Teams often work with a lot of files. The Files list makes it easier to locate the one you need.

Watch this video for a quick tour of the Files list.
Select Files 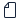 on the left side of Teams for quick access to all your files, arranged in the following views:
on the left side of Teams for quick access to all your files, arranged in the following views:
-
Recent lists every file you've recently viewed or edited.
Tip: Another way to view your recent files is to enter /files in the command bar at the top of Teams.
-
Microsoft Teams contains all the documents that were recently created or edited in the channels that appear in your teams list.
-
Downloads shows all the files you've downloaded from Teams. This list is cleared each time you sign out of Teams.
-
Cloud storage shows the cloud storage services you've connected to Teams. Select a service to view your cloud files.
From here, you can delete any personal file you've added to Teams, upload files, and create new files. Files added to cloud storage are private until you share them.
By default, OneDrive cloud storage will be available. If your IT admin made it possible to add other cloud storage services, you'll see an Add cloud storage button at the bottom of the screen.
To view files in a specific chat or channel
-
Tap Files at the top of the conversation.
To view your recent files
-
Tap More
 and then Files at the bottom right of the screen.
and then Files at the bottom right of the screen.
From there you can also access your cloud storage files.
By default, OneDrive cloud storage will be available. Depending on policies set by your IT admin, you may be able to add other cloud storage services. For information on setting up other cloud storage services, see Add third-party apps to the Files app on iOS.
To view files in a specific chat or channel
-
Tap Files at the top of the conversation.
To view your recent files
-
Tap More
 and then Files at the bottom right of the screen.
and then Files at the bottom right of the screen.
From there you can also access your cloud storage files.
By default, OneDrive cloud storage will be available. Depending on policies set by your IT admin, you may be able to connect other cloud storage services to Teams.
To learn more, see Files in Microsoft Teams.

 will appear. Click that button, and then click a field name to extract more information. For example, pick Population.
will appear. Click that button, and then click a field name to extract more information. For example, pick Population. instead of an icon, then Excel is having a hard time matching your text with data in our online sources. Correct any spelling mistakes and when you press Enter, Excel will do its best to find matching information. Or, click
instead of an icon, then Excel is having a hard time matching your text with data in our online sources. Correct any spelling mistakes and when you press Enter, Excel will do its best to find matching information. Or, click 












 > View all Outlook settings > Mail > Message handling.
> View all Outlook settings > Mail > Message handling.

 button on the Home tab of the Ribbon, read
button on the Home tab of the Ribbon, read 
 .
. .
.

 .
. .
.