In Outlook, you have access to editing tools that give you the ability to find and replace simple text or phrases in an email message. And you can extend your search to find words or phrases that contain specific letters or combinations of letters by using wildcards and codes. You also can find and replace formatting—for example, search by font size, style, language, and paragraph marks—or find and replace different noun forms or verb tenses, such as message versus messages and use versus used.
You can quickly search for every occurrence of a specific word or phrase using the Find option.
-
In the email message or items you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Find.
-
In the Find what box, enter the text that you want to search for.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To find each instance of a word or phrase, choose Find Next.
-
To find all instances of a specific word or phrase at one time, choose Find In > Main Document.
-
Tip: To cancel a search in progress, press ESC.
You can automatically replace a word or phrase with another—for example, you can replace Acme with Apex.
Note: The replacement text will use the same capitalization as the text that it replaces. For example, if you search for AKA and replace it with Also known as, the result will be ALSO KNOWN AS.
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Replace.
Note: You can also choose the Replace tab from the Find dialog.
-
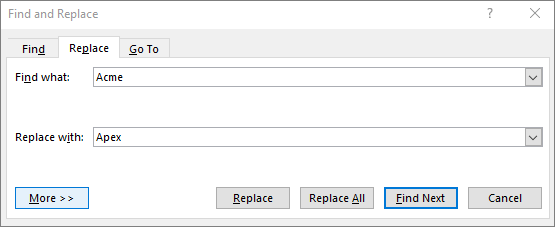
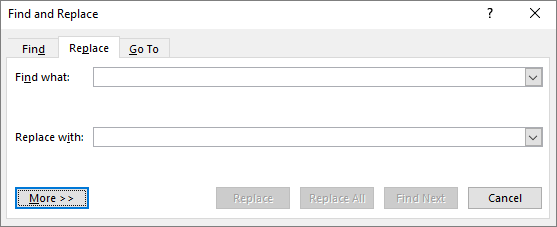
In the Find and Replace dialog box, choose the Replace tab, and in the Find what box, type the text that you want to search for.
-
In the Replace with box, type the replacement text.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To find the next occurrence of the text, choose Find Next.
-
To replace an occurrence of the text, choose Replace and Outlook moves to the next occurrence.
-
To replace all occurrences of the text, choose Replace All.
-
Tip: To cancel a replacement in progress, press ESC.
To help you visually scan a document for every occurrence of a word or phrase, you can search for all occurrences and highlight them on the screen. Although the text is highlighted on the screen, it isn't highlighted when the document is printed.
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Find.
-
In the Find what box, type the text that you want to search for.
-
Choose Reading Highlight > Highlight All.
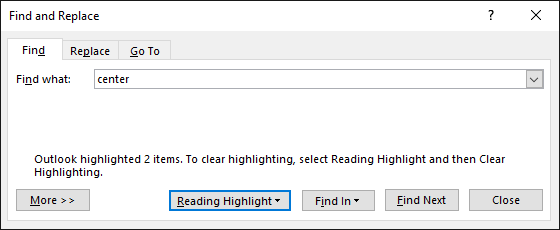
Note: To turn off highlighting on the screen, choose Reading Highlight > Clear Highlighting.
Advanced find and replace
You can search for more than just text. Outlook allows you to search for formatting such as bold or italics, fonts, paragraph marks, spaces, bookmarks, or even languages.
You can search for and replace or remove character formatting. You can search for a specific word or phrase and change the font color, for example, or you can search for specific formatting, such as bold, and change it.
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Replace.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To find text with specific formatting, in the Find what box, type the text to search for.
-
To find formatting only, leave the Find what box blank.
-
-
(Optional) Under Search Options, select a search check box.
-
Choose Format, and then choose the format options that you want to find and replace.
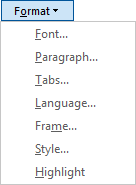
Notes:
-
If you don't see Format, choose More.
-
-
-
In the Replace with box, choose Format, and then choose the replacement format options.
Note: If you also want to replace text you entered in the Find With box, then in the Replace with box, type the replacement text.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To find and replace each instance of the specified formatting, choose Find Next > Replace.
-
To replace all instances of the specified formatting, choose Replace All.
-
You can search for and replace special characters and document elements such as tabs and manual page breaks. For example, you can find all double paragraph marks and replace them with single paragraph marks.
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Find.
-
Choose Special, and then choose an item.
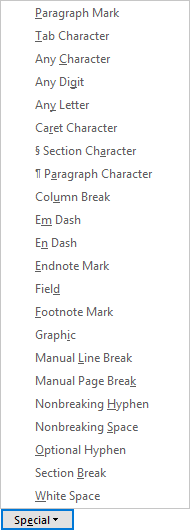
Notes:
-
If you don't see Special, choose More.
-

-
-
To replace the item, choose the Replace tab, and in the Replace with box, enter what you want to use as a replacement.
-
Choose Find Next, Find All, Replace, or Replace All.
Tip: To cancel a search in progress, press ESC.
You can use wildcards to search for text. For example, you can use the asterisk (*) wildcard to search for a string of characters (for example, "s*d" finds "sad" and "started").
Use wildcards to find and replace text
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Find or Replace.
-
Under Search Options, select the Use wildcards check box.
Note: If you don't see Search Options, choose More.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Choose Special, choose a wildcard character, and then in the Find what box, type any additional text. For more information, see the table under "Wildcards for items you want to find and replace," later in this section.
-
In the Find what box, enter a wildcard character directly. For more information, see the table under "Wildcards for items you want to find and replace," later in this section.
Note: If you also want to replace an item you entered in the Find With box, then in the Replace with box, type the replacement text.
-
-
(Optional) If you also want to replace the item you entered in the Find With box, choose the Replace tab, and in the Replace with box, enter what you want to use as a replacement.
-
Choose Find Next, Find All, Replace, or Replace All.
Tip: To cancel a search in progress, press ESC.
Wildcards for items you want to find and replace
-
When you select the Use wildcards check box, Outlook finds only the exact text specified. Notice that the Match case and Find whole words only check boxes are unavailable (dimmed) to indicate that these options are automatically turned on and can't be turned off.
-
When you want to search for a character that's defined as a wildcard, type a backslash (\) before the character. For example, type \? to find a question mark.
-
When you want to group the wildcard characters and text and to indicate the order of evaluation, use parentheses. For example, type <(pre)*(ed)> to find "presorted" and "prevented".
-
When you want to search for an expression and then replace it with the rearranged expression, use the \n wildcard. For example, type (Ashton) (Chris) in the Find what box and \2 \1 in the Replace with box. Outlook will find Ashton Chris and replace it with Chris Ashton.
| To find | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Any single character | ? | s?t finds sat and set |
| Any string of characters | * | s*d finds sad and started |
| The beginning of a word | < | <(inter) finds interesting and intercept, but not splintered |
| The end of a word | > | (in)> finds in and within, but not interesting |
| One of the specified characters | [ ] | w[io]n finds win and won |
| Any single character in this range | [-] | [r-t]ight finds right and sight. Ranges must be in ascending order |
| Any single character except the characters in the range inside the brackets | [!x-z] | t[!a-m]ck finds tock and tuck, but not tack or tick |
| Exactly n occurrences of the previous character or expression | {n} | fe{2}d finds feed but not fed |
| At least n occurrences of the previous character or expression | {n,} | fe{1,}d finds fed and feed |
| From n to m occurrences of the previous character or expression | {n,m} | 10{1,3} finds 10, 100, and 1000 |
| One or more occurrences of the previous character or expression | @ | lo@t finds lot and loot |
Use the following codes to find letters, formatting, fields, or special characters. Note that some codes work only if the Use wildcards option is turned on or turned off.
Codes that work in the Find what box or Replace with box
| To find | Type |
|---|---|
| Paragraph mark ( | ^p (doesn't work in the Find what box when the Use wildcards option is turned on), or ^13 |
| Tab character ( | ^t or ^9 |
| ASCII character | ^nnn, where nnn is the character code. |
| ANSI character | ^0nnn, where 0 is zero and nnn is the character code |
| Em dash ( — ) | ^+ |
| En dash ( – ) | ^= |
| Caret character | ^^ |
| Manual line break ( | ^l or ^11 |
| Column break | ^n or ^14 |
| Page or section break | ^12 (when replacing, inserts a page break) |
| Manual page break | ^m (also finds or replaces section breaks when the Use wildcards option is turned on) |
| Nonbreaking space ( | ^s |
| Nonbreaking hyphen ( | ^~ |
| Optional hyphen ( | ^- |
Code that works only in the Find what box (when Use wildcards is turned on)
| To find | Type |
|---|---|
| Picture or graphic (inline only) | ^g |
Codes that work only in the Find what box (when Use wildcards is turned off)
| To find | Type |
|---|---|
| Any character | ^? |
| Any digit | ^# |
| Any letter | ^$ |
| Unicode character | ^Unnnn where nnnn is the character code |
| Picture or graphic (inline only) | ^1 |
| Footnote mark | ^f or ^2 |
| Endnote mark | ^e |
| Field | ^d |
| Opening field brace (when field codes are visible) | ^19 |
| Closing field brace (when field codes are visible) | ^21 |
| Comment | ^a or ^5 |
| Section break | ^b |
| Em space (Unicode) | ^u8195 |
| En space (Unicode) | ^u8194 |
| White space | ^w (any combination of regular and nonbreaking spaces, and tab characters) |
Codes that work only in the Replace with box
| To find | Type |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows Clipboard contents | ^c |
| Contents of the Find what box | ^& |
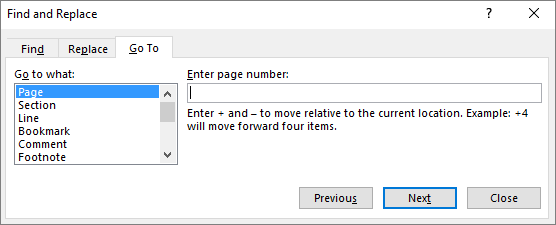
You can go to specific items such as a page, a bookmark, or line in an email message.
-
In the email message or item you're creating, on the Format Text tab, in the Editing group, choose Find > Go To.
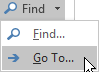
-
In the Go to what list, choose an item.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To go to a specific item, in the Enter box, type the appropriate identifying information for the item and then choose Go To.
-
To go to the next or previous item of the specified type, leave the Enter box blank, and then choose Next or Previous.
-
 )
)  )
) )
) )
) )
) )
)
No comments:
Post a Comment