Filter by using advanced criteria
If the data you want to filter requires complex criteria (such as Type = "Produce" OR Salesperson = "Davolio") you can use the Advanced Filter dialog box.
| Advanced Filter | Example |
| Salesperson = "Davolio" OR Salesperson = "Buchanan" | |
| Type = "Produce" AND Sales > 1000 | |
| Type = "Produce" OR Salesperson = "Buchanan" | |
| (Sales > 6000 AND Sales < 6500 ) OR (Sales < 500) | |
| (Salesperson = "Davolio" AND Sales >3000) OR | |
| Salesperson = a name with 'u' as the second letter | |
| Type = an exact match of "Produce" | |
| A value in a column greater than the average of all values in that column (formula) | Sales > the average of all Sales |
Overview
The Advanced command works differently from the Filter command in several important ways.
-
It displays the Advanced Filter dialog box instead of the AutoFilter menu.
-
You type the advanced criteria in a separate criteria range on the worksheet and above the range of cells or table that you want to filter. Microsoft Office Excel uses the separate criteria range in the Advanced Filter dialog box as the source for the advanced criteria.
Example: Criteria range (A1:C4) and list range (A6:C10) used for the following procedures
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.
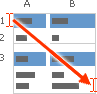
Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent) or, on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
Comparison operators
You can compare two values by using the following operators. When two values are compared by using these operators, the result is a logical value — either TRUE or FALSE.
| Comparison operator | Meaning | Example |
| = (equal sign) | Equal to | A1=B1 |
| > (greater than sign) | Greater than | A1>B1 |
| < (less than sign) | Less than | A1<B1 |
| >= (greater than or equal to sign) | Greater than or equal to | A1>=B1 |
| <= (less than or equal to sign) | Less than or equal to | A1<=B1 |
| <> (not equal to sign) | Not equal to | A1<>B1 |
Using the equal sign to type text or a value
Because the equal sign (=) is used to indicate a formula when you type text or a value in a cell, Excel evaluates what you type; however, this may cause unexpected filter results. To indicate an equality comparison operator for either text or a value, type the criteria as a string expression in the appropriate cell in the criteria range:
=''= entry ''
Where entry is the text or value you want to find. For example:
| What you type in the cell | What Excel evaluates and displays |
| ="=Davolio" | =Davolio |
| ="=3000" | =3000 |
Considering case-sensitivity
When filtering text data, Excel does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase characters. However, you can use a formula to perform a case-sensitive search. For an example, see the section Wildcard criteria.
Using pre-defined names
You can name a range Criteria, and the reference for the range will appear automatically in the Criteria range box. You can also define the name Database for the list range to be filtered and define the name Extract for the area where you want to paste the rows, and these ranges will appear automatically in the List range and Copy to boxes, respectively.
Creating criteria by using a formula
You can use a calculated value that is the result of a formula as your criterion. Remember the following important points:
-
The formula must evaluate to TRUE or FALSE.
-
Because you are using a formula, enter the formula as you normally would, and do not type the expression in the following way:
=''= entry ''
-
Do not use a column label for criteria labels; either keep the criteria labels blank or use a label that is not a column label in the list range (in the examples that follow, Calculated Average and Exact Match).
If you use a column label in the formula instead of a relative cell reference or a range name, Excel displays an error value such as #NAME? or #VALUE! in the cell that contains the criterion. You can ignore this error because it does not affect how the list range is filtered.
-
The formula that you use for criteria must use a relative reference to refer to the corresponding cell in the first row of data. Using the example in the section A value in a column greater than the average of all values in that column (formula), you use C7, and using the example in the section Text that matches a case-sensitive search (formula), you use A7. Then, the formula is evaluated for each row of data in the list range.
-
All other references in the formula must be absolute references.
Multiple criteria, one column, any criteria true
Boolean logic: (Salesperson = "Davolio" OR Salesperson = "Buchanan")
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria for one column, type the criteria directly below each other in separate rows of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 2 | ="=Davolio" | ||
| 3 | ="=Buchanan" |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
-
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 8 | Meat | Davolio | $450 |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, all criteria true
Boolean logic: (Type = "Produce" AND Sales > 1000)
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria in multiple columns, type all the criteria in the same row of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 2 | ="=Produce" | >1000 |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$2.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, any criteria true
Boolean logic: (Type = "Produce" OR Salesperson = "Buchanan")
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria in multiple columns where any criteria can be true, type the criteria in the different columns and rows of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 2 | ="=Produce" | ||
| 3 | ="=Buchanan" |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
-
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$B$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
Multiple sets of criteria, one column in all sets
Boolean logic: ( (Sales > 6000 AND Sales < 6500 ) OR (Sales < 500) )
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
To find rows that meet multiple sets of criteria where each set includes criteria for one column, include multiple columns with the same column heading. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C | D |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales | Sales |
| 2 | >6000 | <6500 | ||
| 3 | <500 |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$D$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 8 | Meat | Davolio | $450 |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
Multiple sets of criteria, multiple columns in each set
Boolean logic: ( (Salesperson = "Davolio" AND Sales >3000) OR (Salesperson = "Buchanan" AND Sales > 1500) )
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
To find rows that meet multiple sets of criteria, where each set includes criteria for multiple columns, type each set of criteria in separate columns and rows. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 2 | ="=Davolio" | >3000 | |
| 3 | ="=Buchanan" | >1500 |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$3.To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range would be:
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
Wildcard criteria
Boolean logic: Salesperson = a name with 'u' as the second letter
To find text values that share some characters but not others, do one or more of the following:
-
Type one or more characters without an equal sign (=) to find rows with a text value in a column that begin with those characters. For example, if you type the text Dav as a criterion, Excel finds "Davolio," "David," and "Davis."
-
Use a wildcard character.
| Use | To find |
| ? (question mark) | Any single character |
| * (asterisk) | Any number of characters |
| ~ (tilde) followed by ?, *, or ~ | A question mark, asterisk, or tilde |
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
In the rows below the column labels, type the criteria that you want to match. Using the example, enter:
|
| A | B | C |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 2 | ="=Me*" | ||
| 3 | ="=?u*" |
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$B$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
|
| A | B | C |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 7 | Beverages | Suyama | $5,122 |
| 8 | Meat | Davolio | $450 |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
Text that matches a case-sensitive search (formula)
Boolean logic: Type = an exact match of "Produce"
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
In the rows below the column labels, type the criteria that you want to match as a formula by using the EXACT function to perform a case-sensitive search. Because you are looking for an exact match in the Type column, which is in column A, you enter A7 as the first argument. Using the example, enter:
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales | Exact Match |
| 2 | =EXACT(A7, "Produce") |
Then, the formula is evaluated for each row of data in the list range.
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $D$1:$D$2.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
| A | B | C | |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
A value in a column greater than the average of all values in that column (formula)
Boolean logic: Sales > the average of all Sales
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
How to copy an example
-
Create a blank workbook or worksheet.
-
Select the example in the Help topic.
Note Do not select the row or column headers.

Selecting an example from Help
-
Press CTRL+C.
-
In the worksheet, select cell A1, and press CTRL+V.
-
To switch between viewing the results and viewing the formulas that return the results, press CTRL+` (grave accent), or on the Formulas tab, in the Formula Auditing group, click the Show Formulas button.
-
|
|
-
In the rows below the column labels, type the criteria that you want to match as a formula that finds a value in the Sales column greater than the average of all the Sales values. Because you are comparing the formula to values in the Sales column, which is in column C, enter C7 as the first argument. Using the example, enter:
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1 | Type | Salesperson | Sales | Calculated Average |
| 2 | =C7>AVERAGE($C$7:$C$10) |
Then, the formula is evaluated for each row of data in the list range.
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $D$1:$D$2.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
 .
. -
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
| A | B | C | |
| 6 | Type | Salesperson | Sales |
| 7 | Beverages | Suyama | $5,122 |
| 9 | produce | Buchanan | $6,328 |
| 10 | Produce | Davolio | $6,544 |
No comments:
Post a Comment