Import data into Office Publisher, Visio, or Word by using the Data Connection Wizard
There is a world of data outside of your Microsoft Office Publisher, Visio, or Word program that you can use inside each program. But how do you import the data and secure it? It is all about making the right connections.
What do you want to do?
Overview of Office data connections
The following sections discuss how external data connections work and how to share the connection information with other applications and users.
Understanding the basics of data connections
Data in your program can come from an external data source, such as a text file, a workbook, or a database. This external data source is connected to your program through a data connection, which is a set of information that describes how to locate, log in, and access the external data source.
The main benefit of connecting to external data is this: You can periodically analyze this data without repeatedly copying the data. Repeatedly copying data is an operation that can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Connection information is stored in your workbook and can also be stored in a connection file, such as in an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc) or in a Data Source Name (DSN) file (.dsn).
To bring external data into your program, you need access to the data. If the external data source that you want to access is not on your local computer, you may need to contact the administrator of the database for a password, user permission, or other connection information. If the data source is a database, make sure that the database is not opened in exclusive mode. If the data source is a text file or a workbook, make sure that another user does not have the text file or workbook open for exclusive access.
Many data sources also require an ODBC driver or OLE DB provider to coordinate the flow of data among your program, the connection file, and the data source.
The following diagram summarizes the key points about data connections.
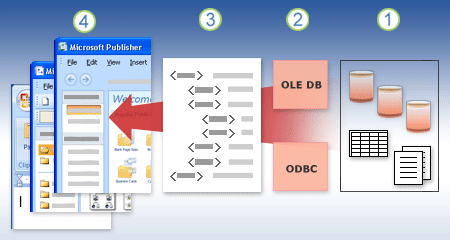
1. There are a variety of data sources that you can connect to: Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Office Access, Microsoft Office Excel, and text files.
2. Each data source has an associated ODBC driver or OLE DB provider.
3. A connection file defines all of the information that you need to access and retrieve data from a data source.
4. Connection information is copied from a connection file into your program.
Sharing connections
Connection files are particularly useful for sharing connections on a consistent basis, making connections more discoverable, helping to improve security, and facilitating data source administration. The best way to share connection files is to put them in a secure and trusted location, such as a network folder or Microsoft Office SharePoint Designer library, where users can read the file, but only designated users can modify the file.
You can create Office Data Connection (ODC) files (.odc) by using Excel, or by using the Data Connection Wizard to connect to new data sources. An .odc file uses custom HTML and XML tags to store the connection information. You can easily view or edit the contents of the file in Excel.
You can share connection files with other users to give them the same access that you have to an external data source. Other users don't have to set up a data source to open the connection file, but they may need to install the ODBC driver or OLE DB provider that is required to access the external data on their computers.
Understanding Microsoft Data Access Components
Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) 2.8 is included with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 and Microsoft Windows XP SP2 and later. With MDAC, you can connect to and use data from a wide variety of relational and nonrelational data sources. You can connect to many different data sources by using Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) drivers or OLE DB providers. Either can be built and shipped by Microsoft or developed by various third parties. When you install Microsoft Office, additional ODBC drivers and OLE DB providers are added to your computer.
To see a complete list of OLE DB providers that are installed on your computer, display the Data Link Properties dialog box from a Data Link file, and then click the Provider tab.
To see a complete list of ODBC providers installed on your computer, display the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, and then click the Drivers tab.
You can also use ODBC drivers and OLE DB providers from other manufacturers to get information from sources other than Microsoft data sources, including other types of ODBC and OLE DB databases. For information about installing these ODBC drivers or OLE DB providers, check the documentation for the database, or contact your database vendor.
Using ODBC to connect to data sources
The following sections describe Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) in more detail.
The ODBC architecture
In the ODBC architecture, an application (such as your program) connects to the ODBC Driver Manager, which in turn uses a specific ODBC driver (such as the Microsoft SQL ODBC driver) to connect to a data source (such as a Microsoft SQL Server database).
Defining connection information
To connect to ODBC data sources, do the following:
-
Ensure that the appropriate ODBC driver is installed on the computer that contains the data source.
-
Define a data source name (DSN) by using either the ODBC Data Source Administrator to store the connection information in the Microsoft Windows registry or a .dsn file, or by using a connect string in Microsoft Visual Basic code to pass the connection information directly to the ODBC Driver Manager.
To define a data source, open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
For more information about the different options, click the Help button in each dialog box.
Machine data sources
Machine data sources store connection information in the Windows registry on a specific computer with a user-defined name. You can use machine data sources on only the computer they are defined on. There are two types of machine data sources — user and system. User data sources can be used by only the current user and are visible to only that user. System data sources can be used by all users on a computer and are visible to all users on the computer. A machine data source is especially useful when you want to provide added security, because it helps ensure that only users who are logged on can view a machine data source, and a machine data source cannot be copied by a remote user to another computer.
File data sources
File data sources (also called DSN files) store connection information in a text file, not in the Windows registry, and are generally more flexible to use than machine data sources. For example, you can copy a file data source to any computer with the correct ODBC driver, so that your application can rely on consistent and accurate connection information to all of the computers that it uses. Or you can place the file data source on a single server, share it between many computers on the network, and easily maintain the connection information in one location.
A file data source can also be unshareable. An unshareable file data source resides on a single computer and points to a machine data source. You can use unshareable file data sources to access existing machine data sources from file data sources.
Using OLE DB to connect to data sources
The following sections describe Object Linking and Embedding Database (OLE DB) in more detail.
The OLE DB architecture
In the OLE DB architecture, the application that accesses the data is called a data consumer (such as Publisher), and the program that enables native access to the data is called a database provider (such as Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server).
Defining connection information
A Universal Data Link file (.udl) contains the connection information that a data consumer uses to access a data source through the OLE DB provider of that data source. You can create the connection information by doing one of the following:
-
In the Data Connection Wizard, use the Data Link Properties dialog box to define a data link for an OLE DB provider.
-
Create a blank text file with a .udl file type, and then edit the file, which displays the Data Link Properties dialog box.
Make data access more secure
When you connect to an external data source or refresh the data, it is important to be aware of potential security issues and to know what you can do about those security issues. Use the following guidelines and best practices to help secure your data.
Storing data connections in a trusted location
A data connection file often contains one or more queries to a data source. By replacing this file, a user who has malicious intent can design a query to access confidential information and distribute it to other users or perform other harmful actions. Therefore, it is important to ensure the following:
-
The connection file was written by a reliable individual.
-
The connection file is secure and that it comes from a trusted location.
To help improve security, connections to external data may be unavailable on your computer. To connect to data when you open a workbook, you must activate data connections by using the Trust Center bar or by putting the workbook in a trusted location.
For more information, see Create, remove, or change a trusted location for your files, Add, remove, or view a trusted publisher, and View my security settings in the Trust Center.
Using credentials in a safe manner
Accessing an external data source usually requires credentials (such as a user name and a password) that are used to authenticate the user. Make sure that these credentials are provided to you in a safe and secure manner, and that you do not inadvertently reveal these credentials to others.
Use strong passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Weak passwords don't mix these elements. Strong password: Y6dh!et5. Weak password: House27. Passwords should be 8 or more characters in length. A pass phrase that uses 14 or more characters is better.
It is critical that you remember your password. If you forget your password, Microsoft cannot retrieve it. Store the passwords that you write down in a secure place away from the information that they help protect.
Avoid saving logon information when you connect to data sources. This information may be stored as plain text in the workbook and the connection file, and a malicious user can access the information to compromise the security of the data source.
When possible, use Windows Authentication (also referred to as a trusted connection), which uses a Windows user account to connect to SQL Server. When a user connects through a Windows user account, SQL Server uses information in the Windows operating system to validate the account name and password. Before you can use Windows Authentication, a server administrator must configure the SQL Server to use this mode of authentication. If Windows Authentication is not available, avoid saving users' logon information. It is more secure for users to enter their logon information each time that they log on.
Create or edit an Office Data Connection file by using Excel
You might want to share an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc) with other users or between different programs. To create or edit an .odc file, you can use Excel.
Create a new ODC file by using Excel
-
Locate the My Data Sources folder on your computer.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To create any type of connection file, right click the +Connect to New Data Source.odc file, and then click Open in Excel on the shortcut menu.
Excel starts. If the Microsoft Office Excel Security Notice message appears, click Enable.
The Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page of the Data Connection Wizard appears. Follow the instructions in the wizard.
-
To create a SQL Server connection file, right click the +New SQL Server Connection.odc file, and then click Open in Excel on the shortcut menu.
Excel starts and the Connect to Database Server page of the of the Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
Edit an existing ODC file by using Excel
-
Locate the folder that contains the .odc file, such as the My Data Sources folder on your computer, or a trusted network folder.
-
Right click the .odc file, and then click Open in Excel on the shortcut menu.
-
The Microsoft Office Excel Security Notice message may appear. If you trust the data source, click Enable.
The data that is retrieved by the .odc file is displayed in the first worksheet of a new workbook, to confirm that you have the correct connection.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Connections.
-
In the Workbook Connections dialog box, select the connection, and then click Properties.
-
Make the changes that you want in the Connection Properties dialog box.
For more information about modifying connection file information, see the Excel Help system.
-
After making all of the changes, click the Definition tab, and then click Export Connection File.
-
In the File Save dialog box, click Save.
-
Close the Connection Properties and Workbook Connections dialog boxes, and then exit Excel without saving the new workbook.
Office Publisher: Import external data by using the Data Connection Wizard
In Microsoft Office Publisher, you import external data by using mail merge. Use mail merge to create a large number of documents that are mostly identical but include some unique information, such as a product announcement that you are sending to your top 100 customers. You can also import text files, Excel worksheets, and Access tables or queries directly, without using a connection file. For more information, see Create a mail merge.
What do you want to do?
-
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an ODBC driver
-
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an ODBC driver
-
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an ODBC driver
Import a text file by using an OLE DB provider
Importing a comma-separated values (CSV) text file (.csv) is straightforward. If your text file is a .csv file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Import the file
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported, and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, select Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider, and then click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Select or enter a database name box, enter the full path to the folder that contains the text file.
To help you locate the folder, click the Browse button next to the box.
-
Click the All tab, select Extended Properties, and then click Edit Value.
-
In the Property Value box, enter one of the following:
-
If the text file has column headers, enter Text;HDR=Yes.
-
If the text file does not have column headers, enter Text;HDR=No.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, under the Name column, select the text file that you want to import, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Ex ample: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import a text file by using an ODBC driver
Importing a text file by using an ODBC driver is, at minimum, a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC text driver. Second, import the text file by using the user DSN. If your text file is a comma-separated values (CSV) file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, on the User DSN tab, click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select Microsoft Text Driver (*.txt; *.csv), and then click Finish.
The ODBC Text Setup dialog box appears.
-
Enter a name in the Data Source Name.
-
Clear the Use Current Directory check box.
-
Click Select Directory.
-
In the Select Directory dialog box, locate the folder that contains the text file that you want to import, make sure that the text file appears in the list below the File Name box, and then click OK.
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import the file
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data Source page, select the User DSN that you just created, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the text file under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a column header
[Categories.txt] ColNameHeader=True
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Example: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, select Microsoft Office 12.0 Access Database Engine OLE DB Provider, and then click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Data source box, enter the full path and file name of the Excel workbook.
-
Click the All tab, select Extended Properties, and then click Edit Value.
-
In the Property Value box, enter one of the following:
-
If the data in the workbook has column headers, enter Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes.
-
If the data in the workbook does not have column headers, enter Excel 8.0;HDR=No.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the worksheet under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an ODBC driver
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select Excel Files, and then click Next.
-
In the Select workbook dialog box, in the Database Name box, enter the folder that contains the Excel workbook, select the workbook in the list, and then click OK.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, under the Name column, select the worksheet that you want to import, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, do one of the following:
-
If the database is a Microsoft Access 2000 or Microsoft Office Access 2003 database, select Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider.
-
If the database is a Microsoft Office Access 2007 database, select Microsoft Office 12.0 Access Database Engine OLE DB Provider.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Select or enter a database name box, enter the full path and file name of the Access database.
If you selected Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider on the Provider tab, to help you locate the database, click the Browse button next to the box.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the table or query under the Name column, and then click Next.
Note: A linked table does not appear in this list. If you want to import a linked table, create a query to the linked table in the Access database before you perform the import operation.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an ODBC driver
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select MS Access database, and then click Next.
The Select Database dialog box appears.
-
In the Select Directory dialog box, locate the folder that contains the Access database that you want to import, make sure that the Access database appears in the list below the File Name box, and then click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the table or query under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Microsoft SQL Server.
-
In the Connect to Database Server page, do the following:
-
Enter the name of the database server in the Server Name box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Under Logon credentials, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click Use Windows Authentication.
-
To use a database user name and password, click Use the following User Name and Password, and then enter the database user name and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
-
Click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or user-defined function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an ODBC driver
Importing data from a SQL Server database by using an ODBC driver is a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC driver. Second, import the data from the SQL Server database.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, select the User DSN tab, and then click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select SQL Server, and then click Finish.
The Create a New Data Source to SQL Server dialog box appears.
-
Enter a data source name in the Name box.
-
Optionally, enter a description of the data source in the Description box.
-
Enter the database server name in the Server box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Click Next.
-
Under How should SQL Server verify the authenticity of the login ID?, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click With Windows NT authentication using the Network login ID.
-
To use a database user name and password, click With SQL Server authentication using login ID and password entered by the user, and then enter the database login ID and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
Click Next twice, and then click Finish.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click Test Data Source .
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "TESTS COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY!", click OK.
-
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import the data from the SQL Server database
-
On the Tools menu, point to Mailings and Catalogs, and then click Mail Merge, E-mail Merge, or Catalog Merge.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the E-mail Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a recipient list.
-
In the Catalog Merge task pane, click Create or connect to a product list.
-
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select the data source name that you defined in the previous section, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Office Visio: Import external data by using the Data Connection Wizard
In Microsoft Office Visio, you import external data so that it can be added directly to shapes in a drawing. Use a drawing to monitor information in a visual manner, such as a network diagram that displays downtime statistics or a flowchart that displays progress bars and meters to summarize project tasks. The following instructions are for text files and SQL Server data sources. You can also import Excel worksheets, Access tables or queries, and SharePoint lists directly into a file without using a connection file. For more information, see Import data from Excel, SQL Server, SharePoint sites, and other external sources.
What do you want to do?
Import a text file by using an OLE DB provider
Importing a comma-separated values (CSV) text file (.csv) is straightforward. If your text file is a .csv file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Import the file
-
On the Data menu, click Link Data to Shapes.
-
On the first page of the Data Selector Wizard, click Other OLE DB or ODBC data source.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
Click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, select Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider, and then click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Select or enter a database name box, enter the full path to the folder that contains the text file.
To help you locate the folder, click the Browse button next to the box.
-
Click the All tab, select Extended Properties, and then click Edit Value.
-
In the Property Value box, enter one of the following:
-
If the text file has column headers, enter Text;HDR=Yes.
-
If the text file does not have column headers, enter Text;HDR=No.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, under the Name column, select the text file that you want to import, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
-
Click Finish.
The Data Selector Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Data Connection page, do one of the following:
-
To use the .odc file that you just created and to accept all the rows and columns in the data source, click Finish.
-
To continue using the Data Selector Wizard, so that you can select specific columns and rows, and so that you can create a unique identifier, click Next.
For more information on each page in the Data Selector Wizard, press F1.
-
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Example: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import a text file by using an ODBC driver
Importing a text file by using an ODBC driver is, at minimum, a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC text driver. Second, import the text file by using the user DSN. If your text file is a comma-separated values (CSV) file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, on the User DSN tab, click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select Microsoft Text Driver (*.txt; *.csv), and then click Finish.
The ODBC Text Setup dialog box appears.
-
Enter a name in the Data Source Name.
-
Clear the Use Current Directory check box.
-
Click Select Directory.
-
In the Select Directory dialog box, locate the folder that contains the text file that you want to import, make sure that the text file appears in the list below the File Name box, and then click OK.
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import the file
-
On the Data menu, click Link Data to Shapes.
-
On the first page of the Data Selector Wizard, click Other OLE DB or ODBC data source.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data Source page, select the User DSN that you just created, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the text file under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
-
Click Finish.
The Data Selector Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Data Connection page, do one of the following:
-
To use the .odc file that you just created, and to accept all the rows and columns in the data source, click Finish.
-
To continue using the Data Selector Wizard, so that you can select specific columns and rows, and so that you can create a unique identifier, click Next.
For more information on each page in the Data Selector Wizard, press F1.
-
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a column header
[Categories.txt] ColNameHeader=True
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Example: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Data menu, click Link Data to Shapes.
-
On the first page of the Data Selector Wizard, click Microsoft SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
In the Connect to Database Server page, do the following:
-
Enter the name of the database server in the Server Name box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Under Logon credentials, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click Use Windows Authentication.
-
To use a database user name and password, click Use the following User Name and Password, and then enter the database user name and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
-
Click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or user-defined function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
-
Click Finish.
The Data Selector Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Data Connection page, do one of the following:
-
To use the .odc file that you just created, and to accept all the rows and columns in the data source, click Finish.
-
To continue using the Data Selector Wizard, so that you can select specific columns and rows, and so that you can create a unique identifier, click Next.
For more information on each page in the Data Selector Wizard, press F1.
-
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an ODBC driver
Importing data from a SQL Server database by using an ODBC driver is a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC driver. Second, import the data from the SQL Server database.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, select the User DSN tab, and then click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select SQL Server, and then click Finish.
The Create a New Data Source to SQL Server dialog box appears.
-
Enter a data source name in the Name box.
-
Optionally, enter a description of the data source in the Description box.
-
Enter the database server name in the Server box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Click Next.
-
Under How should SQL Server verify the authenticity of the login ID?, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click With Windows NT authentication using the Network login ID.
-
To use a database user name and password, click With SQL Server authentication using login ID and password entered by the user, and then enter the database login ID and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
Click Next twice, and then click Finish.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click Test Data Source .
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "TESTS COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY!", click OK.
-
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import the data from the SQL Server database
-
On the Data menu, click Link Data to Shapes.
-
On the first page of the Data Selector Wizard, click Other OLE DB or ODBC data source.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select the data source name that you defined in the previous section, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
-
Click Finish.
The Data Selector Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Data Connection page, do one of the following:
-
To use the .odc file that you just created, and to accept all the rows and columns in the data source, click Finish.
-
To continue using the Data Selector Wizard, so that you can select specific columns and rows, and so that you can create a unique identifier, click Next.
For more information on each page in the Data Selector Wizard, press F1.
-
Office Word: Import external data by using the Data Connection Wizard
In Microsoft Office Word, you import external data by using mail merge. Use mail merge to create a set of documents, such as a form letter that is sent to many customers or a sheet of address labels for a holiday card mailing. You can also import text files, Excel worksheets, and Access tables or queries directly, without using a connection file. For more information, see Create a mail merge.
What do you want to do?
-
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an ODBC driver
-
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an ODBC driver
-
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an ODBC driver
Import a text file by using an OLE DB provider
Importing a comma-separated values (CSV) text file (.csv) is straightforward. If your text file is a .csv file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Import the file
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.
-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, select Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider, and then click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Select or enter a database name box, enter the full path to the folder that contains the text file.
To help you locate the folder, click the Browse button next to the box.
-
Click the All tab, select Extended Properties, and then click Edit Value.
-
In the Property Value box, enter one of the following:
-
If the text file has column headers, enter Text;HDR=Yes.
-
If the text file does not have column headers, enter Text;HDR=No.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, under the Name column, select the text file that you want to import, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Example: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import a text file by using an ODBC driver
Importing a text file by using an ODBC driver is, at minimum, a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC text driver. Second, import the text file by using the user DSN. If your text file is a comma-separated values (CSV) file that does not use the list separator character that is defined on your machine, or if your text file is not a .csv file, you can use a Schema.ini file to specify the correct file format.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, on the User DSN tab, click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select Microsoft Text Driver (*.txt; *.csv), and then click Finish.
The ODBC Text Setup dialog box appears.
-
Enter a name in the Data Source Name.
-
Clear the Use Current Directory check box.
-
Click Select Directory.
-
In the Select Directory dialog box, locate the folder that contains the text file that you want to import, make sure that the text file appears in the list below the File Name box, and then click OK.
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import the file
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data Source page, select the User DSN that you just created, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the text file under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Use a Schema.ini file to specify a different list separator character or text file format
A Schema.ini file is a text file that contains entries that override default text driver settings in the Windows registry. In general, to use a Schema.ini file, you must do the following:
-
Store the Schema.ini file in the same folder as the text file that you are importing.
-
Name the file Schema.ini.
-
On the first line of the Schema.ini file, type the name of the text file that you are linking to, surrounded by brackets.
-
Add additional information to specify the different text file format.
The following sections show common examples for using the Schema.ini file.
Example: Specify a column header
[Categories.txt] ColNameHeader=True
Example: Specify a semicolon character (;) as the delimiter
[Categories.txt] Format=Delimited(;)
Example: Specify a tab character as the delimiter
[Products.txt] Format=TabDelimited
Example: Specify a fixed-width file
[Shippers.txt]Format=FixedLengthCol1=ShipperID Text Width 11Col2=CompanyName Text Width 40Col3=Phone Text Width 24
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, select Microsoft Office 12.0 Access Database Engine OLE DB Provider, and then click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Data source box, enter the full path and file name of the Excel workbook.
-
Click the All tab, select Extended Properties, and then click Edit Value.
-
In the Property Value box, enter one of the following:
-
If the data in the workbook has column headers, enter Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes.
-
If the data in the workbook does not have column headers, enter Excel 8.0;HDR=No.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the worksheet under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from an Excel 97-2003 or 2007 workbook by using an ODBC driver
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select Excel Files, and then click Next.
-
In the Select workbook dialog box, in the Database Name box, enter the folder that contains the Excel workbook, select the workbook in the list, and then click OK.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, under the Name column, select the worksheet that you want to import, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Other/Advanced.
The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
-
On the Provider tab, do one of the following:
-
If the database is an Access 2000 or Access 2003 database, select Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider.
-
If the database is a Office Access 2007 database, select Microsoft Office 12.0 Access Database Engine OLE DB Provider.
-
-
Click Next.
-
On the Connections tab, in the Select or enter a database name box, enter the full path and file name of the Access database.
If you selected Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider on the Provider tab (to help you locate the database) click the Browse button next to the box.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click the Connection tab, and then click Test Connection.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "Test connection succeeded", click OK.
-
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the table or query under the Name column, and then click Next.
Note: A linked table does not appear in this list. If you want to import a linked table, create a query to the linked table in the Access database before you perform the import operation.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from an Access 2000, 2003, or 2007 database by using an ODBC driver
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select MS Access database, and then click Next.
The Select Database dialog box appears.
-
In the Select Directory dialog box, locate the folder that contains the Access database that you want to import, make sure that the Access database appears in the list below the File Name box, and then click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard reappears.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the table or query under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an OLE DB provider
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click Microsoft SQL Server.
-
In the Connect to Database Server page, do the following:
-
Enter the name of the database server in the Server Name box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Under Logon credentials, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click Use Windows Authentication.
-
To use a database user name and password, click Use the following User Name and Password, and then enter the database user name and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
-
Click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or user-defined function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.
Import data from a SQL Server 2000 or 2005 database by using an ODBC driver
Importing data from a SQL Server database by using an ODBC driver is a two-step process. First, if necessary, define a user DSN on your computer for the ODBC driver. Second, import the data from the SQL Server database.
Define a User DSN
-
Open Microsoft Windows Control Panel, double-click the Administrative Tools icon, and then double-click the Data Sources (ODBC) icon.
-
In the ODBC Database Administrator dialog box, select the User DSN tab, and then click Add.
-
In the Create New Data Source dialog box, select SQL Server, and then click Finish.
The Create a New Data Source to SQL Server dialog box appears.
-
Enter a data source name in the Name box.
-
Optionally, enter a description of the data source in the Description box.
-
Enter the database server name in the Server box.
If the database is on your computer, enter (local).
-
Click Next.
-
Under How should SQL Server verify the authenticity of the login ID?, do one of the following:
-
To use your Windows user name and password, click With Windows NT authentication using the Network login ID.
-
To use a database user name and password, click With SQL Server authentication using login ID and password entered by the user, and then enter the database login ID and password in the appropriate boxes.
-
-
Click Next twice, and then click Finish.
-
To ensure that you entered the correct information, click Test Data Source.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you receive an error message, recheck the values that you entered in the previous steps.
-
If you receive the message "TESTS COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY!", click OK.
-
-
Click OK twice.
For more information about different options in the various dialog boxes, click Help.
Import data from a SQL Server database
-
On the Mailings tab, in the Start Mail Merge group, click Select Recipients, and then click Use Existing List.

-
In the Select Data Source dialog box, do one of the following:
-
To use an existing .odc file, double-click the .odc file. The data is imported and you are finished.
-
To create a new .odc file, click New Source, and then follow each step in the procedure.
The Data Connection Wizard appears.
-
-
In the Welcome to the Data Connection Wizard page, click ODBC/DSN.
-
In the Connect to ODBC Data source page, select the data source name that you defined in the previous section, and then click Next.
-
In the Select Database and Table page, select the database in the Database box, select the table, view, or function under the Name column, and then click Next.
-
In the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, enter a name for the .odc file in the File Name box, and then click Finish.
To change the folder location, which is the My Data Sources folder by default, click Browse.
-
Optionally, to make the connection file more discoverable, you can enter additional information in the Description, Friendly Name, and Search Keywords boxes.

Microsoft Office Tutorials: Import Data Into Office Publisher, Visio, Or Word By Using The Data Connection Wizard >>>>> Download Now
ReplyDelete>>>>> Download Full
Microsoft Office Tutorials: Import Data Into Office Publisher, Visio, Or Word By Using The Data Connection Wizard >>>>> Download LINK
>>>>> Download Now
Microsoft Office Tutorials: Import Data Into Office Publisher, Visio, Or Word By Using The Data Connection Wizard >>>>> Download Full
>>>>> Download LINK 0a