This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the LOGNORMDIST function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution of x, where ln(x) is normally distributed with parameters mean and standard_dev. Use this function to analyze data that has been logarithmically transformed.
Important: This function has been replaced with one or more new functions that may provide improved accuracy and whose names better reflect their usage. Although this function is still available for backward compatibility, you should consider using the new functions from now on, because this function may not be available in future versions of Excel.
For more information about the new function, see LOGNORM.DIST function.
Syntax
LOGNORMDIST(x,mean,standard_dev)
The LOGNORMDIST function syntax has the following arguments:
-
X Required. The value at which to evaluate the function.
-
Mean Required. The mean of ln(x).
-
Standard_dev Required. The standard deviation of ln(x).
Remarks
-
If any argument is non-numeric, LOGNORMDIST returns the #VALUE! error value.
-
If x ≤ 0 or if Standard_dev ≤ 0, LOGNORMDIST returns the #NUM! error value.
-
The equation for the lognormal cumulative distribution function is:
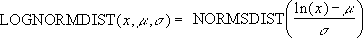
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
| Data | Description | |
| 4 | Value at which to evaluate the function (x) | |
| 3.5 | Mean of ln(x) | |
| 1.2 | Standard deviation of ln(x) | |
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =LOGNORMDIST(A2,A3,A4) | Cumulative lognormal distribution at 4 with the terms above | 0.0390836 |
No comments:
Post a Comment