Filter a table (Power Query)
Note: Power Query is known as Get & Transform in Excel 2016. Information provided here applies to both. To learn more, see Get & Transform in Excel 2016.
In Power Query, you can include or exclude rows according to a specific value. A filtered column contains a small filter icon (  ) in the column header.
) in the column header.
Filter a column using an Auto Filter
-
Select the column that you need to filter.
-
Click the down arrow (
 ).
). -
Uncheck the Select All box to deselect all columns.
-
Select the column values you want to include in your table.
-
Click OK.
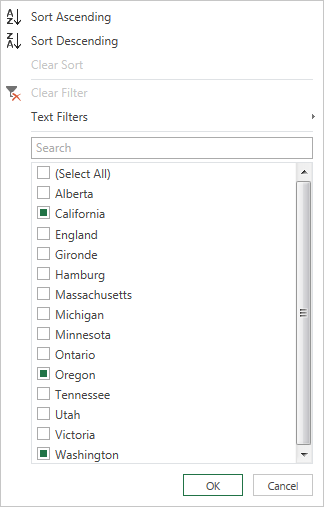
Notes: When you filter a column, only the top 1,000 distinct values in the column will load into the filter list. If there are 1,000 or more values in the column in Query Editor that you are filtering, a message will appears indicating that the list of values in the filter list may be incomplete, and the Load more link is shown. Click the Load more link to load another 1,000 distinct values.
-
If exactly 1,000 distinct values are found again, the list is displayed with a message stating that the list could still be incomplete.
-
If less than 1,000 distinct values are found, the full list of values is shown.
Note: The Query Editor only appears when you load, edit, or create a new query using Power Query.
-
Filter a column using Text Filters
In addition to the To filter a column step, you can filter a Text value using the Text Filters context menu.
-
Click the down arrow (
 ) of the column containing a Text value you want to filter on.
) of the column containing a Text value you want to filter on. -
Click Text Filters, and click an equality type name of Equals, Does Not Equal, Begins With, Ends With, Contains, or Does Not Contain.
Filter a column using Number or Date/Time Filters
In addition to the To filter a column step, you can filter a Number or Date/Time value using the Number Filters or Date/Time Filters menu.
To filter a column using Number Filters or Date/Time
-
Click the down arrow (
 ) of the column containing a Number or Date/Time value you want to filter on.
) of the column containing a Number or Date/Time value you want to filter on. -
Click Number Filters or Date/Time Filters, and an equality type name of Equals, Does Not Equal, Greater Than, Greater Than or Equal To, Less Than, or Less Than Or Equal To.
Filter multiple columns
To filter multiple columns, select an additional column, and repeat one of the column filter steps.
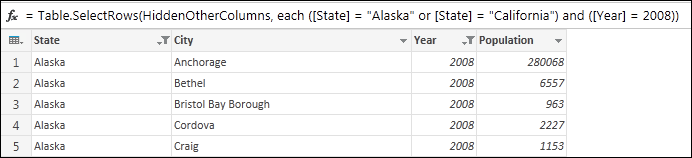
For example, the Table.SelectRows() formula below returns a query filtered by State and Year.
Filter a column by Row Position
Filtering rows by position is similar to filtering rows by value, except that rows are kept or discarded according to their position in the table—rather than by cell values.
With Microsoft Power Query for Excel, you can filter a column by position using several methods:
Note: When you specify a range or pattern, the first data row in a table is row zero (0), not row one (1). You can create an Index column to display the row positions prior to removing rows.
To keep top rows
-
Right-click the table icon (
 ).
). -
Click Keep Top Rows.
-
In the Keep Top Rows dialog box, enter the Number of rows.
To keep the top 100 rows
-
Right-click the table icon (
 ).
). -
Click Keep Top 100 Rows.
To keep a range of rows
-
Right-click the table icon (
 ).
). -
Click Keep Range of Rows.
-
To define your range, in the Keep Range of Rows dialog box, enter the First row and Number of rows.
To remove top rows
-
Right-click the table icon (
 ).
). -
Click Remove Top Rows.
-
In the Remove Top Rows dialog box, enter the Number of rows.
To remove alternate rows
-
Right-click the table icon (
 ).
). -
Click Remove Alternate Rows.
-
To define your alternate row pattern, in the Remove Alternate Rows dialog box, enter the First row to remove, Number of rows to remove, and Number of rows to keep.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community, get support in the Answers community, or suggest a new feature or improvement on Excel User Voice.
No comments:
Post a Comment