These instructions are specific to Microsoft Project 2016, 2013, and 2010.
Review resource workloads by using the Resource Usage view
-
In the Task or Resource tab, click Resource Usage in the View dropdown menu.
-
Review the resource names and their assigned tasks in the table portion of the Resource Usage view.
-
Review the timescale portion of the view to see how work is allocated over the selected time period.
In many resource views, including the Resource Usage view, overallocated resources are shown in red. An overallocation occurs whenever a resource's maximum units have been exceeded for any period of time. In resource sheets, the indicator field for overallocated resources also includes the Resource leveling indicator, which indicates that the resource be leveled. Check for the indicator, and review the task assignments to assess whether the overallocation is acceptable.
For example, suppose that two tasks have a duration of four hours, and that they both start and finish at the same times. If you assign both tasks to Bob, he is technically overallocated, because during that four-hour span of the two tasks, Bob is working at 200 percent. However, if leveling is set to a day-by-day basis, Bob does not need to be leveled, because during the whole day he doesn't exceed his total eight-hour capacity to work.
Note: Along with resource assignments for tasks in the currently opened project, the Resource Usage view also displays summary resource assignments. Summary resource assignments indicate the total amount of work a resource is assigned to in all other projects. Summary resource assignments are only shown if you are connected to Microsoft Project Server and if you have an enterprise project open. If you don't want summary assignment rows to affect the totals shown in the Resource Usage view, you can select the summary assignment rows and then press DELETE.
You can also display and modify the Resource Usage view to see all of the resource assignments and their percentages of work allocation in a timesheet. This view shows all assignments by resource, and shows how fully these resources are allocated to assigned tasks over time.
-
In the Task or Resource tab, click Resource Usage in the View dropdown menu.
-
In the Format tab, click Add Details.
-
In the Available fields list, click Percent Allocation, and then click Show.
-
Review the timescale portion of the view. In the % Alloc. row that you've just added, you can see the percentage of the resource's total available working time that is allocated to assignments during the selected time period. In addition, the timescale portion of the view shows both the resource's overallocated work and its allocation percentage in red, making it possible for you to pinpoint exactly when the resource becomes overallocated.
Tip: You can zoom in on the time period shown in the timescale (for example, you can change the view from days to hours) by clicking Zoom In (+) located at the bottom right corner of the window. Likewise, you can zoom out from the time period (for example, you can change the view from days to weeks) by clicking Zoom Out (-).
Review availability for enterprise resources by using Project Online
To find overallocated or underallocated resources either within a project or across projects, you can access Project Online and view a graph and table of resource availability.
-
From the Project Online Project Center, click Resources in the left side menu.
-
Select the resource or resources whose availability information you want to view by selecting the check box next to their name and then in the Resources tab, click Capacity Planning in the Navigate section.
To select adjacent resources in the list, hold down SHIFT while you click the first and then the last resource. To select nonadjacent resources, hold down CTRL while you click each resource.
-
In the Views section of the Availability tab, select a resource view.
-
To display assignment work grouped first by resources and then by the projects that the resource appears in, select Work by Resource.
-
To display assignment work grouped by the projects that the resource appears in, select Resource Utilization by Project.
-
To display the amount of time that the resource has available to work during a specified time period, select Remaining Availability.
-
To display the amount of work that the resource is assigned to do, select Resource Utilization.
-
If you selected multiple resources on the previous page, you can click in the legend on the chart to select the resources that you want to view in the graph.
The Details table below the graph shows a timescale that displays how much work the resource is assigned to during the specified time period.
Tip: To see a different date range in the chart, click Set Date Ranges in the Availability tab, and then select new dates in the Set Date Range boxes.
Use a graph to view individual workloads
The Resource Graph view displays a bar chart view of an individual resource's workload and availability. This view allows you to quickly discover whether the selected resource is overallocated or underallocated for a specific period of time. You can also see the percentage of units allocated for assignments, along with the resource's maximum units availability.
-
In the Resource tab, select the Resource Graph view in the View section.
-
Review the name of the first resource in the Resource Graph view by scrolling left or right in the left window.
If the resource name is listed in red, then the resource is overallocated. Resources listed in black are allocated either exactly at or under their full capacity.
-
Review the bar chart to see the level of overallocation or underallocation.
Blue bars (by default) indicate the amount of allocated work that is at or below the resource's maximum unit and working time availability for that time period. Red bars (by default) indicate that the resource is overallocated because the resource has exceeded their maximum unit and working time availability for a given time period.
-
Review the highest allocation percentages that occur in the time period shown — that is, the peak units for the resource in the time period.
Peak units are listed at the bottom of the graph.
-
To view the bar graph for the next resource, either press PAGE DOWN or use the scroll bar or the arrow keys.
Top of Page
View a list of resources who are overallocated
You can see a list of only those resources that are overallocated by displaying the Resource Sheet view or the Resource Usage view, and then filtering for overallocated resources.
-
In the View section, click Resource Sheet or Resource Usage from the dropdown.
-
In the View tab, click the Filter dropdown menu in the Data section, and then click Overallocated Resources.
-
To see the full list of resources again, click the Filter dropdown menu and then click No Filter.
Note: Even without filtering for overallocated resources, you can easily see which resources are overallocated, because their names are shown in red in any resource view. Also, in the Resource Sheet and Resource Usage views, the indicator field will suggest that overallocated resources be leveled.
Task views can also be used to display overallocations, though they don't show overallocations in red the way that resource views do. If you are working in a task view, you can step through each task that has resource overallocations, though a task view won't show you which resources (or how many) are overallocated.
While in any task view, such as the Gantt Chart or Network Diagram, in the Resource tab, click Next Overallocation in the Level section.
Group resources who are overallocated
In the Resource Sheet or Resource Usage view, you can group resources who are overallocated. You can also group resources by their peak units, which indicate their maximum percentage allocations on assignments during the project. Reviewing overallocated resources by the extent of their overallocations can help you to focus on the most extensively overallocated resources first.
-
In the View section, click Resource Sheet or Resource Usage.
-
In the View tab, click on the Group by dropdown menu and then click New Group By.
-
In the Field Name box, select Overallocated.
-
In the Order box, select Ascending or Descending.
If you click Ascending, the group of resources that are not overallocated appears first and the group of overallocated resources appears second.
-
To create a nested grouping of peak units, click the Then by box, and then click Peak.
-
Supply a name for the grouping and then click Apply.
The view is grouped according to your specifications. Any resource that has any assignment exceeding 100 percent of peak units at any time during the project is grouped under Overallocated: Yes. If you specify a nested grouping of peak units, you might have additional groupings under headings such as Peak: 200%, Peak: 300%, and so on.
-
To see resources listed in their original order in the Group by box, click [No Group].
Find resources who have available time
If you have resources who are overallocated, you might want to identify resources in the project who have available time, so that you can distribute the workload more evenly. This capacity is also useful if there are additional unassigned tasks and you want to find out who is available to take on more work.
Resource availability is calculated using the following formula:
Resource Availability = Resource Capacity - (Summary Resource Assignment + Calendar Exceptions)
The Summary Resource Assignment is the sum of all work done by the resource, and Calendar Exceptions are any exceptions on the resource's base calendar.
To find resources who can work additional hours on a job, you can display and modify the Resource Usage view to see the amount of time (hours, days, or weeks) that a resource has available for additional assignments. You can also use this view to redistribute work from overallocated resources to underallocated ones.
-
In the View section, click Resource Usage.
-
In the Format tab, in the Details section, check the Remaining Availability box.
-
In the Rem. Avail. (remaining availability) row, review the amount of work that represents remaining availability, or underallocation, for each time period.
You can also display and modify the Resource Graph view to view a bar chart of an individual resource's workload, which can help you to discover who can work additional hours on a task. You can review information about one underallocated resource at a time in the Resource Graph view. You can see the amount of available work by time period.
-
In the View section, click Resource Graph.
-
In the Format tab, click the Graph dropdown menu, and then select Work Availability.
-
For the selected resource, review the amount of available work shown in the bar chart. Scroll through the timescale to see underallocations during varying periods of time.
-
Review the amount of available time for the selected resource at the bottom of the graph.
-
To move to the next resource that has available time, press PAGE DOWN or use the scroll bar or the arrow keys in the left pane.
Top of Page
These instructions are specific to Microsoft Project 2007.
Review resource workloads by using the Resource Usage view
-
On the View menu, click Resource Usage.
-
Review the resource names and their assigned tasks in the table portion of the Resource Usage view.
-
Review the timescale portion of the view to see how work is allocated over the selected time period.
In many resource views, including the Resource Usage view, overallocated resources are shown in red. An overallocation occurs whenever a resource's maximum units have been exceeded for any period of time. In resource sheets, the indicator field for overallocated resources also includes the Resource leveling indicator  , which indicates that the resource be leveled. Check for the indicator, and review the task assignments to assess whether the overallocation is acceptable.
, which indicates that the resource be leveled. Check for the indicator, and review the task assignments to assess whether the overallocation is acceptable.
For example, suppose that two tasks have a duration of four hours, and that they both start and finish at the same times. If you assign both tasks to Bob, he is technically overallocated, because during that four-hour span of the two tasks, Bob is working at 200 percent. However, if leveling is set to a day-by-day basis, Bob does not need to be leveled, because during the whole day he doesn't exceed his total eight-hour capacity to work.
Note: Along with resource assignments for tasks in the currently opened project, the Resource Usage view also displays summary resource assignments. Summary resource assignments indicate the total amount of work a resource is assigned to in all other projects. Summary resource assignments are only shown if you are connected to Microsoft Office Project Server and if you have an enterprise project open. If you don't want summary assignment rows to affect the totals shown in the Resource Usage view, you can select the summary assignment rows and then press DELETE.
You can also display and modify the Resource Usage view to see all of the resource assignments and their percentages of work allocation in a timesheet. This view shows all assignments by resource, and shows how fully these resources are allocated to assigned tasks over time.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Usage.
-
On the Format menu, click Detail Styles.
-
In the Available fields list, click Percent Allocation, and then click Show.
-
Review the timescale portion of the view. In the % Alloc. row that you've just added, you can see the percentage of the resource's total available working time that is allocated to assignments during the selected time period. In addition, the timescale portion of the view shows both the resource's overallocated work and its allocation percentage in red, making it possible for you to pinpoint exactly when the resource becomes overallocated.
Tip: You can zoom in on the time period shown in the timescale (for example, you can change the view from days to hours) by clicking Zoom In  . Likewise, you can zoom out from the time period (for example, you can change the view from days to weeks) by clicking Zoom Out
. Likewise, you can zoom out from the time period (for example, you can change the view from days to weeks) by clicking Zoom Out  .
.
Review availability for enterprise resources by using Project Online
To find overallocated or underallocated resources either within a project or across projects, you can access Project Online and view a graph and table of resource availability.
-
From the Project Online Project Center, click Resources in the left side menu.
-
Select the resource or resources whose availability information you want to view by selecting the check box next to their name and then in the Resources tab, click Capacity Planning in the Navigate section.
To select adjacent resources in the list, hold down SHIFT while you click the first and then the last resource. To select nonadjacent resources, hold down CTRL while you click each resource.
-
In the Views section of the Availability tab, select a resource view.
-
To display assignment work grouped first by resources and then by the projects that the resource appears in, select Work by Resource.
-
To display assignment work grouped by the projects that the resource appears in, select Resource Utilization by Project.
-
To display the amount of time that the resource has available to work during a specified time period, select Remaining Availability.
-
To display the amount of work that the resource is assigned to do, select Resource Utilization.
-
If you selected multiple resources on the previous page, you can click in the legend on the chart to select the resources that you want to view in the graph.
The Details table below the graph shows a timescale that displays how much work the resource is assigned to during the specified time period.
Tip: To see a different date range in the chart, click Set Date Ranges in the Availability tab, and then select new dates in the Set Date Range boxes.
Use a graph to view individual workloads
The Resource Graph view displays a bar chart view of an individual resource's workload and availability. This view allows you to quickly discover whether the selected resource is overallocated or underallocated for a specific period of time. You can also see the percentage of units allocated for assignments, along with the resource's maximum units availability.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Graph.
-
Review the name of the first resource in the Resource Graph view.
If the resource name is listed in red, then the resource is overallocated. Resources listed in black are allocated either exactly at or under their full capacity.
-
Review the bar chart to see the level of overallocation or underallocation.
Blue bars (by default) indicate the amount of allocated work that is at or below the resource's maximum unit and working time availability for that time period. Red bars (by default) indicate that the resource is overallocated because the resource has exceeded their maximum unit and working time availability for a given time period.
-
Review the highest allocation percentages that occur in the time period shown — that is, the peak units for the resource in the time period.
Peak units are listed at the bottom of the graph.
-
To view the bar graph for the next resource, either press PAGE DOWN or use the scroll bar or the arrow keys.
Top of Page
View a list of resources who are overallocated
You can see a list of only those resources that are overallocated by displaying the Resource Sheet view or the Resource Usage view, and then filtering for overallocated resources.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Sheet or Resource Usage.
-
In the view, click Filter, and then click Overallocated Resources.
-
To see the full list of resources again, click Filter, and then click All Resources.
Note: Even without filtering for overallocated resources, you can easily see which resources are overallocated, because their names are shown in red in any resource view. Also, in the Resource Sheet and Resource Usage views, an indicator  appears in the indicator field, indicating that overallocated resources be leveled.
appears in the indicator field, indicating that overallocated resources be leveled.
Task views can also be used to display overallocations, though they don't show overallocations in red the way that resource views do. If you are working in a task view, you can step through each task that has resource overallocations, though a task view won't show you which resources (or how many) are overallocated.
-
While in any task view, such as the Gantt Chart or Network Diagram, on the View menu, point to Toolbars, and then click Resource Management.
-
On the Resource Management toolbar, click Go To Next Overallocation  .
.
Group resources who are overallocated
In the Resource Sheet or Resource Usage view, you can group resources who are overallocated. You can also group resources by their peak units, which indicate their maximum percentage allocations on assignments during the project. Reviewing overallocated resources by the extent of their overallocations can help you to focus on the most extensively overallocated resources first.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Sheet or Resource Usage.
-
On the Project menu, point to Group by, and then click Customize Group By.
-
In the Field Name box, click Overallocated.
-
In the Order box, click Ascending or Descending.
If you click Ascending, the group of resources that are not overallocated appears first and the group of overallocated resources appears second.
-
To create a nested grouping of peak units, click the Then by box, and then click Peak Units.
-
To save this grouping, click Save. Supply a name for the grouping, and if you want the grouping to show in the Group by menu, select the Show in menu check box. Click OK to close the Save Group dialog box.
The view is grouped according to your specifications. Any resource that has any assignment exceeding 100 percent of peak units at any time during the project is grouped under Overallocated: Yes. If you specify a nested grouping of peak units, you might have additional groupings under headings such as Peak: 200%, Peak: 300%, and so on.
-
To see resources listed in their original order in the Group by box, click No Group.
Find resources who have available time
If you have resources who are overallocated, you might want to identify resources in the project who have available time, so that you can distribute the workload more evenly. This capacity is also useful if there are additional unassigned tasks and you want to find out who is available to take on more work.
Resource availability is calculated using the following formula:
Resource Availability = Resource Capacity - (Summary Resource Assignment + Calendar Exceptions)
The Summary Resource Assignment is the sum of all work done by the resource, and Calendar Exceptions are any exceptions on the resource's base calendar.
To find resources who can work additional hours on a job, you can display and modify the Resource Usage view to see the amount of time (hours, days, or weeks) that a resource has available for additional assignments. You can also use this view to redistribute work from overallocated resources to underallocated ones.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Usage.
-
On the Format menu, point to Details, and then click Remaining Availability.
-
In the Rem. Avail. (remaining availability) row, review the amount of work that represents remaining availability, or underallocation, for each time period.
You can also display and modify the Resource Graph view to view a bar chart of an individual resource's workload, which can help you to discover who can work additional hours on a task. You can review information about one underallocated resource at a time in the Resource Graph view. You can see the amount of available work by time period.
-
On the View menu, click Resource Graph.
-
On the Format menu, point to Details, and then click Work Availability.
-
For the selected resource, review the amount of available work shown in the bar chart. Scroll through the timescale to see underallocations during varying periods of time.
-
Review the amount of available time for the selected resource at the bottom of the graph.
-
To move to the next resource that has available time, press PAGE DOWN or use the scroll bar or the arrow keys.
Top of Page

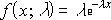
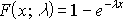
 (Home tab, Font group), and To remove the fill color, click No Fill.
(Home tab, Font group), and To remove the fill color, click No Fill. 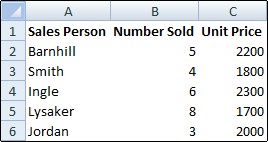










 , which indicates that the resource be leveled. Check for the indicator, and review the task assignments to assess whether the overallocation is acceptable.
, which indicates that the resource be leveled. Check for the indicator, and review the task assignments to assess whether the overallocation is acceptable. . Likewise, you can zoom out from the time period (for example, you can change the view from days to weeks) by clicking Zoom Out
. Likewise, you can zoom out from the time period (for example, you can change the view from days to weeks) by clicking Zoom Out  .
. .
.