Save a workbook in another file format
Most of the time, you'll probably want to save your workbooks in the current file format (.xlsx). But sometimes, you might need to save a workbook in another file format, like the file format of an earlier version of Excel, a text file, or a PDF or XPS file. Just keep in mind that whenever you save a workbook in another file format, some of its formatting, data, and features might not be saved.
For a list of file formats (also called file types) you can (and can't) open or save in Excel 2013, see File formats that are supported in Excel at the end of this article.
-
Open the workbook you want to save.
-
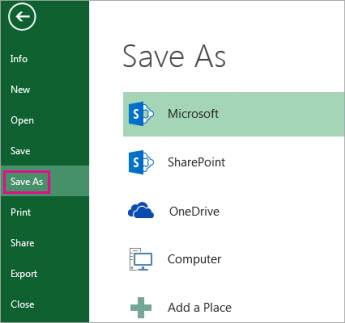
Click File > Save As.
-
Under Places, pick the place where you want to save the workbook. For example, pick OneDrive to save it to your Web location or Computer to save it in a local folder like your Documents.

-
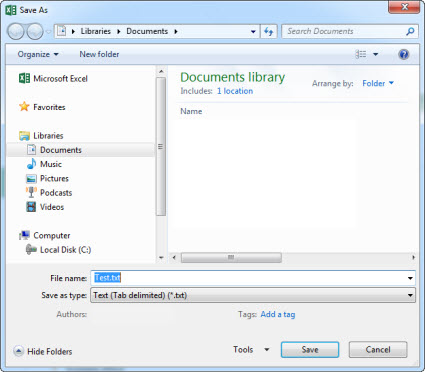
In the Save As dialog box, navigate to the location you want.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format you want. Click the arrows to scroll to file formats that aren't visible in the list.
Note: The file formats you'll see vary, depending on what type of sheet is active in your workbook (a worksheet, chart sheet, or other type of sheet).
-
In the File name box, accept the suggested name or type a new name for the workbook.
Convert an Excel 97-2003 workbook to the current file format
If you opened an Excel 97-2003 workbook but don't need to keep it in that file format, simply convert it to the current file format (.xlsx).
-
Click File > Info.
-
Click Convert.

File formats that are supported in Excel
In Excel 2013, you can open and save files in the following file formats:
Excel file formats
| Format | Extension | Description |
| Excel Workbook | .xlsx | The default XML-based file format for Excel 2007-2013. Cannot store Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macro code or Microsoft Office Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
| Strict Open XML Spreadsheet | .xlsx | An ISO strict version of the Excel Workbook file format (.xlsx). |
| Excel Workbook (code) | .xlsm | The XML-based and macro-enabled file format for Excel 2007-2013. Stores VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
| Excel Binary Workbook | .xlsb | The binary file format (BIFF12) for Excel 2007-2013. |
| Template | .xltx | The default file format for an Excel template for Excel 2007-2013. Cannot store VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
| Template (code) | .xltm | The macro-enabled file format for an Excel template in Excel 2007-2013. Stores VBA macro code or Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
| Excel 97- Excel 2003 Workbook | .xls | The Excel 97 - Excel 2003 Binary file format (BIFF8). |
| Excel 97- Excel 2003 Template | .xlt | The Excel 97 - Excel 2003 Binary file format (BIFF8) for an Excel template. |
| Microsoft Excel 5.0/95 Workbook | .xls | The Excel 5.0/95 Binary file format (BIFF5). |
| XML Spreadsheet 2003 | .xml | XML Spreadsheet 2003 file format (XMLSS). |
| XML Data | .xml | XML Data format. |
| Excel Add-In | .xlam | The XML-based and macro-enabled Add-In format for Excel 2007-2013. An Add-In is a supplemental program that is designed to run additional code. Supports the use of VBA projects and Excel 4.0 macro sheets (.xlm). |
| Excel 97-2003 Add-In | .xla | The Excel 97-2003 Add-In, a supplemental program that is designed to run additional code. Supports the use of VBA projects. |
| Excel 4.0 Workbook | .xlw | An Excel 4.0 file format that saves only worksheets, chart sheets, and macro sheets. You can open a workbook in this file format in Excel 2013, but you cannot save an Excel file to this file format. |
Text file formats
| Format | Extension | Description |
| Formatted Text (Space-delimited) | .prn | Lotus space-delimited format. Saves only the active sheet. |
| Text (Tab-delimited) | .txt | Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on another Microsoft Windows operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| Text (Macintosh) | .txt | Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on the Macintosh operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| Text (MS-DOS) | .txt | Saves a workbook as a tab-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| Unicode Text | .txt | Saves a workbook as Unicode text, a character encoding standard that was developed by the Unicode Consortium. |
| CSV (comma delimited) | .csv | Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on another Windows operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| CSV (Macintosh) | .csv | Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on the Macintosh operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| CSV (MS-DOS) | .csv | Saves a workbook as a comma-delimited text file for use on the MS-DOS operating system, and ensures that tab characters, line breaks, and other characters are interpreted correctly. Saves only the active sheet. |
| DIF | .dif | Data Interchange Format. Saves only the active sheet. |
| SYLK | .slk | Symbolic Link Format. Saves only the active sheet. |
Note: If you save a workbook in any text format, all formatting is lost.
Other file formats
| Format | Extension | Description |
| DBF 3, DBF 4 | .dbf | dBase III and IV. You can open these files formats in Excel, but you cannot save an Excel file to dBase format. |
| OpenDocument Spreadsheet | .ods | OpenDocument Spreadsheet. You can save Excel 2010 files so they can be opened in spreadsheet applications that use the OpenDocument Spreadsheet format, such as Google Docs and OpenOffice.org Calc. You can also open spreadsheets in the .ods format in Excel 2010. Formatting might be lost when saving and opening .ods files. |
| | | Portable Document Format (PDF). This file format preserves document formatting and enables file sharing. When the PDF format file is viewed online or printed, it retains the format that you intended. Data in the file cannot be easily changed. The PDF format is also useful for documents that will be reproduced by using commercial printing methods. |
| XPS Document | .xps | XML Paper Specification (XPS). This file format preserves document formatting and enables file sharing. When the XPS file is viewed online or printed, it retains exactly the format that you intended, and the data in the file cannot be easily changed. |
File formats that use the clipboard
If you copied data to the clipboard in one of the following file formats, you can paste it into Excel using the Paste or Paste Special command (Home > Clipboard > Paste).
| Format | Extension | Clipboard type identifiers |
| Picture | .wmf or .emf | Pictures in Windows Metafile Format (WMF) or Windows Enhanced Metafile Format (EMF). Note: If you copy a Windows metafile picture from another program, Excel pastes the picture as an enhanced metafile. |
| Bitmap | .bmp | Pictures stored in Bitmap format (BMP). |
| Microsoft Excel file formats | .xls | Binary file formats for Excel versions 5.0/95 (BIFF5), Excel 97-2003 (BIFF8), and Excel 2013 (BIFF12). |
| SYLK | .slk | Symbolic Link Format. |
| DIF | .dif | Data Interchange Format. |
| Text (tab-delimited) | .txt | Tab-separated text format. |
| CSV (Comma-delimited) | .csv | Comma-separated values format. |
| Formatted text (Space-delimited) | .rtf | Rich Text Format (RTF). Only from Excel. |
| Embedded object | .gif, .jpg, .doc, .xls, or .bmp | Microsoft Excel objects, objects from properly registered programs that support OLE 2.0 (OwnerLink), and Picture or another presentation format. |
| Linked object | .gif, .jpg, .doc, .xls, or .bmp | OwnerLink, ObjectLink, Link, Picture, or other format. |
| Office drawing object | .emf | Office drawing object format or Picture (Windows enhanced metafile format, EMF). |
| Text | .txt | Display Text, OEM Text. |
| Single File Web Page | .mht, .mhtml | Single File Web Page (MHT or MHTML). This file format integrates inline graphics, applets, linked documents, and other supporting items referenced in the document. |
| Web Page | .htm, .html | Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Note: When you copy text from another program, Excel pastes the text in HTML format, regardless of the format of the original text. |
File formats that are not supported in Excel 2013
The following file formats are no longer supported, so you can't open or save files in these file formats.
To work with your workbook data in a program that isn't supported anymore, try the following:
-
Search the Web for a company that makes file format converters for file formats that aren't supported in Excel.
-
Save your workbook to another file format that can be opened in the other program. For example, save to an XML spreadsheet or text file format that the other program might support as well.
| Format | Extension | Clipboard type identifiers |
| Excel Chart | .xlc | Excel 2.0, 3.0, and 2.x file formats |
| WK1, FMT, WK2, WK3, FM3, WK4 | .wk1, .wk2, .wk3, .wk4, .wks | Lotus 1-2-3 file formats (all versions) |
| Microsoft Works | .wks | Microsoft Works file format (all versions) |
| DBF 2 | .dbf | DBASE II file format |
| WQ1 | .wq1 | Quattro Pro for MS-DOS file format |
| WB1, WB3 | .wb1, .wb3 | Quattro Pro 5.0 and 7.0 for Windows. |
You can save an Excel 2007 or later workbook in the file format of an earlier version of Excel, in a text file format, and in other file formats, such as PDF or XPS. By default, files are saved in the .xlsx file format, but you can change the default file format for saving. If you frequently use the Save As command, you may want to add it to the Quick Access Toolbar.
Save an Excel workbook in a different file format
Important: If you save a workbook in a file format other than the current Excel file format, formats and features that are unique to Excel 2007 and later will not be retained. For more information, see Use Excel with earlier versions of Excel.
-
In Excel, open the workbook that you want to save for use in another program.
-
On the File tab, click Save As.
-
To save the workbook to a different location, specify the drive and location in the file path and folder boxes.
-
In the File name box, accept the suggested name or type a new name for the workbook.
-
In the Save as type list, click the format that you know you can open in the other program.
If needed, click the arrows to scroll to file formats that are not visible in the list.
Note: The file formats that are available vary, depending on what type of sheet is active (a worksheet, chart sheet, or other type of sheet).
Tip: For more information on how to save a workbook in PDF (.pdf) or XPS (.xps) file formats, see Save as PDF or XPS.
Save a different file format in an Excel 2007 and later file format
You can save any file format that you can open in Excel 2007 and later in the current Excel Workbook file format (.xlsx). By doing this, you can use new features that are not supported by other file formats.
Note: When you save a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel as an Excel 2007 and later workbook, some formats and features may not be retained. For information on unsupported Excel 97-2003 features, see Use Excel with earlier versions of Excel.
-
Open the file that you want to save in the current file format.
-
On the File tab, click Save As.
-
To save the file to a different location, specify the drive and location in the file path and folder boxes.
-
In the File name box, accept the suggested name or type a new name for the workbook.
-
In the Save as type list, do one of the following:
-
If you are saving a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel, and the workbook contains macros that you want to retain, click Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xlsm).
-
If you want to save the workbook as a template, click Excel Template (*.xltx).
-
If you are saving a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel, the workbook contains macros that you want to retain, and you want to save the workbook as a template, click Excel Macro-Enabled Template.xltm.
-
If you want to save the workbook in the current Excel Workbook file format, click Excel Workbook (*.xlsx).
-
If you want to save the file in the new binary file format, click Excel Binary Workbook (*.xslb).
-
-
Click Save.
Change the default file format for saving
You can change the file type that is used by default when you save a workbook.
-
On the File tab, click Options.
-
In the Save category, under Save workbooks, in the Save files in this format box, click the file format that you want to use by default.
Add the Save As command to the Quick Access Toolbar
The Save As command is not available as a button on the ribbon. You can, however, add the command to the Quick Access Toolbar.
-
Click the dropdown arrow on the Quick Access Toolbar, and then click More Commands.

-
In the Choose commands from box, make sure that Popular Commands is selected.
-
In the list box, scroll to the Save As button, and then select it.
-
Click Add.
You can save a Microsoft Office Excel 2007 workbook in a different file format. You can save a workbook in an earlier version file format, in text file format, and in other file formats, such as PDF or XPS. You can also save any file format that you can open in Office Excel 2007 as an Excel 2007 workbook. By default, Excel 2007 saves files in the .xlsx file format, but you can change the default file format for saving.
If you frequently use the Save As command, you may want to add it to the Quick Access Toolbar.
Save a file in the Excel 2007 file format
You can save any file format that you can open in Excel 2007 in the current Excel Workbook file format (.xlsx). By doing this, you can use the new features of Excel 2007, such as the larger grid, that are not supported by other file formats.
Note: When you save a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel as an Excel 2007 workbook, some formats and features may not be retained.
-
Open the workbook that you want to save as an Excel 2007 workbook.
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Save As.
, and then click Save As. -
In the File name box, accept the suggested name or type a new name for the workbook.
-
In the Save as type list, do one of the following:
-
If you are saving a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel, and the workbook contains macros that you want to retain, click .xlsm.
-
If you want to save the workbook as a template, click .xltx.
-
If you are saving a workbook that was created in an earlier version of Excel, the workbook contains macros that you want to retain, and you want to save the workbook as a template, click .xltm.
-
If you want to save the workbook in the current Excel Workbook file format, click .xlsx.
-
If you want to save the file in the new binary file format, click .xslb.
-
For more information about file formats, see File formats that are supported in Excel.
-
-
Click Save.
Change the default file format for saving
You can change the file type that is used by default when you save a workbook.
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Excel Options.
, and then click Excel Options. -
In the Save category, under Save workbooks, in the Save files in this format box, click the file format that you want to use by default.
Add the Save As command to the Quick Access Toolbar
The Save As command is not available as a button on the Microsoft Office Fluent user interface Ribbon. You can, however, add the command to the Quick Access Toolbar.
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 .
. -
Right-click Save As, and then click Add to Quick Access Toolbar.
No comments:
Post a Comment