Web browser compatibility in InfoPath Forms Services
InfoPath Forms Services is a server technology that allows users to fill out Microsoft Office InfoPath forms by using a Web browser. Users don't need InfoPath installed on their computers to fill out an InfoPath form, nor are they required to download anything extra from the Web. All users need is access to a browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer, Apple Safari, or Firefox.
This article lists the browsers that are compatible with InfoPath Forms Services. In addition, this article lists the features that are supported in browser-compatible form templates, the features that cannot be used in browser-compatible form templates, and the differences in behavior that may occur when forms that are based on browser-compatible form templates are viewed in different browsers.
In this article
Web browsers that are compatible with InfoPath Forms Services
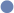 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support 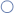 = No support
= No support
Note: If a specific browser version is not listed in the following table, it is not supported. For example, there is no support for older browsers, including Internet Explorer 5.01, Internet Explorer 5.5.x, Internet Explorer for Macintosh, and versions of third-party browsers that are earlier than the ones that are listed in the following table. Although it is possible that browser-enabled forms may function correctly in these browsers, browser-enabled forms have been tested only with the browser versions that are listed in the following table.
The following table shows the specific browsers that are compatible with InfoPath Forms Services.
| Browser | Windows 1 | Unix/Linux | Macintosh |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 (32-bit) | | | |
| Windows Internet Explorer 7.0 (32-bit) | | | |
| Firefox 1.5 | | | |
| Mozilla 1.7 | | | |
| Netscape 7.2 | | | |
| Netscape 8.1 | | | |
| Safari 2.0 | | | |
1Includes Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows XP, and Microsoft Windows 2000.
InfoPath features that are supported in InfoPath Forms Services
Most InfoPath controls and features work identically regardless of whether users are filling out a form in Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, or any other supported browser. However, the same form may appear differently in different browsers. These visual differences can be attributed to the way that the various browsers support Web technologies, such as Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), cascading style sheets (CSS), and JavaScript.
In addition, there are some controls and features that are fully supported only in browsers that support Microsoft ActiveX technologies, such as Internet Explorer 6.0 or Internet Explorer 7.0. In other browsers, these features may behave differently or have limited functionality.
Support for form controls
You can use the following table to determine whether a particular InfoPath control is supported by InfoPath Forms Services.
In some cases, even if the control is supported by InfoPath Forms Services, it may not work the same way in all browsers. For example, you can use rich text boxes in browser-compatible form templates. However, users only see the full range of rich text formatting options when they fill out the form in Internet Explorer.
Similarly, when users view a form in a mobile device browser, some controls appear differently than they do in a desktop browser, and some controls are ignored completely. For example, although you can use a file attachment control in a browser-compatible form template, this control will not appear when the form is viewed in a mobile device browser. For more information about optimizing form templates for use on mobile devices, refer to the See Also links at the top of this article.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 control | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Text box | | |
| Check box | | |
| Button | | |
| Expression box | | |
| List box | | |
| Drop-down list box | | |
| Repeating section | | |
| Hyperlink | | |
| Option button | | |
| Optional section | | |
| Repeating table | | |
| File attachment control | | |
| Date picker 1 | | |
| Rich text box 2 | | |
| ActiveX control | | |
| Bulleted list control | | |
| Choice group | | |
| Choice section | | |
| Combo box | | |
| Horizontal repeating table | | |
| Horizontal region | | |
| Ink picture control | | |
| Master/detail control | | |
| Multiple-selection list box | | |
| Numbered list control | | |
| Picture control | | |
| Plain list control | | |
| Repeating choice group | | |
| Repeating recursive section | | |
| Scrolling region | | |
| Vertical label | | |
1Although you can use date pickers in a browser-compatible form template, the calendar icon and pop-up calendar appear only in supported versions of Internet Explorer. In other browsers, the date picker appears as a text box, but the date formatting options are still supported.
2You cannot enable embedded pictures or specify partial rich-text formatting options for rich text box controls in a browser-compatible form template. Also, the full range of rich text formatting options are available only in supported versions of Internet Explorer. It is possible for users to edit text in a rich text box in any supported browser, but formatting options are unavailable, including changing the text color and applying character formatting.
Support for business logic features
You can use business-logic features in your form template to help prevent data-entry errors and to automate actions in the user's form. When you use InfoPath features like data validation, conditional formatting, and rules, you can define conditions and actions that automatically perform tasks that are based on events, such as the opening or closing of a form, or on values that are entered into your form template.
The following table shows the level to which specific InfoPath business logic features are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Formulas 1 | | |
| Data validation | | |
| Rules | | |
| Conditional formatting 2 | | |
| User roles | | |
1Except xdXDocument:get-Role, Position, and Last functions.
2In mobile device browsers, some conditional formatting features are supported, such as hiding controls based on conditions that occur in the form. However, it isn't possible to use conditional formatting to alter the appearance of a control based on conditions in the form. For example, you can't use conditional formatting to change the color of text in a control.
Support for security-related features
The following table shows the level to which specific InfoPath security features are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Domain security level | | |
| Full-trust security level | | |
| Restricted security level | | |
| Digital signatures 1 | | |
| Form design protection | | |
| Ability to disable Save, Print, and other commands | | |
| Information Rights Management (IRM) | | |
1Digital signatures are not supported in browser-enabled form templates that are rendered in mobile device browsers. In addition, in desktop browsers, it is not possible for users to digitally sign an entire form. However, you can design the form template so that users can digitally sign one or more sections in the form. To do this, you must enable digital signatures for a section control. Also, although users can view digital signatures for a form in any supported browser, they can digitally sign the form sections only in supported versions of Internet Explorer.
Support for data connections
A data connection is a dynamic link between a form and a data source that stores or provides data for that form.
The following table shows the level to which InfoPath data connections are supported in browser-enabled form templates.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Query data from an XML file or a URL that returns XML | | |
| Query data from a Microsoft Windows SharePoint Services list or library | | |
| Query data from a Microsoft SQL Server database | | |
| Query data from a Microsoft Office Access database | | |
| Query data from a Web service | | |
| Query data by using data connection files in a Data Connection Library | | |
The following table shows how the level to which InfoPath features for submitting forms are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Submit data as an e-mail message | | |
| Submit data to a SharePoint library 1 | | |
| Submit data to a Microsoft SQL Server database | | |
| Submit data to a Microsoft Access database | | |
| Submit data to a Web service 2 | | |
| Submit data to a Web application that accepts HTTP POST submissions | | |
| Submit data by using data connection files in a Data Connection Library | | |
1Data can be submitted to a SharePoint library, but data cannot be submitted to a list.
2 You cannot configure the submit data connection in a browser-compatible form template to allow users to submit change information along with their form data to a Web service that accepts a Microsoft ADO.NET DataSet. Change information consists of the modifications that a user makes to the data stored in a database. The database uses a Web service to connect users to the database. ADO.NET can use change information to determine how to update the data in the database.
Support for form-filling features
The following table shows the level to which InfoPath features that are related to filling out forms are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Submit feature | | |
| Save feature 1 | | |
| Print feature | | |
| Merge data from multiple forms | | |
| Export data to Microsoft Office Excel | | |
| Export data to Web | | |
| Ink support | | |
| Offline support | | |
| Find and replace text | | |
| AutoComplete feature 2 | | |
| Spell checking | | |
| AutoSave, AutoRecover, or crash detection features | | |
| Custom task panes | | |
| Add-in menus | | |
1In a browser-enabled form, users can click the Save or Save As buttons to save their forms to a SharePoint library. However, they cannot save their forms to a location on their computers. In addition, users who view forms in a mobile device browser do not see the Save or Save As buttons.
2In browsers other than Internet Explorer, the AutoComplete feature is unavailable, even if the Enable AutoComplete check box is selected for the control.
Support for view-related features
The following table shows the level to which InfoPath view-related features are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 20 07 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Multiple views | | |
| Read-only views | | |
| Print views | | |
| Word print views 1 | | |
| Print multiple views at once 2 | | |
| Print page breaks, headers, or footers | | |
1Microsoft Office Word print views are not supported in browser-enabled form templates. You can publish a form template to InfoPath Forms Services without removing the Word print view. However, when users print the form, the Web browser ignores the Word print view settings.
2The Print Multiple Views functionality is not supported in browser-enabled form templates. You can publish a form template to InfoPath Forms Services without changing any options in the Print Multiple Views dialog box. However, when users print the form, the Web browser uses a read-only view of the current view for printing purposes rather than printing multiple views.
Support for programming features
Developers can use the InfoPath managed code object model to create custom business logic in browser-compatible form templates. When deployed to a server running InfoPath Forms Services, this business logic runs in both a browser and in InfoPath. The following table shows the level to which InfoPath programming features are supported by compatible browsers.
 = Full support
= Full support  = Partial support
= Partial support  = No support
= No support
| InfoPath 2007 feature | Desktop browsers | Mobile device browsers |
| Managed code 1 | | |
| Scripting 2 | | |
| COM add-ins | | |
1In a browser-compatible form template, managed code must be based on the InfoPath managed code object model that is provided by the Microsoft.Office.InfoPath namespace. A subset of the members of the Microsoft.Office.InfoPath namespace provides features, such as Information Rights Management (IRM), that are not supported on the server. For more information on which object model members are supported and which are not supported, refer to the See Also links at the top of this article.
2Any code that is written in VBScript, JScript, or the InfoPath 2003-compatible object model provided by members of the Microsoft.Office.Interop.InfoPath.SemiTrust namespace is not supported on the server.
Thanks for the post.
ReplyDeletealso, check Linux course in Pune