Save a file in Microsoft Office
You can save a file to a folder on your hard disk drive, a network location, the cloud, a DVD, the desktop, flash drive, or save as another file format such as RTF, CSV or PDF. While you must identify the target location, if it is different than the default folder, the saving process is the same regardless of what location you choose.
By default Office programs save files in the default working folder. To save the copy in a different location, click a different folder in the folder list.
Important: Even if you have AutoRecover enabled, you should save the file frequently while you are working on it to avoid losing data because of an unexpected power failure or other problem.
Save a file
-
Press CTRL+S or click the File tab, and then click Save.
Tip: You can also click the Save icon
![[Untitled]](https://support.content.office.net/en-us/media/1363421b-2ff2-4e61-b16d-5c8c48ff4bf6.jpg) on the Quick Access Toolbar.
on the Quick Access Toolbar. -
You must enter a name for the file if you are saving it for the first time.
Note: Beginning in February 2019 we'll start rolling out a feature to Office 365 users on Windows and Mac that makes it easier to save your files to the cloud. By default, if you are signed in, files will be saved to OneDrive. If you want to save the current files to a different location you can open the full Save As window by selecting More save options.
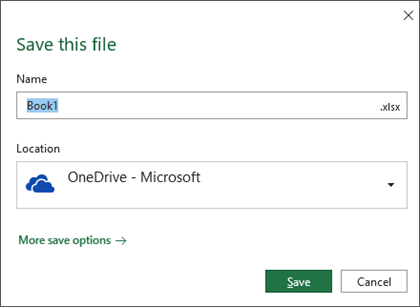
If you haven't received this update yet, then your Office applications will continue to use the classic experience for saving.
Save a copy as a new file (Save As)
Tip: If you're going to create a new file, based on an existing file, but only want your changes saved in the new file it's a good idea to do the Save a Copy process first thing; before you've made any changes. That way your original file will remain unchanged and all your edits will be in the new copy.
-
Press F12 or click File > Save a Copy
-
By default Office will save the copy in the same location as the original. If you want to save the new copy in a different location choose it at this point. If you're happy with the existing location go on to step 3.
-
Give your new copy a name and click Save.
Your original file will be closed and you'll now be working in the new copy you just created.
Tip: If you find yourself creating new files based on existing files often, you may want to use templates to make the process easier and safer. See Create a template for more information.
Choose a different location to save your file
During the Save, or Save a Copy, process described above you can choose a different location to save your file.
-
Select the cloud, web site, or device location where you want to save the file.
Location
Description
Sites – [Your Company Name]
SharePoint or Office 365 Groups document libraries
OneDrive – [Your Company Name]
OneDrive for Business
OneDrive – Personal
OneDrive for consumers via your Microsoft account
This PC
Your local device, including any connected hard drives or flash drives
Browse
Opens the File Explorer so you can navigate to any location on your computer.
-
Select a folder from the Recent Folders list, or click Browse if you don't see the location you want listed there.
-
Confirm the filename you want to use and click Save.
Save as a different, or older, format
You might want to save your file in another format so that you, or somebody else, can open the file in a different program or older version. For example, you might want to save your Word 2016 document as a Rich Text File (RTF) or your Excel workbook as a Comma-Separated Values (CSV) file.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
Choose a file location, such as OneDrive or This PC to store your file.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format that you want to save the file in. For example, click Rich Text Format (.rtf), Word 97-2003 (.doc), Web Page (.htm or .html), or Comma Delimited (.csv).
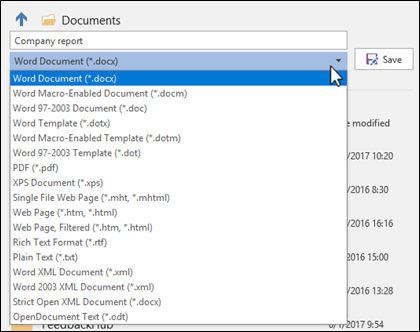
Note: For more information about how to save files in PDF (.pdf) or XPS (.xps) formats, see Save as PDF or Save as XPS.
-
Click Save.
You can save a copy as a new file, or in a different format, or to a different location in Office 2016.
Save a copy as a new file (Save As)
Tip: If you're going to create a new file, based on an existing file, but only want your changes saved in the new file it's a good idea to do the Save a Copy process first thing; before you've made any changes. That way your original file will remain unchanged and all your edits will be in the new copy.
-
Press F12 or click File > Save a Copy
-
By default Office will save the copy in the same location as the original. If you want to save the new copy in a different location choose it at this point. If you're happy with the existing location go on to step 3.
-
Give your new copy a name and click Save.
Your original file will be closed and you'll now be working in the new copy you just created.
Tip: If you find yourself creating new files based on existing files often, you may want to use templates to make the process easier and safer. See Create a template for more information.
Choose a different location to save your file
During the Save, or Save a Copy, process described above you can choose a different location to save your file.
-
Select the cloud, web site, or device location where you want to save the file.
Location
Description
Sites – [Your Company Name]
SharePoint or Office 365 Groups document libraries
OneDrive – [Your Company Name]
OneDrive for Business
OneDrive – Personal
OneDrive for consumers via your Microsoft account
This PC
Your local device, including any connected hard drives or flash drives
Browse
Opens the File Explorer so you can navigate to any location on your computer.
-
Select a folder from the Recent Folders list, or click Browse if you don't see the location you want listed there.
-
Confirm the filename you want to use and click Save.
Save as a different, or older, format
You might want to save your file in another format so that you, or somebody else, can open the file in a different program or older version. For example, you might want to save your Word 2016 document as a Rich Text File (RTF) or your Excel workbook as a Comma-Separated Values (CSV) file.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
Choose a file location, such as OneDrive or This PC to store your file.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format that you want to save the file in. For example, click Rich Text Format (.rtf), Word 97-2003 (.doc), Web Page (.htm or .html), or Comma Delimited (.csv).

Note: For more information about how to save files in PDF (.pdf) or XPS (.xps) formats, see Save as PDF or Save as XPS.
-
Click Save.
Save as a copy, or to a different location in Office 2013.
-
Select the cloud, web site, or device location where you want to save the file.
Location
Description
Sites – [Your Company Name]
SharePoint Server 2013 or earlier document libraries
OneDrive – [Your Company Name]
OneDrive for Business
OneDrive – Personal
OneDrive for consumers via your Microsoft account
Other web locations
Any other websites you have file storage access to.
Computer
Your local device
-
Select a folder from the Recent Folders list, or click Browse if you don't see the location you want listed there.
-
Confirm the filename you want to use and click Save.
- Select what you'd like to do
- Use the Save As dialog box
- Save as a different format
- Save as an earlier version of Office
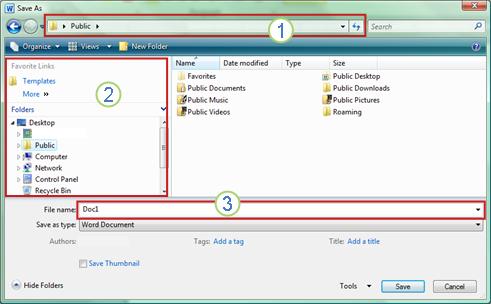
When you use the Save As dialog box, you can also save the file to a new location by using the Navigation pane.
-
To choose a folder or type the path to a folder, use the Address Bar.
-
To quickly see locations you use often, use the Navigation pane.
-
To see more file types, click the arrow.
You can also use the Save As dialog box to rename a file or change the location of where you save the file by clicking a different folder.
You might want to save your file in another format so that you, or somebody else, can open the file in a different program or older version. For example, you might want to save your Word 2016 document as a Rich Text File (RTF) or your Excel workbook as a Comma-Separated Values (CSV) file.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
Choose a file location, such as OneDrive or This PC to store your file.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format that you want to save the file in. For example, click Rich Text Format (.rtf), Web Page (.htm or .html), or Comma Delimited (.csv).

Note: For more information about how to save files in PDF (.pdf) or XPS (.xps) formats, see Save as PDF or Save as XPS.
-
Click Save.
If you are using Office 2010, you can save files in an earlier version of Office by selecting the version in the Save as type list in the Save As dialog box. For example, you can save your Word 2010 document (.docx) as a 97-2003 document (.doc).
Notes:
-
Office 2010 continues the use of the XML-based file formats, such as .docx, .xlsx, and .pptx, introduced in the 2007 Office release. Therefore, files created in Microsoft Word 2010, Microsoft Excel 2010, and Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 can be opened in the 2007 Office release programs without special add-ins or loss of functionality. For more information, see Open XML Formats and file name extensions.
-
For more information about compatibility between files from different releases, see Use the Compatibility Checker.
For information about saving Microsoft Access 2010 .ACCDB files into the older .MDB format see Save an Access 2010 database in an earlier file format.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
Click Save.
- Select what you'd like to do
- Use the Save As dialog box
- Save as a different format
- Save as an earlier version of Office
When you use the Save As dialog box, you can also save the file to a new location by using the Navigation pane.

-
To choose a folder or type the path to a folder, use the Address Bar.
-
To quickly see locations you use often, use the Navigation pane.
-
To see more file types, click the arrow.
You can also use the Save As dialog box to rename a file or change the location of where you save the file by clicking a different folder.
You might want to save your file in another format so that you, or somebody else, can open the file in a different program or older version. For example, you might want to save your Word 2016 document as a Rich Text File (RTF) or your Excel workbook as a Comma-Separated Values (CSV) file.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
Choose a file location, such as OneDrive or This PC to store your file.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format that you want to save the file in. For example, click Rich Text Format (.rtf), Web Page (.htm or .html), or Comma Delimited (.csv).

Note: For more information about how to save files in PDF (.pdf) or XPS (.xps) formats, see Save as PDF or Save as XPS.
-
Click Save.
If you are using Office 2010, you can save files in an earlier version of Office by selecting the version in the Save as type list in the Save As dialog box. For example, you can save your Word 2010 document (.docx) as a 97-2003 document (.doc).
Notes:
-
Office 2010 continues the use of the XML-based file formats, such as .docx, .xlsx, and .pptx, introduced in the 2007 Office release. Therefore, files created in Microsoft Word 2010, Microsoft Excel 2010, and Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 can be opened in the 2007 Office release programs without special add-ins or loss of functionality. For more information, see Open XML Formats and file name extensions.
-
For more information about compatibility between files from different releases, see Use the Compatibility Checker.
For information about saving Microsoft Access 2010 .ACCDB files into the older .MDB format see Save an Access 2010 database in an earlier file format.
By default, the Microsoft Office programs save a file in a default working folder. To save the copy in a different location, click a different folder in the folder list.
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Save, or press CTRL+S.
, and then click Save, or press CTRL+S.Important: If you don't see the Microsoft Office Button
 , click Save on the File menu.
, click Save on the File menu. -
If you are saving the file for the first time, you are asked to give it a name.
You can also use the Save As command to rename a file or change the location of where you save the file.
Save As dialog box in Windows 7 and Windows Vista
You can also save the file to a new location by using the Navigation pane. 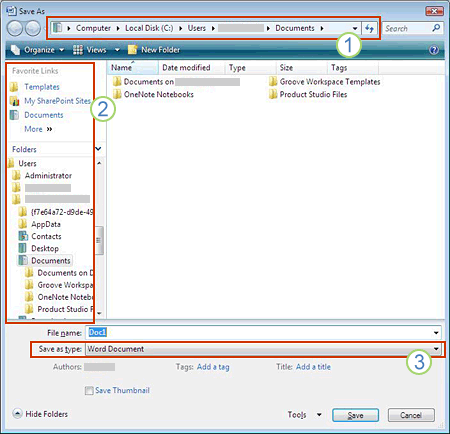
1. To choose a folder or type a path to the folder, use the Address bar.
2. To quickly see locations you use a lot, use the Navigation pane.
3. To see more file types, click the arrow.
Save As dialog box in Microsoft Windows XP
You can also save the file to a new location by using the Save in list or locations saved in your My Places bar. 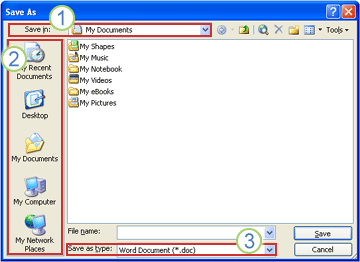
1. To choose a folder, use the Save in list.
2. To quickly see locations you use a lot, use the My Places bar.
3. To see more file types, click the arrow.
To save a copy of your file, do the following:
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Save As, or press CTRL+S.
, and then click Save As, or press CTRL+S.Important: If you don't see the Microsoft Office Button
 , click Save As on the File menu.
, click Save As on the File menu. -
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
Click Save.
To save the copy in a different folder, follow the steps above, but click a different drive in the Save in list or a different folder in the folder list. To save the file in a new folder, click Create New Folder  .
.
If you are using the 2007 Office release, you can share your files with people using an earlier version of Microsoft Office by saving your file in the 97-2003 file format. For example, you can save your Microsoft Office Word 2007 document (.docx) as a 97-2003 document (.doc).
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Save As.
, and then click Save As.Important: If you don't see the Microsoft Office Button
 , click Save As on the File menu.
, click Save As on the File menu.Keyboard shortcut To open the Save As dialog box, press ALT, F, A.
-
In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
-
In the Save as type list, click the file format that you want to save the file in. For example, click Rich Text Format (.rtf), Web Page (.htm or .html), or Comma Delimited (.csv).
-
Click Save.
To learn more about saving your files as a PDF, see Save as PDF; to learn about saving your files as XPS, see Save a file in XPS format.
AutoRecover does not replace regularly saving your files. If you choose not to save the recovery file after you open it, the file is deleted, and your unsaved changes are lost. If you save the recovery file, it replaces the original file (unless you specify a new file name). The more frequently your files are saved, the more information is recovered if there is a power failure or other problem while a file is open.
Refer to the procedure corresponding to the Office 2007 product you're using.
Word 2007
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Word Options.
, and then click Word Options. -
Click Save.
-
Select the Save AutoRecover information every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
Excel 2007
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click Excel Options.
, and then click Excel Options. -
Click Save.
-
Select the Save AutoRecover information every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
InfoPath 2007
-
On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Advanced tab.
-
Select the When filling out forms, save AutoRecover information every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
PowerPoint 2007
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
 , and then click PowerPoint Options.
, and then click PowerPoint Options. -
Click Save.
-
Select the Save AutoRecover information every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
Project 2007
-
On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Advanced tab.
-
Select the Save every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
Publisher 2007
-
On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Advanced tab.
-
Select the Save AutoRecover info every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
Visio 2007
-
On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Save/Open tab.
-
Select the Save AutoRecover info every check box.
-
In the minutes box, type or select a number to determine how often you want to save files.
We're listening
This article was updated by Ben on January 23rd, 2019 as a result of your comments. If you found it helpful, and especially if you didn't, please use the feedback controls below to let us know how we can make it better.
Are you searching Microsoft word? click here: Microsoft word download!
ReplyDelete