Set a task start or finish date (constraint) for a task
You can change a task's start date or finish date in the Start and Finish columns. But be careful! When you change a start time or finish time, Project puts constraints on the tasks that force them to start or end on that date, even if the rest of the schedule changes.
These instructions are specific to Microsoft Project 2016, 2013, and 2010.
What do you want to do?
Add a constraint for a task
If you have an unavoidable constraint, such as an event date, pick the constraint type as well as the date:
-
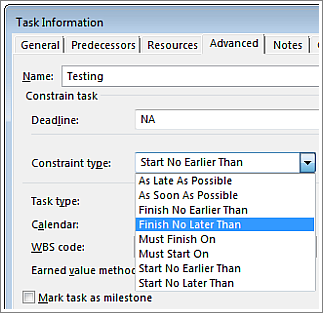
On the Gantt Chart task list, double-click the task.
-
Click the Advanced tab.
-
Pick an option from the Constraint type list.
-
If you pick a constraint other than As Late As Possible or As Soon As Possible, add a date to the Constraint date box.
Project management tip Let Project do what it does best — schedule your project. Set task durations yourself and create links between tasks, and then Project will calculate the task start and finish dates.
Remove a constraint
You can't technically remove a constraint, but you can reset it to the default value, tying it to other tasks rather than to a specific date.
-
On the Gantt Chart task list, double-click the task.
-
Click the Advanced tab.
-
In the Constraint type list, pick one of these options:
-
If your project is scheduled from the finish date, choose As Late As Possible.
-
If your project is scheduled from the start date, choose As Soon As Possible.
-
Available constraints
With Project, you can add eight different constraints to tasks. Those constraints come in three flavors:
-
Flexible constraints, which don't tie a task to a specific date.
-
Semi-flexible constraints, which include earliest start dates or latest finish dates.
-
Inflexible constraints, which have specific start or finish dates.
| Constraint | Type | Description |
| As Late As Possible (ALAP) | Flexible | The task starts as late as it can without delaying other tasks. This is the default constraint when you schedule from the project finish date. |
| As Soon As Possible (ASAP) | Flexible | The task starts as soon as possible. This is the default constraint when you schedule from the project start date. |
| Start No Earlier Than (SNET) | Semi-Flexible | The task starts on or after a specific date. |
| Finish No Earlier Than (FNET) | Semi-Flexible | The task finishes on or after a specific date. |
| Start No Later Than (SNLT) | Semi-Flexible | The task starts on or before a specific date. |
| Finish No Later Than (FNLT) | Semi-Flexible | The task finishes on or before a specific date. |
| Must Finish On (MFO) | Inflexible | The task finishes on a specific date. |
| Must Start On (MSO) | Inflexible | The task starts on a specific date. |
Task constraints vs. task dependencies
It's easy to confuse task constraints (restrictions on when a task can start or finish) with task dependencies (links that show a relationship between tasks).
If you're looking for details on dependencies, see Link tasks in a project.
These instructions are specific to Microsoft Project 2007.
What do you want to do?
About constraints
There are three types of constraints:
-
Flexible constraints do not have specific dates associated with them. Setting these constraints allows you to start tasks as early as possible or as late as possible, with the task ending before the project finish, given other constraints and task dependencies in the schedule.
-
Semi-flexible constraints require an associated date that controls the earliest or latest start or finish date for a task. These constraints allow a task to finish at any time, as long as it meets the start or finish deadline.
-
Inflexible constraints require an associated date that controls the start or finish date of the task. These constraints are useful when you need to make your schedule take into account external factors, such as the availability of equipment or resources, deadlines, contract milestones, and start and finish dates.
The following table lists the constraints provided in Project.
| Constraint type | Constraint name | Description |
| Flexible | As Late As Possible (ALAP) | Schedules the task as late as possible with the task ending before the project ends and without delaying subsequent tasks. This is the default constraint for tasks when you schedule from the project finish date. Do not enter a task start or finish date with this constraint. |
| Flexible | As Soon As Possible (ASAP) | Schedules the task to begin as early as possible. This is the default constraint for tasks when you schedule from the project start date. Do not enter a start or finish date with this constraint. |
| Semi-Flexible | Start No Earlier Than (SNET) | Schedules the task to start on or after a specified date. Use this constraint to ensure that a task does not start before a specified date. |
| Semi-Flexible | Finish No Earlier Than (FNET) | Schedules the task to finish on or after a specified date. Use this constraint to ensure that a task does not finish before a certain date. |
| Semi-Flexible | Start No Later Than (SNLT) | Schedules the task to start on or before a specified date. Use this constraint to ensure that a task does not start after a specified date. |
| Semi-Flexible | Finish No Later Than (FNLT) | Schedules the task to finish on or before a specified date. Use this constraint to ensure that a task does not finish after a certain date. |
| Inflexible | Must Finish On (MFO) | Schedules the task to finish on a specified date. Sets the early, scheduled, and late finish dates to the date that you type and anchors the task in the schedule. |
| Inflexible | Must Start On (MSO) | Schedules the task to start on a specified date. Sets the early, scheduled, and late start dates to the date that you type and anchors the task in the schedule. |
If you manually enter a start date or a finish date for a task, Project changes the constraint type for that task to Start No Earlier Than (SNET) or Finish No Earlier Than (FNET). These semi-flexible constraint types force the task to start or end on the specified date regardless of subsequent changes that would otherwise affect the task's place in the overall project plan.
For optimal scheduling flexibility, we recommend that you allow Project to use flexible constraints to calculate the start and finish dates for tasks based on the durations and task dependencies that you enter. Only if you have unavoidable constraints, such as an event date that cannot be moved, should you consider setting a constraint for a task manually.
Why?
Constraining a task that is dependent on another task can produce unwanted results, as illustrated in the following example:
The task "Pour foundation" is linked so that it starts as soon as "Dig hole" finishes. "Dig hole" is supposed to happen on the 10th. If you enter an inflexible constraint that forces "Pour foundation" to start on the 10th and then "Dig hole" finishes early, Project will not be able to take advantage of the early finish and move "Pour foundation" to start earlier.
Rather than setting specific dates for a task, consider assigning an As Soon As Possible (ASAP) constraint and enter a deadline for the task. Entering a deadline causes Project to display a deadline marker in the Gantt Chart view, and an indicator alerts you when the task's finish date moves past the deadline.
Set the start and finish dates for a task
For optimal scheduling flexibility, we recommend that you allow Project to calculate the start and finish dates for tasks based on the durations and task dependencies that you enter. However, if you have unavoidable constraints, such as an event date, you can set a specific start or finish date for a task.
-
On the View menu, click Gantt Chart.
-
Click the task that you are scheduling, and then click Task Information
 .
. -
Click the Advanced tab.
-
Select a constraint type from the Constraint type list.
-
If you select a constraint other than As Late As Possible or As Soon As Possible, type a constraint date in the Constraint date box, or select a date from the calendar.
Note: When you schedule your project from a start date and type a date in the Start field of a task (or drag a Gantt bar to change the start date), Project sets a Start No Earlier Than (SNET) constraint for that task. If you type a date in the Finish field of a task, Project automatically sets a Finish No Earlier Than (FNET) constraint.
If you are having trouble with your task constraints, you may find the information in the following sections helpful.
Set a deadline date for a task
You can set a deadline date for a task to keep track of its finish date without locking the schedule with an inflexible constraint. Project updates the schedule as needed, keeps track of deadline dates, and shows a symbol  in the indicator column if a task finishes after its deadline.
in the indicator column if a task finishes after its deadline.
To set a deadline date for a task:
-
On the View menu, click Gantt Chart.
-
Click the task that you are assigning a deadline.
-
Click Task Information
 , and then click the Advanced tab.
, and then click the Advanced tab. -
Enter the deadline date in the Deadline box.
Tip: If you decide later that you no longer want the deadline set for this task, you can remove the deadline by clearing the Deadline box.
-
Click OK to save the deadline. A green arrow
 appears next to the bar for the task in the Gantt Chart view. Project will not notify you if a deadline date is passed.
appears next to the bar for the task in the Gantt Chart view. Project will not notify you if a deadline date is passed.
Note: When a task slips past its deadline date, Project calculates the negative slack for that task. For example, if a task finishes a day later than it was scheduled to finish, it displays a total slack of -1d.
Change the constraint type for a task
You can change the constraint type for a task in the Project Guide, the Task Information dialog box, or the Constraint Dates table.
Make constraint changes by using the Project Guide
-
On the Project Guide toolbar, click Tasks
 .
. -
On the Tasks pane, click Set deadlines and constrain tasks.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To select a single task, click the task name.
-
To select more than one task, hold down CTRL and click each task name.
-
To select all of the tasks in your project, click Select All.
-
-
Under Constrain a task, select the constraint type that you want to use for the selected task or tasks.
-
Click Done.
Make constraint changes in the Task Information dialog box
-
Click the task that has the constraint, and then click Task Information
 .
. -
On the Advanced tab, review or change the constraint type.
Note: Task constraints are also clearly marked in the indicator column with a constraint symbol (either  or
or  ). Rest the pointer on the constraint indicator to see the constraint type and date.
). Rest the pointer on the constraint indicator to see the constraint type and date.
Make constraint changes in the Constraint Dates table
-
On the View menu, click More Views.
-
In the Views list, click Task Sheet, and then click Apply.
-
On the View menu, point to Table, and then click More Tables.
-
Click Task.
-
In the Tables list, click Constraint Dates, and then click Apply.
The task sheet changes to show the Constraint Dates table, which shows the task name, duration, and constraint type for all constraints (including As Soon As Possible), and the constraint date, if applicable.
-
Do either or both of the following:
-
To change the type of a constraint, click the arrow in the Constraint Type field, and then click the constraint type that you want.
-
To change the date of a constraint, in the Constraint Date field, type or select the date that you want.
If you change a constraint to As Soon As Possible (ASAP) or As Late As Possible (ALAP), the Constraint Date field shows NA.
-
No comments:
Post a Comment