User Goal: Manage costs
| | If you plan to track cost information, you've come to the right place. Learn how and where to enter various cost details so you can view and analyze your total costs from time to time as your project progresses. Knowing where your money is going will help you make better decisions to complete your project within budget. |
Cost management tips before you start
This article is one of many project management goals on the Project management road map.
-
Estimating project costs Cost histories of projects that are similar to the project you're planning can be useful when you get started. It helps prevent costly mistakes. If your organization has Project Management Office (PMO) experts, you might also discuss your cost and budget plans with them, or ask an experienced and knowledgeable team member to review your task and resource cost estimates. Cost estimates are tricky—larger organizations follow PMO guidelines or hire professional cost estimators.
-
Knowing what types of costs there are in Project Most project costs come from work resources—the people who work on assigned tasks or the materials and equipment needed to complete a project. Resource costs are typically based on hourly pay rates or unit rates, but they can also be one-time costs like consultant fees, vendor costs, or travel costs. Costs that aren't associated with resources are typically entered as fixed costs for specific tasks or the entire project.
-
Entering costs Resource costs are entered in the Resource sheet view for hourly workers, salaried workers, contractors, material costs, or other one-time resource costs, such as cost for insurance or bonds. Task costs are entered in a cost table you can add to any task sheet.
-
Getting your cost totals Project calculates cost totals for any costs you enter so you can quickly see how your project costs tally up. Share this cost information with your project stakeholders, who might be looking for it.
-
Setting your budget When cost totals resemble the budget you and your stakeholders had in mind for the project, saving a baseline establishes those cost totals as your project's budget. You usually do this after you've entered all of the information your project needs, and before any work starts. A baseline budget is required if you plan to track and manage costs, especially if you'll be doing any earned value analysis to analyze cost variances throughout your project. For more information, see Set and save a baseline.
-
Performing costs analysis Export your cost data to Excel for in-depth data analysis, using Excel PivotTables, charts, and other features such as conditional formatting and sparklines (as shown in the following picture).
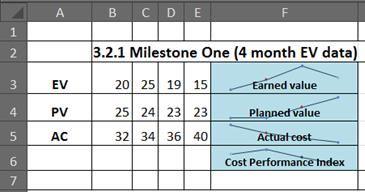
Or use Visual Reports in Project to view a PivotChart of earned value (commonly known as an S curve).

You can even take your Project data further and create an advanced analysis using the ANOVA analysis features of the Analysis ToolPak in Excel. The sky's the limit when it comes to analyzing Project costs!
Enter costs in your project
| Firsts things first—you start by entering pay rates for the people who'll do the work and unit rates for the materials you'll need to complete your project. | |
| Then you'll enter the "fixed" resource costs for equipment, along with any one-time resource costs you want to track in your project. | |
| Next, you can add any one-time, miscellaneous costs to specific tasks or to the project summary task that represents the entire project. | |
| After you enter costs for resources, tasks, or both, examine the cost totals to see if they need to be adjusted to meet your goal for costs. | |
| At some point, you'll want to report project cost information to other people in your organization. Use a predefined cost report, such as a Cash Flow or Earned Value report, or instantly view your cost data in a visual report, such as an Excel PivotChart or Visio PivotDiagram. |
Manage your project costs
| After entering your cost estimates, save them with your baseline plan to establish your budget. This lets you compare your planned costs with the actual costs your project incurs as it progresses, and predicts whether your project costs will stay within budget or not. | |
| Keep an eye on how the work on tasks is progressing and how actual costs are adding up to determine if your project will stay within budget or is at risk of going over budget. | |
| Project automatically calculates actual costs based on the actual work accumulated or materials consumed on tasks, but if needed, you can enter actual costs on any assigned tasks that have been completed. | |
| Perform earned value analysis at any point during the project to find out if the money spent so far is in line with the work that was done, and matches the baseline costs you set for tasks, resources, and assignments. | |
| Learn how to export your schedule to a format that is United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business (UN/CEFACT) compliant. |
No comments:
Post a Comment