoft Exchange
This feature requires you to use a Microsoft Exchange Server 2000, Exchange Server 2003, or Exchange Server 2007 account. Most home and personal accounts don't use Microsoft Exchange.
To get an Exchange digital ID—for example, through Key Management Service—your Exchange administrator must have security running on the server and must give you a special password, called a token. Your Exchange will then send you a message verifying your token. For more information, see your Exchange administrator.
-
On the Tools menu, click Trust Center, and then click E-mail Security.
-
Under Digital IDs (Certificates), click Get a Digital ID.
-
Click Set up Security for me on the Exchange.
-
Click OK.
-
In the Digital ID Name box, type your name.
-
In the Token box, type the special password that your Exchange administrator assigned to you.
-
In the Microsoft Office Outlook Security Password dialog box, type a different password for the digital ID, and then type the password again in the Confirm box.
You will receive a message in your Inbox from your Exchange administrator that will require you to enter the password you created in this step.
-
In the dialog box that appears, enter your password, click the Remember password for check box, and then enter the number of minutes for which you want Outlook to remember your password.
-
In the Root Certificate Store message that appears, click Yes.
No comments:
Post a Comment