An introduction to optimization with the Excel Solver tool
 This article was adapted from Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Data Analysis and Business Modeling by Wayne L. Winston. Visit Microsoft Learning to learn more about this book.
This article was adapted from Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Data Analysis and Business Modeling by Wayne L. Winston. Visit Microsoft Learning to learn more about this book.
This classroom-style book was developed from a series of presentations by Wayne Winston, a well known statistician and business professor who specializes in creative, practical applications of Excel. So be prepared — you may need to put your thinking cap on.
In this article
Overview
-
How can a large drug company determine the monthly product mix at their Indianapolis plant that maximizes corporate profitability?
-
If Microsoft produces Xbox consoles at three different locations, how can they minimize the cost of meeting demand for them?
-
What price for Xbox consoles and games will maximize Microsoft's profit from Xbox sales?
-
Microsoft would like to undertake 20 strategic initiatives that will tie up money and skilled programmers for the next five years. They do not have enough resources for all 20 projects; which ones should they undertake?
-
How do bookmakers find the best set of "ratings" for NFL teams, in order to set accurate point spreads?
-
How should I allocate my retirement portfolio among high-tech stocks, value stocks, bonds, cash, and gold?
In all these situations, we want to find the best way to do something. More formally, we want to find the values of certain cells in a worksheet that optimize (maximize or minimize) a certain objective. Microsoft Office Excel Solver tool helps you answer optimization problems.
An optimization model has three parts: the target cell, the changing cells, and the constraints. The target cell represents the objective or goal. We want to either minimize or maximize the amount in the target cell. In the example of a drug company's product mix given above, the plant manager would presumably want to maximize the profitability of the plant during each month. The cell that measures profitability would be the target cell. The target cells for each situation described at the beginning of the chapter are listed in Table 26-1 on the next page.
Keep in mind, however, that in some situations you might have multiple target cells. For example, Microsoft might have a secondary goal to maximize Xbox market share.
Table 26-1 List of Target Cells
| Model | Maximize or minimize | Target cell |
| Drug company product mix | Maximize | Monthly profit |
| Xbox shipping | Minimize | Distribution costs |
| Xbox pricing | Maximize | Profit from Xbox consoles and games |
| Microsoft project initiatives | Maximize | Net present value (NPV) contributed by selected projects |
| NFL ratings | Minimize | Difference between scores predicted by ratings and actual game scores |
| Retirement portfolio | Minimize | Risk factor of portfolio |
Changing cells are the worksheet cells that we can change or adjust to optimize the target cell. In the drug company example, the plant manager can adjust the amount produced for each product during a month. The cells in which these amounts are recorded are the changing cells in this model. Table 26-2 lists the appropriate changing cell definitions for the models described at the beginning of the chapter.
Table 26-2 List of Changing Cells
| Model | Changing cells |
| Drug company product mix | Amount of each product produced during the month |
| Xbox shipping | Amount produced at each plant each month that is shipped to each customer |
| Xbox pricing | Console and game prices |
| Microsoft project initiatives | Which projects are selected |
| NFL ratings | Team ratings |
| Retirement portfolio | Fraction of money invested in each asset class |
Table 26-3 List of Problem Constraints
| Model | Constraints |
| Drug company product mix | Product mix uses no more resources than are available Do not produce more of a product than can be sold |
| Xbox shipping | Do not ship more units each month from a plant than plant capacity |
| Xbox pricing | Prices can't be too far out of line with competitors' prices |
| Microsoft project initiatives | Projects selected can't use more money or skilled programmers than are available |
| NFL ratings | None |
| Retirement portfolio | Invest all our money somewhere (cash is a possibility) |
The best way to understand how to use Solver is by looking at some detailed examples. In later chapters, you'll learn how to use Solver to address each of the problems presented in this chapter, as well as several other important business problems.
To install Solver, click the Microsoft Office Button, click Excel Options, and click Add-Ins. In the Manage box at the bottom of the window, select Excel Add-ins, and click Go. Check the Solver Add-in box in the Add-Ins dialog box, and click OK. After Solver is installed, you can run Solver by clicking Solver in the Analysis group on the Data tab. Figure 26-1 shows the Solver Parameters dialog box. In the next few chapters, you'll see how to use this dialog box to input the target cell, changing cells, and constraints for a Solver model.
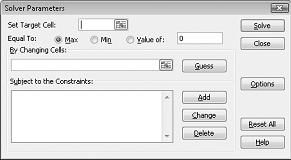
Figure 26-1 The Solver Parameters dialog box
After you have input the target cell, changing cells, and constraints, what does Solver do? To answer this question, you need some background in Solver terminology. Any specification of the changing cells that satisfies the model's constraints is known as a feasible solution. For instance, in our example, any product mix that satisfies the following three conditions would be a feasible solution:
-
Does not use more raw material or labor than is available.
-
Does not produce more of each product than is demanded.
-
Does not produce a negative amount of any product.
Essentially, Solver searches all feasible solutions and finds the one that has the "best" target cell value (the largest value for maximum optimization, the smallest for minimum optimization). Such a solution is called an optimal solution. As you'll see in Chapter 27, "Using Solver to Determine the Optimal Product Mix," some Solver models have no optimal solution and some have a unique solution. Other Solver models have multiple (actually, an infinite number of) optimal solutions. In the next chapter, we'll begin our study of Solver examples by examining the drug company product mix problem.
Problems
For each situation described below, identify the target cell, changing cells, and constraints.
-
I am borrowing $100,000 for a 15-year mortgage. The annual rate of interest is 8 percent. How can I determine my monthly mortgage payment?
-
How should an auto company allocate its advertising budget between different advertising formats?
-
How should cities transport students to more distant schools to obtain racial balance?
-
If a city has only one hospital, where should it be located?
-
How should a drug company allocate its sales-force efforts among their products?
-
A drug company has $2 billion allocated to purchasing bio-tech companies. Which companies should they buy?
-
The tax rate charged to a drug company depends on the country in which a product is produced. How can a drug company determine where each drug should be made?
No comments:
Post a Comment