How does versioning work in a SharePoint list or library
When versioning is enabled in your SharePoint list or library, you can store, track, and restore items in a list and files in a library whenever they change. Versioning, combined with other settings, such as checkout, gives you a lot of control of the content that is posted on your site and can provide real value if you ever have a need to look at or restore an old version of an item or file.
Note: Versioning is on by default in SharePoint libraries, and off by default in SharePoint lists. For more info on setting up versioning, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
Updated January 19, 2017 thanks to customer feedback.
Versioning overview
Anyone with permission to manage lists can turn versioning on or off for a library. Versioning is available for list items in all default list types—including calendars, issue tracking lists, and custom lists. It is also available for all file types that can be stored in libraries, including Web Part pages. For more info on setting up and using versioning, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
Note: If you are an Office 365 customer, versioning is now turned on by default when you create new OneDrive for Business libraries, and it will automatically save the last ten versions of a document. This will help you prevent losing important documents or data. If you have existing libraries on your OneDrive for Business site or on your team site that do not have versioning enabled, you can turn versioning on for them at any time.
You can use versioning to:
-
Track history of a version When versioning is enabled, you can see when an item or file was changed and who changed it. You can also see when properties (information about the file) were changed. For example, if someone changes the due date of a list item, that information appears in the version history. You can also see the comments people make when they check files into libraries.
-
Restore a previous version If you made a mistake in a current version, if the current version is corrupt, or if you simply like a previous version better, you can replace the current version with a previous one. The restored version becomes the new current version.
-
View a previous version You can view a previous version without overwriting your current version. If you are viewing version history within a Microsoft Office document, such as a Word or Excel file, you can compare the two versions to determine what the differences are.
When versions are created
When versioning is enabled, versions are created in the following situations:
-
When a list item or file is first created or when a file is uploaded.
Note: If file checkout is required, you must check the file in to create its first version.
-
When a file is uploaded that has the same name as an existing file and the Add as a new version to existing files check box is selected.
-
When the properties of a list item or file are changed.
-
When a file is opened, edited, and saved. A version is created when you first click Save. It retains the new version number for the duration of the current editing session, even though you might save it several times. When you close it and then reopen it for another editing session, another version is created.
-
During co-authoring of a document, when a different user begins working on the document or when a user clicks save to upload changes to the library. The default period for creating new versions during co-authoring is 30 minutes. This is configurable by an administrator per web application in SharePoint on-premises. This setting is not configurable in SharePoint Online. To change the time for on-premises versions of SharePoint, see Configure the co-authoring versioning period in SharePoint.
There can be up to three current versions of a file at any given time: the checked-out version, the latest minor or draft version, and the latest published or major version. All other versions are considered historical versions. Some current versions are only visible to users who have permissions to view them.
Major and minor versions
Some organizations track both major and minor versions of files in their libraries. Others only track the major versions. Major versions are identified by whole numbers, such as 5.0; minor versions are identified by decimal numbers, such as 5.1.
Most organizations use minor versions when files are under development, and major versions when certain milestones are reached or when the files are ready for review by a wide audience. In many organizations, draft security is set to allow only the owner of a file and people who have permissions to approve files. That means that minor versions cannot be seen by anyone else until a major version is published.
Major versions are available for lists, but minor versions are not available. Each version of a list item is numbered with a whole number. If your organization requires approval of items in a list, the items remain in Pending status until they are approved by someone who has permissions to approve them. While in Pending status they are numbered with decimal numbers and are referred to as drafts.
For more on enabling and setting up versioning, including major and minor versions, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
Version numbering
Version numbers are automatically added each time you create a new version. In a list or library that has major versioning enabled, the versions have whole numbers, such as 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and so on. In libraries, your administrator might enable versioning for both major and minor versions. When minor versions are being tracked, they have decimal numbers such as 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and so on. When one of those versions is published as a major version, its number becomes 2.0. Subsequent minor versions are numbered 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, and so on.
When you discard a checkout, the version number does not change. If the most recent version was version 3.0, it remains at 3.0 after you discard the checkout.
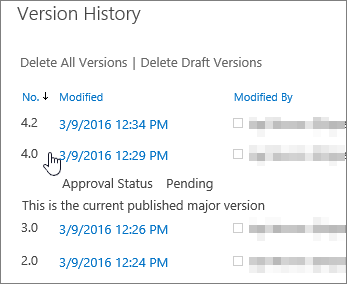
When you delete a version, the version goes to the Recycle Bin and its number goes with it. The Version History will show the remaining version numbers. The other version numbers do not change. For example, if you have a document that has minor versions 4.1 and 4.2, and you decide to delete version 4.1, the resulting version history shows only versions 4.0 and 4.2. The following picture shows this.
For more on enabling and setting up versioning, including major and minor versions, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
Is there any limit to the number of available versions?
Some organizations allow unlimited versions of files and others apply limitations. You might discover, after checking in the latest version of a file, that an old version is missing. If your most recent version is 26.0 and you notice that there is no longer a version 1.0, it means that the administrator configured the library to allow only 25 major versions of a file. The addition of the 26th version causes the first version to be deleted. Only versions 2.0 through 26.0 remain. Similarly, if a 27th version is added, only versions 3.0 through 27.0 remain.
The administrator may also decide to limit the number of minor versions to just those for a set number of the most recent versions. For example, if 25 major versions are allowed, the administrator might decide to retain minor drafts for only the most recent five major versions. The default number of minor versions between major versions is 512. If you attempt to save another minor version, you will see an error message that tells you that you must first publish the document. Your site administrator can change the default to allow fewer minor versions.
If a list or library limits the number of major versions, the earliest versions are deleted when the limit is reached. For example, if only 20 versions are retained, and your team creates 25 versions, only versions 6 through 25 are kept. If another version is created, only versions 7 through 26 are kept. If your list or library limits versions, you should make sure that contributors are aware that earlier versions will be deleted when the version limit is reached.
In a library that limits the number of major versions that it keeps minor versions for, the minor versions are deleted for the previous major versions when the version limit is reached. For example, if you keep drafts for only 10 major versions, and your team creates 15 major versions, only the major versions will be kept for the earliest versions. The minor versions that are associated with the five earliest major versions — such as 1.2 or 2.3 — are deleted, but the major versions — 1, 2, and so on — are kept, unless your library also limits major versions.
Limiting the number of versions is generally a good practice. It means you can conserve space on the server and reduce clutter for users. But, if your organization is required to save all versions for legal or other reasons, don't apply any limits.
=-0
Important: If your organization limits the number of versions that it stores, the oldest versions are permanently deleted when the limit is reached. They are not sent to the Recycle Bin.
For more on enabling and setting up versioning, including limits, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
Determining who can see draft items
You can configure who can view drafts of list items and files. Drafts are created in two situations:
-
When a minor version of a file is created or updated in a library that tracks major and minor versions.
-
When a list item or file is created or updated but not yet approved in a list or library in which content approval is required.
When you track major and minor versions, you can specify whether people must have permission to edit files before they can view and read a minor version. When this setting is applied, people who have permission to edit the file can work on the file, but those who have permission only to read the file cannot see the minor version. For example, you may not want everyone who has access to your library to see comments or revisions while a file is being edited. If major and minor versions are being tracked and no one has published a major version yet, the file is not visible for people who do not have permission to see draft items.
When content approval is required, you can specify if files that are pending approval can be viewed by people with permission to read, people with permission to edit, or only the author and people with permission to approve items. If both major and minor versions are being tracked, the author must publish a major version before the file can be submitted for approval. When content approval is required, people who have permission to read content but do not have permission to see draft items will see the last approved or major version of the file.
Control how many versions are stored
You can limit how many versions of list items or files are saved in a list or library, which can help to preserve server space. If your team creates a large number of versions, limiting the number of versions may help your team to better manage and locate previous versions. For example, if your team keeps many versions over several months or year.
s, it may be difficult for members to browse through the version history to find the versions that they need. If your team needs to view or retain any of its previous versions, either do not limit the number of versions to keep or set the number of versions that you keep to a high number.
If your library tracks major and minor versions, you can choose how many major versions of files to keep, and how many the minor versions for each major version to keep. By default, each major version can have up to 511 drafts (minor versions).
Depending on the way your team works, your team may be more likely to need its most recent minor versions, such as a version that was edited recently. Over time, your team may be less likely to need an older minor version. Usually, a major version represents a milestone, such as a file submitted for review or publication, whereas a minor version is a work in progress that isn't ready for all site participants to read.
If a list or library limits the number of major versions, the earliest versions are deleted when the limit is reached. For example, if only 20 versions are retained, and your team creates 25 versions, only versions 6 through 25 are kept. If another version is created, only versions 7 through 26 are kept. If your list or library limits versions, you should make sure that contributors are aware that earlier versions will be deleted when the version limit is reached.
In a library that limits the number of major versions that it keeps minor versions for, the minor versions are deleted for the previous major versions when the version limit is reached. For example, if you keep drafts for only 10 major versions, and your team creates 15 major versions, only the major versions will be kept for the earliest versions. The minor versions that are associated with the five earliest major versions — such as 1.2 or 2.3 — are deleted, but the major versions — 1, 2, and so on — are kept, unless your library also limits major versions.
Enabling, configuring, and using versioning in lists and libraries
Versioning is turned on automatically when a library is created, and not when a list is created. Anyone with permission to manage lists can turn on or off versioning. On many sites that is the same person who manages the site, because the lists and libraries inherit permissions from the site. In addition to enabling versioning, the site owner (or another person managing the list or library) decides whether to require content approval, who can view draft items, and if checkout is required. Each of these decisions has an impact on how versioning works. For example, if the person managing a library decides to require check-out, version numbers are only created when a file is checked in. If content approval is required, major version numbers are not applied until files are approved by someone who has permission to do so.
Important: If the people who work in your library are planning to co-author documents, do not configure the library to require check-out. People cannot work as co-authors when the documents that they need are checked out.
To learn how to turn on versioning for a list or library, see Enable and configure versioning for a list or library.
How does versioning work with required content approval?
If versioning is enabled in your library, the person who sets it up determines whether to track both major and minor versions and also determines who can see the minor versions. In most cases, when content approval is required, only the owner of the file, and people who have permission to approve items, can see the minor versions. In other libraries, anyone who can edit files in the library, or anyone who has Read permission to the library, can see all versions. After a version is approved, everyone who has Read permission to the list or library can see the version.
Although lists do not have major and minor versions, any item that is in Pending status is considered a draft. In most cases, only the creator of the item and persons who have Full Control or Design permissions can see drafts. A draft shows up in Pending status for those people, but others only see the most recent Approved version in the version history. If the file is rejected, it stays in Pending status until someone who has the necessary permissions deletes it.
By default, a pending item or file is visible only to its creator and to the people with permission to manage lists, but you can specify if other groups of users can view the item or file. If your library is set up to track both major and minor versions, the person who edits the file must first publish a major version of the file.
For more info on setting up approval for documents, see Require approval of items in a site list or library.
Note: Draft security, in some lists and libraries, is configured to allow all site users to see both Pending and Approved versions.
How does versioning work with file checkout?
When you check out a file from a library that has versioning turned on, a new version is created every time you check it back in. And, if major and minor versions are turned on, you can decide, at check-in, which type of version you are checking in. In libraries where checkout is required, versions are only created upon check-in.
In libraries where checkout is not required, a new version is created the first time you save after opening the file. Each subsequent save overwrites the version that you created with the first save. If you close the application and then reopen the document, the first save will, once again, produce a version. This can cause the number of versions to proliferate very rapidly.
For more info on check in and out, see Check out, check in, or discard changes to files in a library.
Important: If you are co-authoring a document, do not check it out unless you have good reason to prevent others from working on the document.
Requiring check-out (Libraries only)
Requiring check-out can help your team make the most of versioning, because people specifically designate when a version is to be created. A version is created only when someone checks out a file, changes it, and then checks it back in. When check-out is not required, a version is created when someone first saves a file and this version is updated when the person closes it. If that person or someone else then opens and saves the file again, another version is created. Depending on the situation, you might not intend for multiple versions to be created, for example, if you must close a file to attend a meeting before you finish making changes to the file.
When check-out is required, people cannot add files, change files, or change the file properties without first checking out the file. When people check in files, they are prompted to provide comments about the changes that they made, which helps to create a more meaningful version history.
Note: If the library will be storing Microsoft Project (.mpp) files that are synchronized with task lists on your site, the Require check-out box should be cleared.
For more info on requiring checkout, see Set up a library to require check-out of files.
List or library permissions
Lists and libraries have permissions related to versioning and check-out that vary depending on the permission level that is applied to a user or a specific group. Someone who can edit permission levels can configure these permissions differently or can create a new group with customized permission levels.
These permissions enable flexibility in how you manage your library. For example, you may want someone to be able to delete versions of a file without having permission to delete the file itself. The permission to Delete Versions is not the same as the permission to Delete Items, so you can provide a customized level of control.
The following table shows the permissions that are related to versioning and check-out and which default permission levels they apply to.
| Permission | Default permission level |
| View Versions | Full Control, Design, Contribute, and Read |
| Delete Versions | Full Control, Design, and Contribute |
| Override Check-Out | Full Control and Design |
| Approve Items | Full Control and Design |
For more info on permissions, see Understanding permission levels in SharePoint.
Leave us a comment
Was this article helpful? If so, please let us know at the bottom of this page. If it wasn't helpful, let us know what was confusing or missing. Please include your version of SharePoint, OS, and browser. We'll use your feedback to double-check the facts, add info, and update this article.
No comments:
Post a Comment