Create a chart
Some of the content in this topic may not be applicable to some languages.
Which Office program are you using?
Word
Charts display data in a graphical format. This can help you and your audience visualize relationships between data. When you create a chart, you can select from many chart types (for example, a stacked column chart or a 3-D exploded pie chart). After you create a chart, you can customize it by applying chart quick layouts or styles.
Important: You must have Excel installed to create or change a chart. You can order a copy of Excel on the Microsoft Web site.
Learn the elements of a chart
Charts contain several elements, such as a title, axis labels, a legend, and gridlines. You can hide or display these elements, and you can also change their location and formatting.
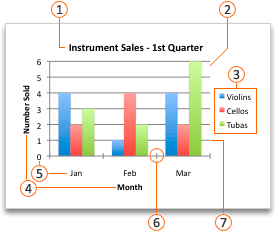
 Chart title
Chart title
 Plot area
Plot area
 Legend
Legend
 Axis titles
Axis titles
 Axis labels
Axis labels
 Tick marks
Tick marks
 Gridlines
Gridlines
Create a chart
You can create a chart in Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. However, the chart data is entered and saved in an Excel sheet. If you insert a chart in Word or PowerPoint, a new sheet is opened in Excel. When you save a Word document or PowerPoint presentation that contains a chart, the chart's underlying Excel data is automatically saved within the Word document or PowerPoint presentation.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
On the Charts tab, under Insert Chart, click a chart type, and then click the one that you want to add.
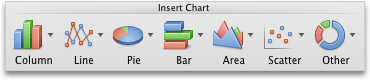
When you insert a chart into Word or PowerPoint, an Excel sheet opens that contains a table of sample data.
-
In Excel, replace the sample data with the data that you want to plot in the chart. If you already have your data in another table, you can copy the data from that table and then paste it over the sample data. See the following table for guidelines on how to arrange the data to fit your chart type.
| For this chart type | Arrange the data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area, bar, column, doughnut, line, radar, or surface chart | In columns or rows, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bubble chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pie chart | In one column or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock chart | In columns or rows in the following order, using names or dates as labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X Y (scatter) chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
or
|
-
To change the number of rows and columns that are included in the chart, rest the pointer on the lower-right corner of the selected data, and then drag to select additional data. In the following example, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.
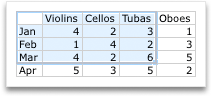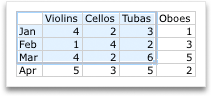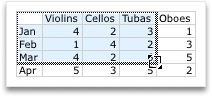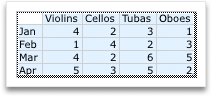
-
To see the results of your changes, switch to Word.
Note: When you close the Word document that contains the chart, the chart's Excel data table closes automatically.
Change which chart axis is emphasized
After you create a chart, you might want to change the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For example, your first version of a chart might plot the rows of data from the table on the chart's vertical (value) axis, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the following example, the chart emphasizes sales by instrument.
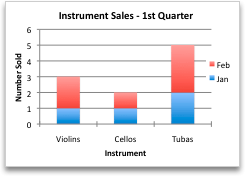
However, if you want the chart to emphasize the sales by month, you can reverse the way the chart is plotted.
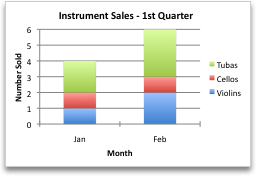
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click Plot series by row
 or Plot series by column
or Plot series by column  .
.
If Switch Plot is not available
Switch Plot is available only when the chart's Excel data table is open and only for certain chart types.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click the arrow next to Edit, and then click Edit Data in Excel.

-
Apply a predefined chart layout
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Quick Layouts, click the layout that you want.
To see more layouts, point to a layout, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a quick layout that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Apply a predefined chart style
Chart styles are a set of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes affect the whole chart.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Styles, click the style that you want.
To see more styles, point to a style, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a style that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Add a chart title
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
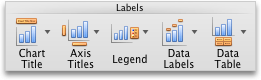
Click the chart, and then click the Chart Layout tab.
-
Under Labels, click Chart Title, and then click the one that you want.
-
Select the text in the Chart Title box, and then type a chart title.
See also
PowerPoint
Charts display data in a graphical format. This can help you and your audience visualize relationships between data. When you create a chart, you can select from many chart types (for example, a stacked column chart or a 3-D exploded pie chart). After you create a chart, you can customize it by applying chart quick layouts or styles.
Important: You must have Excel installed to create or change a chart. You can order a copy of Excel on the Microsoft Web site.
Learn the elements of a chart
Charts contain several elements, such as a title, axis labels, a legend, and gridlines. You can hide or display these elements, and you can also change their location and formatting.

 Chart title
Chart title
 Plot area
Plot area
 Legend
Legend
 Axis titles
Axis titles
 Axis labels
Axis labels
 Tick marks
Tick marks
 Gridlines
Gridlines
Create a chart
You can create a chart in Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. However, the chart data is entered and saved in an Excel sheet. If you insert a chart in Word or PowerPoint, a new sheet is opened in Excel. When you save a Word document or PowerPoint presentation that contains a chart, the chart's underlying Excel data is automatically saved within the Word document or PowerPoint presentation.
-
On the Charts tab, under Insert Chart, click a chart type, and then click the one that you want to add.

When you insert a chart into Word or PowerPoint, an Excel sheet opens that contains a table of sample data.
-
In Excel, replace the sample data with the data that you want to plot in the chart. If you already have your data in another table, you can copy the data from that table and then paste it over the sample data. See the following table for guidelines on how to arrange the data to fit your chart type.
| For this chart type | Arrange the data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area, bar, column, doughnut, line, radar, or surface chart | In columns or rows, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bubble chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pie chart | In one column or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock chart | In columns or rows in the following order, using names or dates as labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X Y (scatter) chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
or
|
-
To change the number of rows and columns that are included in the chart, rest the pointer on the lower-right corner of the selected data, and then drag to select additional data. In the following example, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.

-
To see your changes, switch to PowerPoint.
Note: When you close the PowerPoint presentation that contains the chart, the chart's Excel data table closes automatically.
Change which chart axis is emphasized
After you create a chart, you might want to change the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For example, your first version of a chart might plot the rows of data from the table on the chart's vertical (value) axis, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the following example, the chart emphasizes sales by instrument.

However, if you want the chart to emphasize the sales by month, you can reverse the way the chart is plotted.

-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click Plot series by row
 or Plot series by column
or Plot series by column  .
.
If Switch Plot is not available
Switch Plot is available only when the chart's Excel data table is open and only for certain chart types.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click the arrow next to Edit, and then click Edit Data in Excel.

-
Apply a predefined chart layout
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Quick Layouts, click the layout that you want.

To see more layouts, point to a layout, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a quick layout that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Apply a predefined chart style
Chart styles are a set of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes affect the whole chart.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Styles, click the style that you want.

To see more styles, point to a style, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a style that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Add a chart title
-
Click the chart, and then click the Chart Layout tab.
-
Under Labels, click Chart Title, and then click the one that you want.

-
Select the text in the Chart Title box, and then type a chart title.
See also
Excel
Charts display data in a graphical format. This can help you and your audience visualize relationships between data. When you create a chart, you can select from many chart types (for example, a stacked column chart or a 3-D exploded pie chart). After you create a chart, you can customize it by applying chart quick layouts or styles.
Note: The Excel Workbook Gallery in Excel for Mac 2011 replaces the former Chart Wizard. By default, the Excel Workbook Gallery opens when you open Excel. From the gallery, you can browse templates and create a new workbook based on one of them. If you don't see the Excel Workbook Gallery, on the File menu, click New from Template.
Learn the elements of a chart
Charts contain several elements, such as a title, axis labels, a legend, and gridlines. You can hide or display these elements, and you can also change their location and formatting.

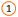 Chart title
Chart title
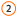 Plot area
Plot area
 Legend
Legend
 Axis titles
Axis titles
 Axis labels
Axis labels
 Tick marks
Tick marks
 Gridlines
Gridlines
Create a chart
-
On a sheet, arrange the data that you want to plot in a chart. See the following table for guidelines on how to arrange the data to fit your chart type.
| For this chart type | Arrange the data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area, bar, column, doughnut, line, radar, or surface chart | In columns or rows, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bubble chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pie chart | In one column or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock chart | In columns or rows in the following order, using names or dates as labels, as in the following examples:
or
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X Y (scatter) chart | In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
or
|
-
Select the rows and columns that you want to appear in the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Insert Chart, click a chart type, and then click the one that you want to add.

-
To change the number of rows and columns that are included in the chart, rest the pointer on the lower-right corner of the selected data, and then drag to select additional data. In the following example, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.
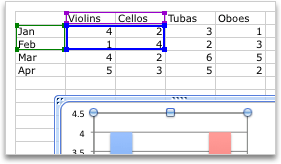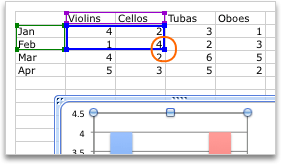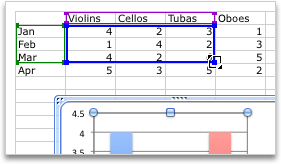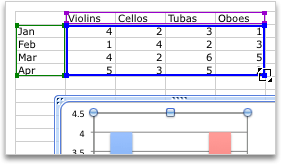
Tip: To prevent that data from being displayed in the chart, you can hide rows and columns in the table.
Change which chart axis is emphasized
After you create a chart, you might want to change the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For example, your first version of a chart might plot the rows of data from the table on the chart's vertical (value) axis, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the following example, the chart emphasizes sales by instrument.

However, if you want the chart to emphasize the sales by month, you can reverse the way the chart is plotted.

-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Data, click Plot series by row
 or Plot series by column
or Plot series by column  .
.
Apply a predefined chart layout
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Quick Layouts, click the layout that you want.

To see more layouts, point to a layout, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a quick layout that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Apply a predefined chart style
Chart styles are a set of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes affect the whole chart.
-
Click the chart.
-
On the Charts tab, under Chart Styles, click the style that you want.

To see more styles, point to a style, and then click
 .
.To immediately undo a style that you applied, press
 + Z .
+ Z .
Add a chart title
-
Click the chart, and then click the Chart Layout tab.
-
Under Labels, click Chart Title, and then click the one that you want.

-
Select the text in the Chart Title box, and then type a chart title.
No comments:
Post a Comment