Create or delete a Number or Currency field
You add a Number field to a table when you need to store numeric data, such as sales figures. This article explains how to use Microsoft Office Access 2007 to add and delete a Number field in new and existing database tables.
In this article
Understand Number fields
If you are new to Office Access 2007, remember that the data in a database is stored in one or more tables. You can view the information in a datasheet — a grid that resembles a Microsoft Office Excel 2007 worksheet — or in a data-entry form or a report, but the database stores all data in one or more tables. In turn, each table consists of a set of fields (columns), and each field is set to accept one specific type of data. For example, you set a field to the Date/Time data type when you need to store dates and times, and you set a field to the Number data type when you need to store numbers for use in mathematical calculations.
Number field specifications
You use a Number field for all mathematical calculations except those involving money and those that require a high degree of accuracy, or for figures that you don't want to round up or down (you use a Currency field to prevent rounding). The size of the values that you store in a Number field depends on how you set the Field Size property. For example, you can set Number fields to contain 1-byte, 2-byte, 4-byte, 8-byte, or 16-byte values, plus Replication IDs (globally unique identifier values, or GUIDs) and decimal values.
You set the field size by opening the table in Design view and changing the Field Size property. For information about changing the properties of a Number field, see the section Set or change field properties. For information about the field properties, see the section Number field property reference.
The following table lists the values that each Field Size setting can contain and explains when to use each size setting.
| Field Size setting | Description |
| Byte | A 1-byte integer containing values from 0 to 255. |
| Integer | A 2-byte integer containing values from -32,768 to +32,767. |
| Long Integer | A 4-byte integer containing values from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. |
| Single | A 4-byte integer containing values from -3.4 x 1038 to +3.4 x 1038 and up to 7 significant digits. |
| Double | An 8-byte floating point number containing values from -1.797 x 10308 to +1.797 x 10308 and up to 15 significant digits. |
| Replication ID | A 16-byte globally unique identifier (GUID). Randomly generated GUIDs are long enough that they are not likely to overlap. You use them for a variety of applications, such as tracking goods. |
| Decimal | A 12-byte integer with a defined decimal precision that can contain values from -1028 to +1028. The default precision is 0. The default scale (the number of decimal places displayed) is 18. You can set the scale up to 28. |
In addition to setting field sizes and other field properties, you can apply custom and predefined display formats and input masks to your number data.
For more information about formatting Number data, see the article Format a number or currency field. For information about input masks, see the article Create an input mask to enter field or control values in a specific format.
Methods for creating a Number field
Office Access 2007 provides several ways to add a Number field to a new or existing table:
-
Datasheet view You can add a Number field to a new or existing table in Datasheet view by adding a new field and then typing a number into a blank row in the field, or by pasting a number into a blank row. You can also select the Number data type from a drop-down list and set properties such as Is Required, which forces users to enter a date in the field, and Unique, which forces users to enter a non-duplicate value in the field.
-
Design view You use Design view to add a Number field and set properties for the field that you cannot set in Datasheet view. Those properties include input masks and a default value for the field. For more information about the properties, see the section Number field property reference.
Add a Number field in Datasheet view
The steps in this section explain how to add a Number field to an existing table and a new table in Datasheet view. If you are new to Access, a datasheet is a grid that is similar in appearance to an Office Excel 2007 worksheet.
Add a Number field to an existing table
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
In the Navigation Pane, double-click the table that you want to change.
Access opens the table in Datasheet view.
-
If necessary, scroll horizontally to the first blank field. By default, Access displays Add New Field in the header row of all new fields, like so:

-
Double-click the header row, and then type a name for the new field.
-
Select the first blank row under the header, and then type or paste a block of numbers. Access infers the Number data type for the field when you enter numbers or paste numbers.
-or-
On the Datasheet tab, in the Data Type & Formatting group, from the Data Type list, select Number, and then from the Format list, select the number format you want.
If you type or paste data into the field, Access sets the Field Size setting based on the size of the number that you enter.
-
Save your changes.
Add a Number field to a new table
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
On the Create tab, in the Tables group, click Table.
Access opens the new table in Datasheet view. This figure illustrates a new table:
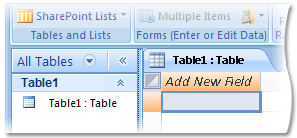
-
Click Save
 , and in the Save As dialog box, enter a name for the new table.
, and in the Save As dialog box, enter a name for the new table. -
Double-click the header row for the first table field (the one labeled Add New Field), and then type a name for the field.
-
Select the first blank row under the header, and then type a block of numbers. Access infers the Number data type for the field when you enter numbers.
In addition, Access sets the Field Size property based on the size of the number that you enter or paste.
Add a Number field in Design view
You use Design view to add a Number field to a new or existing table and then to set or change the field properties that you can't set or change in Datasheet view. For example, you can specify an input mask or a default value. The steps in this section explain how to add a Number field and set properties for the field.
Add a Number field to an existing table
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
In the Navigation Pane, right-click the table that you want to change, and then click Design View
 .
. -
In the Field Name column, select the first blank row, and then type a name for the field.
-
Select the adjacent cell in the Data Type column, and then select Number from the list.
-
Save your changes.
Add a Number field to a new table
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
On the Create tab, in the Tables group, click Table.
-
Click Save, and in the Save As dialog box, enter a name for the new table.
-
Right-click the document tab for the new table and click Design View on the shortcut menu.
-
In the Field Name column, select the first blank row and type a name for the field.
-
Select the adjacent cell in the Data Type column, and then select Number from the list.
-
Save your changes. If you want to set properties for the field, leave the table open in Design view and go to the next steps.
Set or change field properties
-
On the General tab in the lower section of the table designer, under Field Properties, locate the property that you want to change.
-
Select the field next to the property name. Depending on the property, you enter data (such as default text or an input mask), start the Expression Builder by clicking ..., or select an option from a list.
For information about how to use each field property, select the property and then press F1.
Delete a Number field
You can use Datasheet view or Design view to delete a Number field from a table. However, when you delete a Number field that contains data, you lose that data permanently — you cannot undo the deletion. For that reason, you should back up your database before you delete any table fields or other database components.
Delete a Number field in Datasheet view
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
In the Navigation Pane, double-click the table that you want to change.
Access opens the table in Datasheet view.
-
Locate the Number field, right-click the header row (the field name), and then click Delete Column.
Delete a Number field in Design view
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Open.
, and then click Open. -
In the Open dialog box, select and open the database.
-
In the Navigation Pane, right-click the table that you want to change, and then click Design View.
Access opens the table in Design view.
-
Click the row selector (the blank square) next to the Number field, and then press DELETE.
-or-
Right-click the row selector, and then click Delete Rows.
-
Click Yes to confirm the deletion.
Number field property reference
When you use Design view to add a Number field to a table, you can set and change several properties for the field. This table lists and describes the Number field properties and explains the implications of setting or changing them.
| Property | Usage |
| Field Size | Controls the size of the value that you can enter and store in the field. For more information about the Field Size property, see Number field specifications earlier in this article. |
| Format | You enter custom formatting characters to define a display format. Formats defined here appear in datasheets, forms, and reports. For more information about custom formats, see the article Format a number or currency field. |
| Decimal Places | Sets the number of decimal places for the values in the field. Default value: Auto. Other possible values range from 0 to 15. |
| Input Mask | You define an input mask when you need to control how users enter data in the field. For more information about using input masks, see the article Create an input mask to enter field or control values in a specific format. |
| Caption | Specifies the name of your Text field. This property accepts up to 2,048 characters. If you don't specify a caption, Access applies the default field name. |
| Default Value | Specifies the value that automatically appears in a field when you create a new record. |
| Validation Rule | Specifies the requirements for data entered into an entire record, an individual field, or a control. When users enter data that violates the rule, you can use the Validation Text property to specify the resulting error message. Maximum length: 2,048 characters. For more information about creating validation rules, see the article Create a validation rule to validate data in a field. |
| Validation Text | Specifies the text in the error message that appears when users violate a validation rule. Maximum length: 255 characters. For more information about creating validation rules, see the article Create a validation rule to validate data in a field. |
| Required | When this property is set to Yes, you must enter a value in the field or in any controls bound to the field. In addition, the value cannot be null. |
| Indexed | You use an index to speed up queries, sorting, and grouping operations run against large amounts of data. You can also use indexes to prevent users from entering duplicate values. Choices:
|
| Smart Tags | You specify one or more smart tags for the field and any controls bound to the field. Smart tags are components that recognize the types of data in a field and allow you to take action based on that type. For example, in an E-mail Address field, a smart tag can create a new mail message or add the address to a list of contacts. Click Build (...) to see a list of available smart tags. |
| Text Align | Specifies the alignment for data. Choices:
|
No comments:
Post a Comment