GETPIVOTDATA function
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the GETPIVOTDATA function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns data stored in a PivotTable. You can use GETPIVOTDATA to retrieve summary data from a PivotTable, provided the summary data is visible in the report.
Note: You can quickly enter a simple GETPIVOTDATA formula by typing = (the equal sign) in the cell you want to return the value to and then clicking the cell in the PivotTable that contains the data you want to return.
Syntax
GETPIVOTDATA(data_field, pivot_table, [field1, item1, field2, item2], ...)
The GETPIVOTDATA function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Data_field Required. The name, enclosed in quotation marks, for the data field that contains the data that you want to retrieve.
-
Pivot_table Required. A reference to any cell, range of cells, or named range of cells in a PivotTable. This information is used to determine which PivotTable contains the data that you want to retrieve.
-
Field1, Item1, Field2, Item2 Optional. 1 to 126 pairs of field names and item names that describe the data that you want to retrieve. The pairs can be in any order. Field names and names for items other than dates and numbers are enclosed in quotation marks. For OLAP PivotTables, items can contain the source name of the dimension and also the source name of the item. A field and item pair for an OLAP PivotTable might look like this:
"[Product]","[Product].[All Products].[Foods].[Baked Goods]"
Remarks
-
Calculated fields or items and custom calculations are included in GETPIVOTDATA calculations.
-
If pivot_table is a range that includes two or more PivotTables, data will be retrieved from whichever report was created most recently in the range.
-
If the field and item arguments describe a single cell, the value of that cell is returned regardless of whether it is a string, number, error, and so on.
-
If an item contains a date, the value must be expressed as a serial number or populated by using the DATE function so that the value will be retained if the worksheet is opened in a different locale. For example, an item referring to the date March 5, 1999 could be entered as 36224 or DATE(1999,3,5). Times can be entered as decimal values or by using the TIME function.
-
If pivot_table is not a range in which a PivotTable is found, GETPIVOTDATA returns #REF!.
-
If the arguments do not describe a visible field, or if they include a report filter in which the filtered data is not displayed, GETPIVOTDATA returns the #REF! error value.
Example
For practical purposes, the example data shown below doesn't contain actual PivotTable data, but here's a snapshot of the data. The formulas and results are shown in the example.
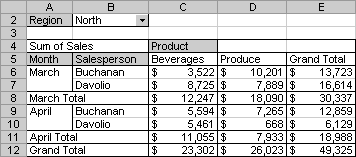
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
| Formula | Result |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sales", $A$4) | Returns the grand total of the Sales field, $49,325. |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sum of Sales", $A$4) | Also returns the grand total of the Sales field, $49,325; the field name can be entered exactly as it looks on the sheet, or as its root (without "Sum of," "Count of," and so on). |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sales", $A$4, "Month", "March") | Returns the grand total for March, $30,337. |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sales", $A$4, "Month", "March", "Product", "Produce", "Salesperson", "Buchanan") | Returns $10,201. |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sales", $A$4, "Region", "South") | Returns #REF! error value because the South region data is not visible. |
| GETPIVOTDATA("Sales", $A$4, "Product", "Beverages", "Salesperson", "Davolio") | Returns #REF! error value because there is no total value of beverage sales for Davolio. |
No comments:
Post a Comment