Create a 3-D reference to the same cell range on multiple worksheets
A reference that refers to the same cell or range on multiple sheets is called a 3-D reference. A 3-D reference is a useful and convenient way to reference several worksheets that follow the same pattern and contain the same type of data, such as when you consolidate budget data from different departments in your organization.
What do you want to do?
Learn about a 3-D reference
You can use a 3-D reference to add up budget allocations between three departments, Sales, HR, and Marketing, each on a different worksheet, by using the following 3-D reference:
=SUM(Sales:Marketing!B3)
You can even add another worksheet, and then move it into the range that your formula refers to. For example, to add a reference to cell B3 in the Facilities worksheet, move the Facilities worksheet between the Sales and HR worksheets as shown in the following example.
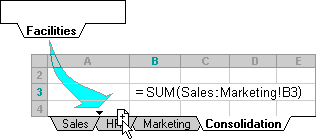
Because your formula contains a 3-D reference to a range of worksheet names, Sales:Marketing!B3, all worksheets in the range are included in the new calculation.
Learn how 3-D references change when you move, copy, insert, or delete worksheets
The following examples explain what happens when you insert, copy, delete, or move worksheets that are included in a 3-D reference. The examples use the formula =SUM(Sheet2:Sheet6!A2:A5) to add cells A2 through A5 on worksheets 2 through 6.
Insert or copy If you insert or copy worksheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6 (the endpoints in this example), then Excel includes all values in cells A2 through A5 from the added worksheets in the calculations.
Delete If you delete worksheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6, then Excel removes their values from the calculation.
Move If you move worksheets from between Sheet2 and Sheet6 to a location outside of the referenced worksheet range, then Excel removes their values from the calculation.
Move an endpoint If you move Sheet2 or Sheet6 to another location in the same workbook, then Excel adjusts the calculation to include the new worksheets between them unless you reverse the order of the endpoints in the workbook. If you reverse the end points, the 3-D reference changes the endpoint worksheet. For example, say that you have a reference to Sheet2:Sheet6: If you move Sheet2 after Sheet6 in the workbook, then the formula will point to Sheet3:Sheet6. If you move Sheet6 in front of Sheet2, the formula will adjust to point to Sheet2:Sheet5.
Delete an endpoint If you delete Sheet2 or Sheet6, then Excel removes the values on that worksheet from the calculation.
Create a 3-D reference
-
Click the cell where you want to enter the function.
-
Type = (equal sign), enter the name of the function, and then type an opening parenthesis.
You can use the following functions in a 3-D reference:
| Function | Description |
| Calculates average (arithmetic mean) of numbers. | |
| Calculates average (arithmetic mean) of numbers; includes text and logicals. | |
| Counts cells that contain numbers. | |
| Counts cells that are not empty. | |
| Returns the harmonic mean of a data set of positive numbers: the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of reciprocals. | |
| Returns the kurtosis of a data set. | |
| Returns the k-th largest value in a data set. For example, the fifth largest number. | |
| Finds largest value in a set of values. | |
| Finds largest value in a set of values; includes text and logicals. | |
| Returns the median, or the number in the middle of the set of given numbers. | |
| Finds smallest value in a set of values. | |
| Finds smallest value in a set of values; includes text and logicals. | |
| PERCENTILE | Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1. Provided for compatibility with earlier versions of Excel. |
| Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive. | |
| Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, inclusive. | |
| PERCENTRANK | Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1) of the data set. Provided for compatibility with earlier versions of Excel. |
| Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set. | |
| Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, inclusive) of the data set. | |
| QUARTILE | Returns the quartile of a data set, based on percentile values from 0..1. Provided for compatibility with earlier versions of Excel. |
| Returns the quartile of a data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive. | |
| Returns the quartile of a data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, inclusive. | |
| Multiplies numbers. | |
| RANK | Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers: its size relative to other values in the list. Provided for compatibility with earlier versions of Excel. |
| Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers: its size relative to other values in the list. | |
| Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers: its size relative to other values in the list. | |
| Returns the skewness of a distribution. | |
| Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set. | |
| Calculates standard deviation based on a sample. | |
| Calculates standard deviation of an entire population. | |
| Calculates standard deviation based on a sample; includes text and logicals. | |
| Calculates standard deviation of an entire population; includes text and logicals. | |
| Returns the mean of the interior of a data set. | |
| Adds numbers. | |
| Estimates variance based on a sample. | |
| Calculates variance for an entire population. | |
| Estimates variance based on a sample; includes text and logicals. | |
| Calculates variance for an entire population; includes text and logicals. |
-
Click the tab for the first worksheet that you want to reference.
-
Hold down SHIFT and click the tab for the last worksheet that you want to reference.
-
Select the cell or range of cells that you want to reference.
-
Complete the formula, and then press ENTER.
Create a name for a 3-D reference
-
On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click Define Name.
-
In the New Name dialog box, in the Name box, type the name you want to use for your reference. Names can be up to 255 characters in length.
-
In the Refers to box, select the equal sign (=) and the reference, then press BACKSPACE.
-
Click the tab for the first worksheet to be referenced.
-
Hold down SHIFT and click the tab for the last worksheet to be referenced.
-
Select the cell or range of cells to be referenced.
No comments:
Post a Comment