Examples of query criteria
When you want to limit the results of a query based on the values in a field, you use query criteria. A query criterion is an expression that Access compares to query field values to determine whether to include the record that contains each value. For example, = "Chicago" is an expression that Access can compare to values in a text field in a query. If the value for that field in a given record is "Chicago", Access includes the record in the query results.
This topic lists several examples of query criteria. It assumes that you are familiar with designing simple select queries.
To learn more about queries, see the article Introduction to queries.
In this topic
Overview
A criterion is similar to a formula — it is a string that may consist of field references, operators, and constants. Query criteria are also called expressions.
The following video shows how to use criteria for a text field.

The following table shows some sample criteria and explains how they work.
| Criterion | Description |
| >25 and <50 | This criterion applies to a Number field, such as Price or UnitsInStock. It includes only those records where the Price or UnitsInStock field contains a value greater than 25 and less than 50. |
| DateDiff ("yyyy", [BirthDate], Date()) > 30 | This criterion applies to a Date/Time field, such as BirthDate. Only records where the number of years between a person's birthdate and today's date is greater than 30 are included in the query result. |
| Is Null | This criterion can be applied to any type of field to show records where the field value is null. |
Criteria can look very different from each other. Some criteria are simple, and use basic operators (such as "<") and constants (such as "50"). Others are complex, and use functions (such as "DateDiff") or field references (such as "[BirthDate]"). This topic provides multiple examples of commonly used criteria, grouped by the data type they apply to. You can use the examples given in this topic as a starting point to write your own criteria.
To add criteria to a query, you must open the query in Design view. Then, you identify the fields for which you want to specify criteria. If a field that you want to specify a criterion for is not already in the design grid, you can add it by dragging it from the query design window to the design grid, or by double-clicking the field. When the field that you want is in the design grid, you enter the criterion in the Criteria row for that field.
Use the Expression Builder to enter criteria
You can use the Expression Builder when you want to use criteria that contain functions. The Expression Builder provides features to help you use each function correctly. For more information about the Expression Builder, see the article Use the Expression Builder.
All of the criteria that you specify in the Criteria row are combined
Criteria that you specify for different fields in the Criteria row are combined by using the AND operator. For example, you might specify the criterion ="Chicago" for the City field and the criterion < DateAdd("yyyy", -40, Date()) for the BirthDate field. The two criteria are interpreted together, like this:
City = "Chicago" AND BirthDate < DateAdd("yyyy", -40, Date())
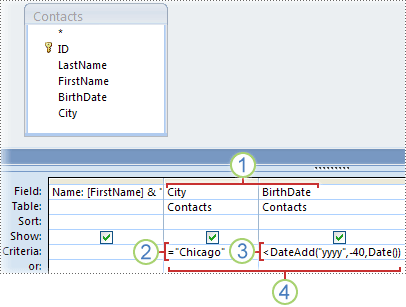
1. The City and BirthDate fields include criteria.
2. Only records where the value of the City field is Chicago will satisfy this criterion.
3. Only records of those who are at least 40 years old will satisfy this criterion.
4. Only records that meet both criteria will be included in the result.
Specify alternate criteria by using the Or row
If you have alternate criteria, or two sets of independent criteria where it is sufficient to satisfy one set, you use both the Criteria and the or rows in the design grid.
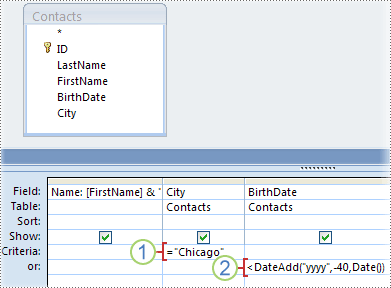
1. The City criterion is specified in the Criteria row.
2. The BirthDate criterion is specified in the or row.
Criteria specified in the Criteria and or rows are combined using the OR operator, as shown below:
City = "Chicago" OR BirthDate < DateAdd("yyyy", -40, Date())
If you need to specify more alternatives, use the rows below the or row.
Before you continue with the examples, note the following:
-
If the criteria is temporary or changes often, you can filter the query result instead of frequently modifying the query criteria. A filter changes a query result without altering the design of the query. For more information about filters, see the See Also section.
-
If the criteria fields don't change, but the values that you want to use do change frequently, you can create a parameter query. A parameter query asks you for input when you run the query, and then uses your input to create the query criteria. For more information about making a query ask for input, see the See Also section.
Criteria for Text, Memo, and Hyperlink fields
The following examples are for the CountryRegion field in a query that is based on a table that stores contacts information. The criterion is specified in the Criteria row of the field in the design grid.
| To include records that... | Use this criterion | Query result |
| Exactly match a value, such as China | "China" | Returns records where the CountryRegion field is set to China. |
| Do not match a value, such as Mexico | Not "Mexico" | Returns records where the CountryRegion field is set to a country/region other than Mexico. |
| Begin with the specified string, such as U | Like U* | Returns records for all countries/regions whose names start with "U", such as UK, USA, and so on. Note: When used in an expression, the asterisk (*) represents any string of characters — it is also called a wildcard character. For a list of such characters, see the article Access wildcard character reference. |
| Do not begin with the specified string, such as U | Not Like U* | Returns records for all countries/regions whose names start with a character other than "U". |
| Contain the specified string, such as Korea | Like "*Korea*" | Returns records for all countries/regions that contain the string "Korea". |
| Do not contain the specified string, such as Korea | Not Like "*Korea*" | Returns records for all countries/regions that do not contain the string "Korea". |
| End with the specified string, such as "ina" | Like "*ina" | Returns records for all countries/regions whose names end in "ina", such as China and Argentina. |
| Do not end with the specified string, such as "ina" | Not Like "*ina" | Returns records for all countries/regions that do not end in "ina", such as China and Argentina. |
| Contain null (or missing) values | Is Null | Returns records where there is no value in the field. |
| Do not contain null values | Is Not Null | Returns records where the value is not missing in the field. |
| Contain zero-length strings | "" (a pair of quotes) | Returns records where the field is set to a blank (but not null) value. For example, records of sales made to another department might contain a blank value in the CountryRegion field. |
| Do not contain zero-length strings | Not "" | Returns records where the CountryRegion field has a nonblank value. |
| Contains null values or zero-length strings | "" Or Is Null | Returns records where there is either no value in the field, or the field is set to a blank value. |
| Is not empty or blank | Is Not Null And Not "" | Returns records where the CountryRegion field has a nonblank, non-null value. |
| Follow a value, such as Mexico, when sorted in alphabetical order | >= "Mexico" | Returns records of all countries/regions, beginning with Mexico and continuing through the end of the alphabet. |
| Fall within a specific range, such as A through D | Like "[A-D]*" | Returns records for countries/regions whose names start with the letters "A" through "D". |
| Match one of two values, such as USA or UK | "USA" Or "UK" | Returns records for USA and UK. |
| Contain one of the values in a list of values | In("France", "China", "Germany", "Japan") | Returns records for all countries/regions specified in the list. |
| Contain certain characters at a specific position in the field value | Right([CountryRegion], 1) = "y" | Returns records for all countries/regions where the last letter is "y". |
| Satisfy length requirements | Len([CountryRegion]) > 10 | Returns records for countries/regions whose name is more than 10 characters long. |
| Match a specific pattern | Like "Chi??" | Returns records for countries/regions, such as China and Chile, whose names are five characters long and the first three characters are "Chi". Note: The characters ? and _, when used in an expression, represent a single character — these are also called wildcard characters. The character _ cannot be used in the same expression with the ? character, nor can it be used in an expression with the * wildcard character. You may use the wildcard character _ in an expression that also contains the % wildcard character. |
Hyperlink criteria are a little tricky
By deafult, a criterion that you specify for a Hyperlink field is applied to the display text portion of the field value, not the link destination. To specify criteria for the destination Uniform Resource Locator (URL) portion of the value, use the HyperlinkPart expression. The syntax you use looks like this:
HyperlinkPart([Table1].[Field1],1) = "http://www.microsoft.com/"
Table1 is the name of the table containing the hyperlink field, Field1 is the hyperlink field, and http://www.microsoft.com is the URL that you want to match.
Criteria for Number, Currency, and AutoNumber fields
The following examples are for the UnitPrice field in a query that is based on a table that stores products information. The criterion is specified in the Criteria row of the field in the query design grid.
| To include records that... | Use this criterion | Query Result |
| Exactly match a value, such as 100 | 100 | Returns records where the unit price of the product is $100. |
| Do not match a value, such as 1000 | Not 1000 | Returns records where the unit price of the product is not $1000. |
| Contain a value smaller than a value, such as 100 | < 100 | Returns records where the unit price is less than $100 (<100). The second expression (<=100) displays records where the unit price is less than or equal to $100. |
| Contain a value larger than a value, such as 99.99 | >99.99 | Returns records where the unit price is greater than $99.99 (>99.99). The second expression displays records where the unit price is greater than or equal to $99.99. |
| Contain one of the two values, such as 20 or 25 | 20 or 25 | Returns records where the unit price is either $20 or $25. |
| Contain a value that falls with a range of values | >49.99 and <99.99 | Returns records where the unit price is between (but not including) $49.99 and $99.99. |
| Contain a value that falls outside a range | <50 or >100 | Returns records where the unit price is not between $50 and $100. |
| Contain one of many specific values | In(20, 25, 30) | Returns records where the unit price is either $20, $25, or $30. |
| Contain a value that ends with the specified digits | Like "*4.99" | Returns records where the unit price ends with "4.99", such as $4.99, $14.99, $24.99, and so on. Note: The characters * and %, when used in an expression, represent any number of characters — these are also called wildcard characters. The character % cannot be used in the same expression with the * character, nor can it be used in an expression with the ? wildcard character. You may use the wildcard character % in an expression that also contains the _ wildcard character. |
| Contain null null (or missing) values | Is Null | Returns records where no value is entered in the UnitPrice field. |
| Contain non-null values | Is Not Null | Returns records where the value is not missing in the UnitPrice field. |
Criteria for Date/Time fields
The following examples are for the OrderDate field in a query based on a table that stores Orders information. The criterion is specified in the Criteria row of the field in the query design grid.
| To include records that ... | Use this criterion | Query result |
| Exactly match a value, such as 2/2/2006 | #2/2/2006# | Returns records of transactions that took place on Feb 2, 2006. Remember to surround date values with the # character so that Access can distinguish between date values and text strings. |
| Do not match a value, such as 2/2/2006 | Not #2/2/2006# | Returns records of transactions that took place on a day other than Feb 2, 2006. |
| Contain values that fall before a certain date, such as 2/2/2006 | < #2/2/2006# | Returns records of transactions that took place before Feb 2, 2006. To view transactions that took place on or before this date, use the <= operator instead of the < operator. |
| Contain values that fall after a certain date, such as 2/2/2006 | > #2/2/2006# | Returns records of transactions that took place after Feb 2, 2006. To view transactions that took place on or after this date, use the >= operator instead of the > operator. |
| Contain values that fall within a date range | >#2/2/2006# and <#2/4/2006# | Returns records where the transactions took place between Feb 2, 2006 and Feb 4, 2006. You can also use the Between operator to filter for a range of values, including the end points. For example, Between #2/2/2006# and #2/4/2006# is the same as >=#2/2/2006# and <=#2/4/2006# . |
| Contain values that fall outside a range | <#2/2/2006# or >#2/4/2006# | Returns records where the transactions took place before Feb 2, 2006 or after Feb 4, 2006. |
| Contain one of two values, such as 2/2/2006 or 2/3/2006 | #2/2/2006# or #2/3/2006# | Returns records of transactions that took place on either Feb 2, 2006 or Feb 3, 2006. |
| Contain one of many values | In (#2/1/2006#, #3/1/2006#, #4/1/2006#) | Returns records where the transactions took place on Feb 1, 2006, March 1, 2006, or April 1, 2006. |
| Contain a date that falls in a specific month (irrespective of year), such as December | DatePart("m", [SalesDate]) = 12 | Returns records where the transactions took place in December of any year. |
| Contain a date that falls in a specific quarter (irrespective of year), such as the first quarter | DatePart("q", [SalesDate]) = 1 | Returns records where the transactions took place in the first quarter of any year. |
| Contain today's date | Date() | Returns records of transactions that took place on the current day. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records where the OrderDate field is set to Feb 2, 2006. |
| Contain yesterday's date | Date()-1 | Returns records of transactions that took place the day before the current day. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for Feb 1, 2006. |
| Contain tomorrow's date | Date() + 1 | Returns records of transactions that took place the day after the current day. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for Feb 3, 2006. |
| Contain dates that fall during the current week | DatePart("ww", [SalesDate]) = DatePart("ww", Date()) and Year( [SalesDate]) = Year(Date()) | Returns records of transactions that took place during the current week. A week starts on Sunday and ends on Saturday. |
| Contain dates that fell during the previous week | Year([SalesDate])* 53 + DatePart("ww", [SalesDate]) = Year(Date())* 53 + DatePart("ww", Date()) - 1 | Returns records of transactions that took place during the last week. A week starts on Sunday and ends on Saturday. |
| Contain dates that fall during the following week | Year([SalesDate])* 53+DatePart("ww", [SalesDate]) = Year(Date())* 53+DatePart("ww", Date()) + 1 | Returns records of transactions that will take place next week. A week starts on Sunday and ends on Saturday. |
| Contain a date that fell during the last 7 days | Between Date() and Date()-6 | Returns records of transactions that took place during the last 7 days. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the period Jan 24, 2006 through Feb 2, 2006. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the current month | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Now()) And Month([SalesDate]) = Month(Now()) | Returns records for the current month. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for Feb 2006. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the previous month | Year([SalesDate])* 12 + DatePart("m", [SalesDate]) = Year(Date())* 12 + DatePart("m", Date()) - 1 | Returns records for the previous month. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for Jan 2006. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the next month | Year([SalesDate])* 12 + DatePart("m", [SalesDate]) = Year(Date())* 12 + DatePart("m", Date()) + 1 | Returns records for the next month. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for Mar 2006. |
| Contain a date that fell during the last 30 or 31 days | Between Date( ) And DateAdd("M", -1, Date( )) | A month's worth of sales records. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the period Jan 2, 2006. to Feb 2, 2006 |
| Contain a date that belongs to the current quarter | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Now()) And DatePart("q", Date()) = DatePart("q", Now()) | Returns records for the current quarter. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the first quarter of 2006. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the previous quarter | Year([SalesDate])*4+DatePart("q",[SalesDate]) = Year(Date())*4+DatePart("q",Date())- 1 | Returns records for the previous quarter. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the last quarter of 2005. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the next quarter | Year([SalesDate])*4+DatePart("q",[SalesDate]) = Year(Date())*4+DatePart("q",Date())+1 | Returns records for the next quarter. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the second quarter of 2006. |
| Contain a date that falls during the current year | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Date()) | Returns records for the current year. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the year 2006. |
| Contain a date that belongs to the previous year | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Date()) - 1 | Returns records of transactions that took place during the previous year. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the year 2005. |
| Contain a date that belongs to next year | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Date()) + 1 | Returns records of transactions with next year's date. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the year 2007. |
| Contain a date that falls between Jan 1 and today (year to date records) | Year([SalesDate]) = Year(Date()) and Month([SalesDate]) <= Month(Date()) and Day([SalesDate]) <= Day (Date()) | Returns records of transactions with dates that fall between Jan 1 of the current year and today. If today's date is 2/2/2006, you see records for the period Jan 1, 2006 to to 2/2/2006. |
| Contain a date that occurred in the past | < Date() | Returns records of transactions that took place before today. |
| Contain a date that occurrs in the future | > Date() | Returns records of transactions that will take place after today. |
| Filter for null (or missing) values | Is Null | Returns records where the date of transaction is missing. |
| Filter for non-null values | Is Not Null | Returns records where the date of transaction is known. |
The following video has more information about using date-related expressions:

No comments:
Post a Comment