Work with hyperlinks in Excel
For quick access to related information in another file or on a web page, you can insert a hyperlink in a worksheet cell. You can also insert hyperlinks in specific chart elements.
Note: Most of the screen shots in this article were taken in Excel 2016. If you have a different version your view might be slightly different, but unless otherwise noted, the functionality is the same.
Learn more about hyperlinks
A hyperlink is a link from a document that opens another page or file when you click it. The destination is frequently another web page, but it can also be a picture, or an email address, or a program. The hyperlink itself can be text or a picture.
When a site user clicks the hyperlink, the destination is shown in a Web browser, opened, or run, depending on the type of destination. For example, a hyperlink to a page shows the page in the web browser, and a hyperlink to an AVI file opens the file in a media player.
How hyperlinks are used
You can use hyperlinks to do the following:
-
Navigate to a file or web page on a network, intranet, or Internet
-
Navigate to a file or web page that you plan to create in the future
-
Send an email message
-
Start a file transfer, such as downloading or an FTP process
When you point to text or a picture that contains a hyperlink, the pointer becomes a hand  , indicating that the text or picture is something that you can click.
, indicating that the text or picture is something that you can click.
What a URL is and how it works
When you create a hyperlink, its destination is encoded as a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as:
http://example.microsoft.com/news.htm
file://ComputerName/SharedFolder/FileName.htm
A URL contains a protocol, such as HTTP, FTP, or FILE, a Web server or network location, and a path and file name. The following illustration defines the parts of the URL:
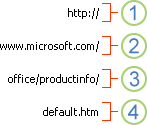
1. Protocol used (http, ftp, file)
2. Web server or network location
3. Path
4. File name
Absolute and relative hyperlinks
An absolute URL contains a full address, including the protocol, the Web server, and the path and file name.
A relative URL has one or more missing parts. The missing information is taken from the page that contains the URL. For example, if the protocol and web server are missing, the web browser uses the protocol and domain, such as .com, .org, or .edu, of the current page.
It is common for pages on the web to use relative URLs that contain only a partial path and file name. If the files are moved to another server, any hyperlinks will continue to work as long as the relative positions of the pages remain unchanged. For example, a hyperlink on Products.htm points to a page named apple.htm in a folder named Food; if both pages are moved to a folder named Food on a different server, the URL in the hyperlink will still be correct.
In an Excel workbook, unspecified paths to hyperlink destination files are by default relative to the location of the active workbook. You can set a different base address to use by default so that each time that you create a hyperlink to a file in that location, you only have to specify the file name, not the path, in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
Create a hyperlink to a new file
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a hyperlink.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink
 .
.
You can also right-click the cell or graphic and then click Hyperlink on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click Create New Document.
-
In the Name of new document box, type a name for the new file.
Tip: To specify a location other than the one shown under Full path, you can type the new location preceding the name in the Name of new document box, or you can click Change to select the location that you want and then click OK.
-
Under When to edit, click Edit the new document later or Edit the new document now to specify when you want to open the new file for editing.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the hyperlink, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
Create a hyperlink to an existing file or web page
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a hyperlink.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink
 .
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Hyperlink on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click Existing File or Web Page.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To select a file, click Current Folder, and then click the file that you want to link to.
You can change the current folder by selecting a different folder in the Look in list.
-
To select a web page, click Browsed Pages and then click the web page that you want to link to.
-
To select a file that you recently used, click Recent Files, and then click the file that you want to link to.
-
To enter the name and location of a known file or web page that you want to link to, type that information in the Address box.
-
To locate a web page, click Browse the Web
 , open the web page that you want to link to, and then switch back to Excel without closing your browser.
, open the web page that you want to link to, and then switch back to Excel without closing your browser.
-
-
If you want to create a hyperlink to a specific location in the file or on the web page, click Bookmark, and then double-click the bookmark that you want.
Note: The file or web page that you are linking to must have a bookmark.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the hyperlink, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
Create a hyperlink to a specific location in a workbook
To link to a location in the current workbook or another workbook, you can either define a name for the destination cells or use a cell reference.
-
To use a name, you must name the destination cells in the destination workbook.
How to name a cell or a range of cells
-
Select the cell, range of cells, or nonadjacent selections that you want to name.
-
Click the Name box at the left end of the formula bar
 .
.
 Name box
Name box -
In the Name box, type the name for the cells, and then press Enter.
Note: Names can't contain spaces and must begin with a letter.
-
-
On a worksheet of the source workbook, click the cell where you want to create a hyperlink.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink
 .
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Hyperlink on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, do one of the following:
-
To link to a location in your current workbook, click Place in This Document.
-
To link to a location in another workbook, click Existing File or Web Page, locate and select the workbook that you want to link to, and then click Bookmark.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Or select a place in this document box, under Cell Reference, click the worksheet that you want to link to, type the cell reference in the Type in the cell reference box, and then click OK.
-
In the list under Defined Names, click the name that represents the cells that you want to link to, and then click OK.
-
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the hyperlink, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
Create a custom hyperlink by using the HYPERLINK function
You can use the HYPERLINK function to create a hyperlink that opens a document that is stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet. When you click the cell that contains the HYPERLINK function, Excel opens the file that is stored at the location of the link.
Syntax
HYPERLINK(link_location,friendly_name)
Link_location is the path and file name to the document to be opened as text. Link_location can refer to a place in a document — such as a specific cell or named range in an Excel worksheet or workbook, or to a bookmark in a Microsoft Word document. The path can be to a file stored on a hard disk drive, or the path can be a universal naming convention (UNC) path on a server (in Microsoft Excel for Windows) or a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) path on the Internet or an intranet.
-
Link_location can be a text string enclosed in quotation marks or a cell that contains the link as a text string.
-
If the jump specified in link_location does not exist or can't be navigated, an error appears when you click the cell.
Friendly_name is the jump text or numeric value that is displayed in the cell. Friendly_name is displayed in blue and is underlined. If friendly_name is omitted, the cell displays the link_location as the jump text.
-
Friendly_name can be a value, a text string, a name, or a cell that contains the jump text or value.
-
If friendly_name returns an error value (for example, #VALUE!), the cell displays the error instead of the jump text.
Examples
The following example opens a worksheet named Budget Report.xls that is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report and displays the text "Click for report":
=HYPERLINK("http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls", "Click for report")
The following example creates a hyperlink to cell F10 on the worksheet named Annual in the workbook Budget Report.xls, which is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the hyperlink displays the contents of cell D1 as the jump text:
=HYPERLINK("[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls]Annual!F10", D1)
The following example creates a hyperlink to the range named DeptTotal on the worksheet named First Quarter in the workbook Budget Report.xls, which is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the hyperlink displays the text "Click to see First Quarter Department Total":
=HYPERLINK("[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls]First Quarter!DeptTotal", "Click to see First Quarter Department Total")
To create a hyperlink to a specific location in a Microsoft Word document, you must use a bookmark to define the location you want to jump to in the document. The following example creates a hyperlink to the bookmark named QrtlyProfits in the document named Annual Report.doc located at example.microsoft.com:
=HYPERLINK("[http://example.microsoft.com/Annual Report.doc]QrtlyProfits", "Quarterly Profit Report")
In Excel for Windows, the following example displays the contents of cell D5 as the jump text in the cell and opens the file named 1stqtr.xls, which is stored on the server named FINANCE in the Statements share. This example uses a UNC path:
=HYPERLINK("\\FINANCE\Statements\1stqtr.xls", D5)
The following example opens the file 1stqtr.xls in Excel for Windows that is stored in a directory named Finance on drive D, and displays the numeric value stored in cell H10:
=HYPERLINK("D:\FINANCE\1stqtr.xls", H10)
In Excel for Windows, the following example creates a hyperlink to the area named Totals in another (external) workbook, Mybook.xls:
=HYPERLINK("[C:\My Documents\Mybook.xls]Totals")
In Microsoft Excel for the Macintosh, the following example displays "Click here" in the cell and opens the file named First Quarter that is stored in a folder named Budget Reports on the hard drive named Macintosh HD:
=HYPERLINK("Macintosh HD:Budget Reports:First Quarter", "Click here")
You can create hyperlinks within a worksheet to jump from one cell to another cell. For example, if the active worksheet is the sheet named June in the workbook named Budget, the following formula creates a hyperlink to cell E56. The link text itself is the value in cell E56.
=HYPERLINK("[Budget]June!E56", E56)
To jump to a different sheet in the same workbook, change the name of the sheet in the link. In the previous example, to create a link to cell E56 on the September sheet, change the word "June" to "September."
Create a hyperlink to an email address
When you click a hyperlink to an email address, your email program automatically starts and creates an email message with the correct address in the To box, provided that you have an email program installed.
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a hyperlink.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink
 .
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Hyperlink on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click E-mail Address.
-
In the E-mail address box, type the email address that you want.
-
In the Subject box, type the subject of the email message.
Note: Some web browsers and email programs may not recognize the subject line.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the hyperlink.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the hyperlink, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
You can also create a hyperlink to an email address in a cell by typing the address directly in the cell. For example, a hyperlink is created automatically when you type an email address, such as someone@example.com.
Create an external reference link to worksheet data on the web
You can insert one or more external reference (also called links) from a workbook to another workbook that is located on your intranet or on the Internet. The workbook must not be saved as an HTML file.
-
Open the source workbook and select the cell or cell range that you want to copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy.

-
Switch to the worksheet that you want to place the information in, and then click the cell where you want the information to appear.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste Special.
-
Click Paste Link.
Excel creates an external reference link for the cell or each cell in the cell range.
Note: You may find it more convenient to create an external reference link without opening the workbook on the web. For each cell in the destination workbook where you want the external reference link, click the cell, and then type an equal sign (=), the URL address, and the location in the workbook. For example:
='http://www.someones.homepage/[file.xls]Sheet1'!A1
='ftp.server.somewhere/file.xls'!MyNamedCell
Select a hyperlink without activating the link
To select a hyperlink without activating the link to its destination, do one of the following:
-
Click the cell that contains the hyperlink, hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
 , and then release the mouse button.
, and then release the mouse button. -
Use the arrow keys to select the cell that contains the hyperlink.
-
If the hyperlink is represented by a graphic, hold down Ctrl, and then click the graphic.
Change a hyperlink
You can change an existing hyperlink in your workbook by changing its destination, its appearance, or the text or graphic that is used to represent it.
Change the destination of a hyperlink
-
Select the cell or graphic that contains the hyperlink that you want to change.
Tip: To select a cell that contains a hyperlink without going to the hyperlink destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
 , and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic.
, and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic.-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Hyperlink.

You can also right-click the cell or graphic and then click Edit Hyperlink on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
In the Edit Hyperlink dialog box, make the changes that you want.
Note: If the hyperlink was created by using the HYPERLINK worksheet function, you must edit the formula to change the destination. Select the cell that contains the hyperlink, and then click the formula bar to edit the formula.
Change the appearance of hyperlink text
You can change the appearance of all hyperlink text in the current workbook by changing the cell style for hyperlinks.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click Cell Styles.
-
Under Data and Model, do the following:
-
To change the appearance of hyperlinks that have not been clicked to go to their destinations, right-click Hyperlink, and then click Modify.
-
To change the appearance of hyperlinks that have been clicked to go to their destinations, right-click Followed Hyperlink, and then click Modify.
Note: The Hyperlink cell style is available only when the workbook contains a hyperlink. The Followed Hyperlink cell style is available only when the workbook contains a hyperlink that has been clicked.
-
-
In the Style dialog box, click Format.
-
On the Font tab and Fill tab, select the formatting options that you want, and then click OK.
Notes:
-
The options that you select in the Format Cells dialog box appear as selected under Style includes in the Style dialog box. You can clear the check boxes for any options that you don't want to apply.
-
Changes that you make to the Hyperlink and Followed Hyperlink cell styles apply to all hyperlinks in the current workbook. You can't change the appearance of individual hyperlinks.
-
Change the text or graphic for a hyperlink
-
Select the cell or graphic that contains the hyperlink that you want to change.
Tip: To select a cell that contains a hyperlink without going to the hyperlink destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
 , and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic.
, and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic. -
Do one or more of the following:
-
To change the hyperlink text, click in the formula bar, and then edit the text.
-
To change the format of a graphic, right-click it, and then click the option that you need to change its format.
-
To change text in a graphic, double-click the selected graphic, and then make the changes that you want.
-
To change the graphic that represents the hyperlink, insert a new graphic, make it a hyperlink with the same destination, and then delete the old graphic and hyperlink.
-
Copy or move a hyperlink
-
Right-click the hyperlink that you want to copy or move, and then click Copy or Cut on the shortcut menu.
-
Right-click the cell that you want to copy or move the hyperlink to, and then click Paste on the shortcut menu.
Set the base address for the hyperlinks in a workbook
By default, unspecified paths to hyperlink destination files are relative to the location of the active workbook. Use this procedure when you want to set a different default path. Each time that you create a hyperlink to a file in that location, you only have to specify the file name, not the path, in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
Follow one of the steps depending on the Excel version you are using:
-
In Excel 2016, Excel 2013, and Excel 2010:
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Info.
-
Click Properties, and then select Advanced Properties.
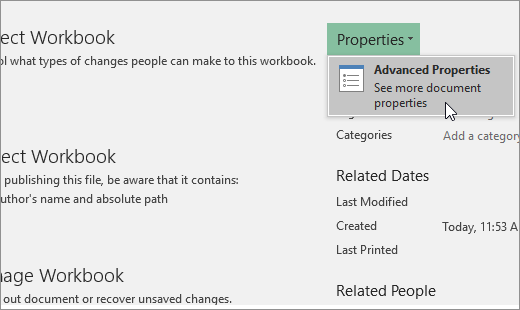
-
In the Summary tab, in the Hyperlink base text box, type the path that you want to use.
Note: You can override the hyperlink base address by using the full, or absolute, address for the hyperlink in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
-
-
In Excel 2007:
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , click Prepare, and then click Properties.
, click Prepare, and then click Properties. -
In the Document Information Panel, click Properties, and then click Advanced Properties.
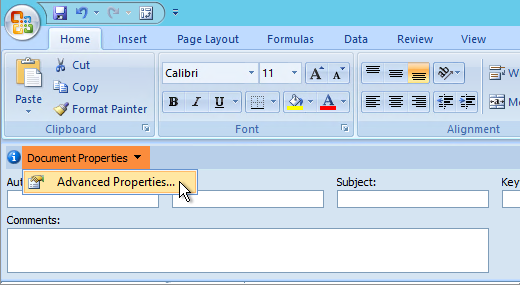
-
Click the Summary tab.
-
In the Hyperlink base box, type the path that you want to use.
Note: You can override the hyperlink base address by using the full, or absolute, address for the hyperlink in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
-
Delete a hyperlink
To delete a hyperlink, do one of the following:
-
To delete a hyperlink and the text that represents it, right-click the cell that contains the hyperlink, and then click Clear Contents on the shortcut menu.
-
To delete a hyperlink and the graphic that represents it, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic, and then press Delete.
-
To turn off a single hyperlink, right-click the hyperlink, and then click Remove Hyperlink on the shortcut menu.
-
To turn off several hyperlinks at once, do the following:
-
In a blank cell, type the number 1.
-
Right-click the cell, and then click Copy on the shortcut menu.
-
Hold down Ctrl and select each hyperlink that you want to turn off.
Tip: To select a cell that has a hyperlink in it without going to the hyperlink destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
 , and then release the mouse button.
, and then release the mouse button. -
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste, and then click Paste Special.

-
Under Operation, click Multiply, and then click OK.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click Cell Styles.
-
Under Good, Bad, and Neutral, select Normal.
-
See also
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community, get support in the Answers community, or suggest a new feature or improvement on Excel User Voice.
No comments:
Post a Comment