Find and transfer Outlook data files from one computer to another
Outlook saves backup information in a variety of different locations. Depending on what type of account you have, you can back up your emails, your personal address book, your navigation pane settings, your signatures, templates, and more.
If you're using a Microsoft Exchange, Office 365, or Outlook.com account, your email messages are backed up on your email server. In most cases, you won't have a Personal Folders file (.pst) for these types of accounts.
In order to view some of the backup files for Outlook, you'll need to unhide system folders and file name extensions. For information on how to perform that task, see How to unhide folders and file name extensions.
Backup information for Office 365, Exchange, or Outlook.com accounts
For Office 365 accounts, Exchange accounts, or Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, or Live.com accounts not accessed by POP or IMAP, you won't have a Personal Folders (.pst) file. You may have an Offline Folders (.ost) file, but that file is automatically recreated by Outlook when you add a new email account. You can't move that file from one computer to another.
For Office 365 accounts, Exchange accounts, or Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, or Live.com accounts not accessed by POP or IMAP, the following information can be transferred from one computer to another.
Navigation Pane settings
You can find these settings in one of the following locations:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook\profile name.xml
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook\profile name.xml
Print styles
You can find the Outlprnt file in one of the following locations:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook\Outlprnt
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook\Outlprnt
Signatures
You can find the various files that make up your Outlook signatures in one of the following locations:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Signatures
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Signatures
Stationery
Stationery can be stored in two different locations depending on whether you have the 32-bit or 64-bit version of Outlook installed. You can find the various files that make up your Outlook stationery in one of the following locations:
-
All versions of Windows drive:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Stationery
-
All versions of Windows drive:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\ Microsoft Shared\Stationery
Custom forms
You can find the various files that make up your custom Outlook forms in one of the following locations:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Forms
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Forms
Dictionary
Your custom dictionary files are stored in one of two places:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\UProof
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\UProof
Templates
Any Outlook templates you've created are stored in one of two places. Templates will have an .oft extension.
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Templates
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Templates
Send/Receive settings
Your send and receive settings include which accounts are checked at what frequency. You can find your send and receive settings file in one of the following locations. The file will have an .srs extension.
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Email, calendar, contact, and task information for POP and IMAP accounts
If you have a POP or IMAP account, all of your information is already stored in a Personal Folders (.pst) file. You can move this file to a new computer and retain your information. Moving a .pst file from one computer to another doesn't transfer your email account settings. If you need to set up Outlook on a new computer, copy your .pst file from the old computer, then set up your email account on your new computer. You can then open the .pst file from the new computer.
The location of your .pst file depends on your version of Outlook, your version of Windows, and how you set up your account or created the .pst file. You can find your .pst file in one of the following locations:
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
-
Windows 10 drive:\Users\<username>\Roaming\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
-
Older versions of Windows drive:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Note: Your configuration might not include all of these files as some are created only when you customize Outlook features.
Can't find the folders?
Some of the folders might be hidden folders. To display hidden folders in Windows, do the following:
-
Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
-
Open Folder Options.
To locate Folder Options, in the search box at the top of window, type Folder Options. In Control Panel for Windows XP, type Folder Options in the Address box.
-
On the View tab, under Advanced settings, under Files and Folders, under Hidden files and folders, select Show hidden files and folders.
Outlook Data File (.pst)
Outlook Data Files (.pst) contain your e-mail messages, calendars, contacts, tasks, and notes. You must use Outlook to work with the items in a .pst file.
When you archive Outlook information, items are saved in a .pst files.
Note: Microsoft Exchange Server accounts save your information on the mail server. To use Cached Exchange Mode or to work offline, copies of your items are saved in an offline Outlook Data File (.ost). See the Outlook Data Files (.ost) section for more information. Also, some organizations allow you to export or archive your items to a .pst file.
The fastest way to open the folder where your Outlook Data File (.pst and .ost) is saved is to do the following:
-
In Outlook 2010, click the File tab.
-
Click Account Settings, and then click Account Settings.
-
On the Data tab, click an entry, and then click Open Folder Location.
Outlook Data Files (.pst) created by using Outlook 2010 are saved on your computer in the Documents\Outlook Files folder. If you are using Windows XP, these files are created in the My Documents\Outlook Files folder.
If you upgraded to Outlook 2010 on a computer that already had data files created in previous versions of Outlook, these files are saved in a different location in a hidden folder.
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Tip: For information about hidden folders in Windows, see Windows Help and Support.
Outlook Data File (.ost)
The .ost file is synchronized with the items on the server that runs Exchange. Because your data remains on the Exchange server, you can re-create this .ost file on your new computer without having to back up the .ost file.
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Personal Address Book (.pab)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Note: Personal Address Books (.pab) are not supported in Outlook 2010. When you upgrade to Outlook 2010, you are prompted to import any .pab file into Contacts. If you choose not to import the .pab file when you first run Outlook 2010, you can import it later by using the Import command in the Microsoft Office Backstage view.
Offline Address Book (.oab)
The Offline Address Book (.oab) is used by Microsoft Exchange Server accounts. It contains information, such as names, e-mail address, titles, and office locations, from the Global Address List (GAL) on the server that runs Exchange.
You do not have to back up or restore this file. This is file is created and updated automatically.
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Navigation Pane settings (.xml)
This file includes information about the contents of the Navigation Pane.
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Outlook\profile name.xml
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook\profile name.xml
Registered Microsoft Exchange extensions (.dat)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Outlook Contacts Auto-Complete List
The Auto-Complete List is a feature that displays suggestions for names and e-mail addresses as you begin to type them. These suggestions are possible matches from a list of names and e-mail addresses from the e-mail messages that you have sent.
In Outlook 2007, the Auto-Complete List file (.nk2) is stored in the following locations:
Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
In Outlook 2010, the Auto-Complete List file (.nk2) is discontinued. The Auto-Complete List entries are now saved in your Microsoft Exchange Server mailbox or in the Outlook Data File (.pst) for your account.
Exchange Server accounts
If you are using an Exchange Server account, your Auto-Complete List is saved in your mailbox on the server that runs Exchange. This enables your Auto-Complete List to be used from any computer that you use Outlook with your Exchange account.
How can I tell if I have a Microsoft Exchange Server account?
Click the File tab. Click Account Settings, and then click Account Settings. On the E-mail tab, the list of accounts indicates the type of each account.
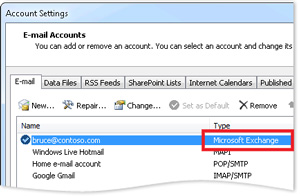
POP3 accounts
The Auto-Complete List is saved in the Outlook Data File (.pst). See the section Outlook Data File (.pst) for location information.
IMAP and Outlook.com accounts
The Auto-Complete List is saved in the Outlook Data File (.pst). The Outlook Data Files (.pst) for these account types differ from other Outlook Data Files (.pst) in Outlook. These files are used as copies of information on your mail server account and not intended to be moved or restored. A new Outlook Data File (.pst) is created when you configure an IMAP or an Outlook.com (formerly Hotmail) account in a different Outlook profile or on another computer. Your Auto-Complete List, therefore, is unique to the computer and profile where the account is set up and the entries do not appear in any other profile or computer that you use.
Rules (.rwz)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Note: If you upgraded to Outlook 2010 from a version of Outlook earlier than Microsoft Outlook 2002, you might have an .rwz file on your computer's hard disk drive. The .rwz file is no longer needed, and the information about rules is now kept on the server running Microsoft Exchange, and in the Outlook Data File (.pst) for POP3 and IMAP e-mail accounts. You can delete the file.
If you use the Rules Import and Export feature, the default location for .rwz files is your Documents folder.
Print styles (Outlprnt with no extension)
Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Signatures (.rtf, .txt, .htm)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Signatures
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Signatures
Stationery (.htm)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Stationery
Windows 7 and Windows Vista 64-bit with Outlook 2010 32-bit drive:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Stationery
Windows XP drive:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Stationery
Custom forms
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Forms
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Forms
Dictionary (.dic)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\UProof
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\UProof
Templates (.oft)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Templates
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Templates
Send/Receive settings (.srs)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Outlook
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook
Message (.msg, .htm, .rtf)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista drive:\Users\user\Documents
Windows XP drive:\Documents and Settings\user\My Documents
How to unhide folders and file name extensions
Some of the folders might be hidden folders, and Windows might have file name extensions (such as .pst, .ost, .pab) turned off. To show hidden folders and file name extensions, do the following:
-
Open Control Panel.
-
In Windows 10, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
-
In Windows 8, press the Windows key + X, then click Control Panel.
-
In Windows 7, click Start > Control Panel.
-
-
In the View by list, make sure either Large icons or Small icons is selected so that you can see all the icons in Control Panel.
-
Click Folder Options.
-
Click the View tab.
-
In the Advanced settings box:
-
Under Files and Folders, uncheck the Hide extensions for known file types box
-
Under Hidden files and folders, click the Show hidden files, folders, and drives button.
-
Click OK.
-
No comments:
Post a Comment