An e-mail profile is made up of e-mail accounts, data files, and information about where your e-mail is stored.
What is an e-mail profile?
E-mail profiles are what Outlook uses to remember which e-mail accounts you use and where the data for each account is stored. Each profile provides Outlook with the following information:
-
What account information to use This information includes the user name, display name, e-mail server name, and Internet service provider (ISP) account password.
-
Where the e-mail data is delivered and stored In Outlook, data is delivered and stored either on the e-mail server or a in .pst file on your computer. This data includes rules, messages, contacts, calendars, notes, tasks, journals, Search Folders, and other settings.
Outlook e-mail profiles are stored in the Windows registry. When Outlook starts, it retrieves the profile information from the registry.
Note: You use the Mail icon in Control Panel to access options for configuring Outlook e-mail profiles. The Mail icon won't appear unless you have Outlook installed and have run the program at least one time.
When you run Outlook for the first time, a startup wizard guides you through the process of creating a new profile. The profile thus created runs whenever you start Outlook. Most people maintain only one profile — however, you might sometimes find it useful to have more than one. For example, you might want to use one profile for work mail and a second profile for personal mail. Also, if other people use the same computer that you do, their accounts and settings can be kept in separate profiles that have different names.
You cannot use passwords to protect Outlook profiles. To help protect your Outlook data from intrusion by other people, you should use a password-protected Windows user account.
Important: You cannot switch from one e-mail profile to another while Outlook is running.
A basic profile consists of one or more e-mail accounts and a storage file. A private individual might have an Internet e-mail account, such as a POP3 account, while corporate workers might have a Microsoft Exchange account. Accounts of other types (including IMAP4 and HTTP accounts) can be added to any profile, and so can additional storage files (such as an Archive.pst file for keeping older messages). Sometimes extra services, such as fax and address book directories, may be included as well.
Note: While a profile can include multiple Internet-type accounts, it can include only one Exchange account.
Most people need only a single profile. When Outlook runs for the first time, the first profile is created automatically and is named "Outlook." Whenever Outlook starts, this default profile runs automatically. When you add or modify e-mail accounts, or include an additional .pst file to use, you are modifying your profile. You can modify your profile at any time, but you cannot change the name of a profile after it is first created.
-
Select the Windows icon, type Control Panel in the search box and select it.
-
In Control Panel, search Mail, and select it.
-
The Mail icon won't appear unless you have Outlook installed and have run the program at least once.
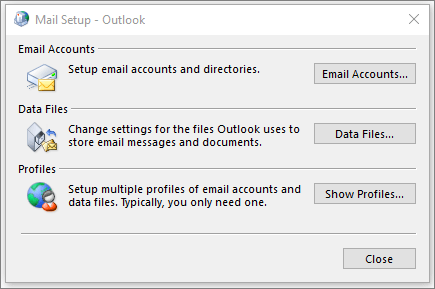
The Mail Setup dialog box opens.
-
Do any of the following:
-
To add another e-mail account, click E-mail Accounts.
-
To modify Outlook data storage options, click Data Files.
-
To see a list of the profiles that you currently have, click Show Profiles.
-
You may need more than one profile in either of the following situations:
-
If you use Outlook on a single computer that you share with other people whom you trust
For example, if you and your spouse have separate e-mail accounts, each of you can also have a separate profile, each with the appropriate accounts and settings. -
If you maintain multiple Exchange accounts
If you need more than one profile, you can create an additional profile at any time, and add to it the accounts and settings that you want. When you switch from one profile to another, you change the e-mail accounts and settings that are available to you in an Outlook session.
-
Select the Windows icon, type Control Panel in the search box and select it.
-
In Control Panel, search Mail, and select it.
-
The Mail icon won't appear unless you have Outlook installed and have run the program at least once.
The Mail Setup dialog box opens.

-
Click Show Profiles.
-
Click Add.
-
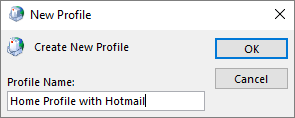
Type a name for the profile, and then click OK.
-
Add an e-mail account to use in your profile by following the directions on your screen.
-
Select the Windows icon, type Control Panel in the search box and select it.
-
In Control Panel, search Mail, and select it.
-
The Mail icon won't appear unless you have Outlook installed and have run the program at least once.
The Mail Setup dialog box opens.

-
Click Show Profiles.
-
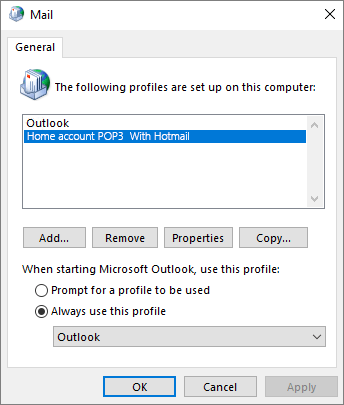
Under When starting Microsoft Office Outlook, use this profile, click Always use this profile, and then click the profile that you want to use in the list.
-
Select the Windows icon, type Control Panel in the search box and select it.
-
In Control Panel, search Mail, and select it.
-
The Mail Setup dialog box opens.

-
Click Show Profiles.
-
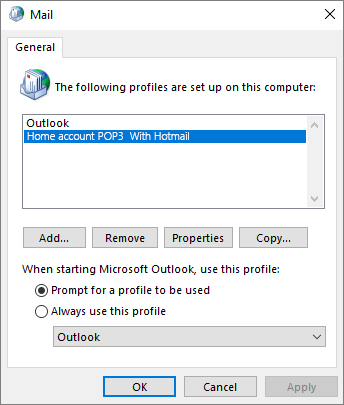
Under When starting Microsoft Office Outlook, use this profile, click Prompt for a profile to be used.
-
When Outlook starts, click the profile that you want to use in the Profile Name list.
When you use multiple profiles, there is usually one that you use the most often. Using the Prompt for a profile to be used option, you can configure Outlook to always select that profile in the Profile Name box. Then all you have to do to use that profile is click OK:
-
In the Choose Profile dialog box, in the Profile Name list, click the profile that you want to be automatically selected.
-
Click Options and then, under Options, select the Set as default profile check box.
No comments:
Post a Comment